HiveMQ Kafka Extension Customization
Version 4.4.0 of HiveMQ and the HiveMQ Enterprise Extension for Kafka introduces the HiveMQ Kafka Extension Customization SDK.
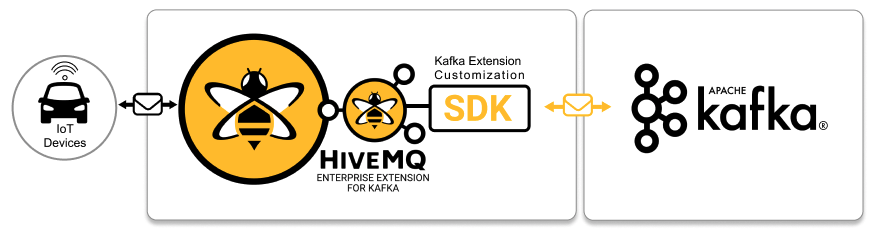
Our flexible new API gives you the ability to customize the management of your Kafka topics and implement custom logic for bi-directional message transfer between HiveMQ and your Kafka clusters. Use the API to programmatically specify sophisticated custom-handling of message transformations between HiveMQ and Kafka.
Features
The HiveMQ Kafka Extension Customization SDK gives you more control and a deeper integration of MQTT messages with your Kafka cluster.
Requirements
-
Java 11 or higher
-
Java IDE that supports Gradle (for example, IntelliJ)
-
HiveMQ Professional or Enterprise Edition version 4.4.0 or higher
-
HiveMQ Enterprise Extension for Kafka version 4.4.0 or higher
-
Kafka cluster that runs Kafka version 0.11 or higher
-
Administrative rights for the Kafka cluster
Quick Start
The Customization SDK for the HiveMQ Enterprise Extension for Kafka uses the same Input/Output principle as the HiveMQ Extension SDK.
The quickest way to learn about the new Customization SDK is to check out our Hello World Customization project on GitHub and use it as the basis for your own customization.
The hivemq-kafka-hello-world-customization project gets you started with the following transformations in the HiveMQ Kafka Extension Customization SDK:
-
Accept an MQTT PUBLISH message and create a new Kafka record from it.
-
Convert the topic of the MQTT PUBLISH to a Kafka topic.
-
Verify the Kafka topic exists on the Kafka cluster and create the topic if necessary.
-
Create a new Kafka record with the following information:
-
The MQTT topic string converted to a properly-formatted Kafka topic.
-
The MQTT message payload set as the Kafka value.
-
MQTT 5 user properties used as the Kafka topic header.
-
-
Send the record to the HiveMQ customization framework for publication to the referenced Kafka cluster.
The Hello World project also shows these transformations from Kafka records to MQTT publishes:
-
Accept a Kafka record and create a new MQTT PUBLISH message from it.
-
Convert the topic of the Kafka record to an MQTT topic.
-
Create a new MQTT Publish with the following information:
-
Kafka record value set as the MQTT message payload.
-
Kafka topic header used as the MQTT 5 user properties.
-
-
Send the record to the HiveMQ customization framework for publication on the HiveMQ cluster.
MQTT to Kafka Customization
The MQTT to Kafka Transformer lets you extend the capabilities of your HiveMQ Enterprise Extension for Kafka to meet the specific needs of your individual use case.
Implement this transformer to programmatically create customized KafkaRecords from MQTT PublishPackets:
-
Access data from all fields and properties of specific incoming MQTT PUBLISH messages:
-
MQTT QoS
-
MQTT retained message flag
-
MQTT topic
-
MQTT payload format indicator
-
MQTT message expiry
-
MQTT response topic
-
MQTT correlation data
-
MQTT content type
-
MQTT message payload
-
MQTT 5 user properties
-
-
Set information for the target Kafka record as desired:
-
Kafka key
-
Kafka value
-
Kafka headers
-
Kafka timestamp
-
Kafka topic
-
-
Create multiple Kafka records from a single MQTT PUBLISH message.
MQTT to Kafka Transformer Configuration
With the MQTT to Kafka Transformer, you can add your own code to implement the transformation of MQTT messages into Kafka records.
To enable the use of a custom MQTT to Kafka transformer, you extend the kafka-configuration.xml file of your HiveMQ Enterprise Extension for Kafka.
| Setting | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
The unique identifier of the transformer. This string can only contain the following characters |
|
|
The identifier of the referenced Kafka cluster |
|
|
A list of MQTT topic filters |
|
|
The canonical class name of the transformer that is used |
|
|
Optional setting to define the maximum size in bytes that a request to Kafka can contain. This value determines the largest MQTT message size that you can send to Kafka. |
The default maximum message size that Kafka brokers accept is 1 MB. If you configure the max-request-byte-size to forward MQTT messages that are larger than 1 MB to Kafka, check that the maximum message size of your Kafka broker is adjusted accordingly.
|
<mqtt-to-kafka-transformers>
<mqtt-to-kafka-transformer>
<id>my-transformer</id>
<cluster-id>cluster01</cluster-id>
<mqtt-topic-filters>
<mqtt-topic-filter>transform/#</mqtt-topic-filter>
</mqtt-topic-filters>
<transformer>com.hivemq.transformers.MyTransformer</transformer>
<!-- 100 * 1024 * 1024 = 104857600 = 100 MiB-->
<kafka-max-request-size-bytes>104857600</kafka-max-request-size-bytes>
</mqtt-to-kafka-transformer>
</mqtt-to-kafka-transformers>MQTT to Kafka Objects and Methods
MqttToKafkaInitInput
The MqttToKafkaInitInput interface provides context for the setup of an MqttToKafkaTransformer and is used to call the associated KafkaCluster and KafkaTopicService of the selected transformer during extension start.
| Method | Information |
|---|---|
|
Kafka topic service that manages the Kafka topics |
|
Kafka cluster that is configured to this MQTT to Kafka transformer |
@Override
public void init(final @NotNull MqttToKafkaInitInput input) {
final KafkaCluster kafkaCluster = input.getKafkaCluster();
log.info(
"Hello-World-Transformer for Kafka cluster '{}' with boot strap servers '{}' initialized",
kafkaCluster.getId(),
kafkaCluster.getBootstrapServers());
}MqttToKafkaTransformer
The MqttToKafkaTransformer interface is a transformer for the programmatic creation of KafkaRecords from MQTT PublishPackets.
The HiveMQ Enterprise Extension for Kafka executes the MqttToKafkaTransformer transformer for each MQTT PUBLISH message your HiveMQ cluster receives that matches the <mqtt-topic-filters> you configure in the <mqtt-to-kafka-transformer> tag of your kafka-configuration.xml file. The transformer can publish a virtually unlimited number of KafkaRecords via the MqttToKafkaOutput object.
Your compiled implementation (.class files) of the MqttToKafkaTransformer and all associated dependencies must be placed in a java archive (.jar) in the customizations folder of your HiveMQ Enterprise Extension for Kafka. Additionally, you must configure an <mqtt-to-kafka-transformer> that references the canonical name of the implementing class in the kafka-extension.xml file.
|
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
Contains the information of the MQTT |
|
Returns the post-transformation |
public class HelloWorldTransformer implements MqttToKafkaTransformer {
@Override
public void init(final @NotNull MqttToKafkaInitInput input) {
// Insert your own business logic
}
@Override
public void transformMqttToKafka(
final @NotNull MqttToKafkaInput mqttToKafkaInput, final @NotNull MqttToKafkaOutput mqttToKafkaOutput) {
// Insert your own business logic
}
}MqttToKafkaInput
The MqttToKafkaInput object is the input parameter of the MqttToKafkaTransformer. The MqttToKafkaInput object contains the PublishPacket to which the transformation is applied and allows access to the KafkaCluster and the KafkaTopicService of the Kafka cluster the transformer references:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
|
Kafka topic service that manages the Kafka topics |
|
PUBLISH packet that is received on the configured MQTT topic |
|
Kafka cluster that is configured to the MQTT to Kafka transformer |
@Override
public void transformMqttToKafka(
final @NotNull MqttToKafkaInput mqttToKafkaInput, final @NotNull MqttToKafkaOutput mqttToKafkaOutput) {
final PublishPacket publishPacket = mqttToKafkaInput.getPublishPacket();
final String kafkaClusterId = mqttToKafkaInput.getKafkaCluster().getId();
final KafkaTopicService kafkaTopicService = mqttToKafkaInput.getKafkaTopicService();
}MqttToKafkaOutput
The MqttToKafkaOutput object provides the following methods:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
|
Can be used to create Kafka records |
|
List of Kafka records that are written to the associated Kafka cluster |
final KafkaRecordBuilder recordBuilder = mqttToKafkaOutput.newKafkaRecordBuilder().topic(kafkaTopic);
publishPacket.getPayload().ifPresent(recordBuilder::value);
mqttToKafkaOutput.setKafkaRecords(List.of(recordBuilder.build()));| If the setKafkaRecords list is empty, the MQTT message drops and no Kafka record is written. |
Kafka Topic Service
The KafkaTopicService interface enables the programmatic interaction with Kafka topics. The service automatically maps to the configured Kafka cluster and can be used to inquire the state of Kafka topics on the Kafka cluster. The service can also be used to create new topics on the Kafka cluster.
The KafkaTopicService interface provides the following methods:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
|
Returns the state of a single Kafka topic |
|
Returns the states of multiple Kafka topics |
|
Creates a single Kafka topic |
|
Creates multiple Kafka topics |
public class MyTransformer implements MqttToKafkaTransformer {
private static final @NotNull Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyTransformer.class);
@Override
public void transformMqttToKafka(@NotNull MqttToKafkaInput mqttToKafkaInput, @NotNull MqttToKafkaOutput mqttToKafkaOutput) {
// PUBLISH packet from Input
final PublishPacket publishPacket = mqttToKafkaInput.getPublishPacket();
// KafkaTopicService from Input
final KafkaTopicService kafkaTopicService = mqttToKafkaInput.getKafkaTopicService();
// QoS from PUBLISH
final String qos = String.valueOf(publishPacket.getQos().getQosNumber());
// Payload from MQTT Publish
final ByteBuffer message = publishPacket.getPayload().orElse(ByteBuffer.allocate(0));
// MQTT topic from PUBLISH
final String mqttTopic = publishPacket.getTopic();
// Transform MQTT topic to Kafka topic
final String kafkaTopic = mqttTopic.replaceAll("/", ".");
// Check for Kafka topic and create if necessary
final KafkaTopicService.KafkaTopicState kafkaTopicState = kafkaTopicService.getKafkaTopicState(kafkaTopic);
if (kafkaTopicState != KafkaTopicService.KafkaTopicState.EXISTS) {
kafkaTopicService.createKafkaTopic(kafkaTopic);
}
// Create Kafka Record
final KafkaRecord record = mqttToKafkaOutput.newKafkaRecordBuilder()
.topic(kafkaTopic)
.key(mqttTopic)
.value(message)
.header("qos", qos)
.build();
log.info("Transforming MQTT message from topic {}", mqttTopic);
// Set KafkaRecord to Output
mqttToKafkaOutput.setKafkaRecords(List.of(record));
}
}
The KafkaTopicService can overwrite an existing Kafka topic. If this is not the desired behavior, use the getKafkaTopicState method to verify whether the topic exists, before you call the createKafkaTopic method of the KafkaTopicService.
|
Kafka to MQTT Customization
The Kafka to MQTT Transformer lets you extend the capabilities of your HiveMQ Enterprise Extension for Kafka to meet the specific needs of your individual use case.
Implement this transformer to programmatically create customized MQTT PublishPackets from KafkaRecords.
-
Access data from all fields of a specific Kafka record:
-
key
-
value
-
headers
-
timestamp
-
topic
-
-
Set information in the generated MQTT PUBLISH message as desired:
-
QoS
-
Retain flag
-
Topic
-
Payload format indicator
-
Message expiry
-
Response topic
-
Correlation data
-
Content type
-
Payload
-
User properties
-
-
Create multiple MQTT PUBLISH messages from a Kafka record
Kafka to MQTT Transformer Configuration
With the Kafka to MQTT Transformer, you can add your own code to implement the transformation of Kafka records into MQTT messages.
To enable the use of a custom Kafka to MQTT transformer, you extend the kafka-configuration.xml file of your HiveMQ Enterprise Extension for Kafka.
| Setting | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
The unique identifier of the transformer. This string can only contain the following characters |
|
|
The identifier of the referenced Kafka cluster |
|
|
The canonical class name of the transformer that is used |
|
|
A list of the Kafka topics and/or topic patterns to which the transformer applies |
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<kafka-configuration xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="kafka-extension.xsd">
<kafka-clusters>
<kafka-cluster>
<id>cluster01</id>
<bootstrap-servers>127.0.0.1:9092</bootstrap-servers>
</kafka-cluster>
</kafka-clusters>
<kafka-to-mqtt-transformers>
<kafka-to-mqtt-transformer>
<id>transformer01</id>
<cluster-id>cluster01</cluster-id>
<transformer>com.hivemq.extensions.kafka.transformer.MyCustom2MqttTransformer</transformer>
<kafka-topics>
<kafka-topic>first-kafka-topic</kafka-topic>
<kafka-topic>second-kafka-topic</kafka-topic>
<!-- Arbitrary number of Kafka topics -->
<kafka-topic-pattern>first-pattern-*</kafka-topic-pattern>
<kafka-topic-pattern>second-pattern-*</kafka-topic-pattern>
<!-- Arbitrary number of Kafka topic patterns -->
</kafka-topics>
</kafka-to-mqtt-transformer>
</kafka-to-mqtt-transformers>
</kafka-configuration>Kafka to MQTT Objects and Methods
KafkaToMqttTransformer
The KafkaToMqttTransformer interface is a transformer for the programmatic creation of MQTT PublishPackets from KafkaRecords.
The HiveMQ Enterprise Extension for Kafka executes the KafkaToMqttTransformer implementation for every Kafka record that matches the <kafka-topics> you configure in the <kafka-to-mqtt-transformer> tag of your kafka-configuration.xml file. The transformer can publish a virtually unlimited number of MQTT PublishPackets via the KafkaToMqttOutput object.
Your compiled implementation (.class files) of the KafkaToMqttTransformer and all associated dependencies must be placed in a java archive (.jar) in the customizations folder of your HiveMQ Enterprise Extension for Kafka. Additionally, you must configure a <kafka-to-mqtt-transformer> that references the canonical name of the implementing class in the kafka-extension.xml file.
|
Multiple threads can call methods concurrently. To ensure that all threads behave properly and prevent unintended interactions, your implementation of the KafkaToMqttTransformer interface must be thread-safe. Additionally, exception handling must be done inside the methods of your KafkaToMqttTransformer implementation.Transformer methods are not permitted to throw an Exception of any kind.To prevent loss of data, as long as a method continues to throw an exception for a Kafka record, the Kafka extension attempts to convert the record. This loop prevents the Kafka extension from processing further data for the affected partition. If a method in your transformer throws an exception, fix and redeploy your transformer and disable/enable the Kafka extension. To troubleshoot your transformer, monitor the kafka-extension.total.retry.count metric in the Kafka Extension Customization SDK Metrics. An increase in the retry metric can indicate an issue with your transformer. Additionally, check your hivemq.log file for warnings related to the performance of your transformer. |
hivemq.log fileTransformer with id test-transformer threw an unhandled RuntimeException with message null while processing a record from topic test, partition test-1 with offset 1000. Transformers are responsible for their own exception handling.
One instance of your KafkaToMqttTransformer implementation is created for each transformer-mapping that you reference in your kafka-configuration.xml.
|
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
Contains the information of the |
|
Returns the post-transformation |
public class KafkaToMqttHelloWorldTransformer implements KafkaToMqttTransformer {
@Override
public void init(@NotNull final KafkaToMqttInitInput input) {
// Insert your own business logic
}
@Override
public void transformKafkaToMqtt(@NotNull final KafkaToMqttInput kafkaToMqttInput,
@NotNull final KafkaToMqttOutput kafkaToMqttOutput) {
// Insert your own business logic
}
}KafkaToMqttInitInput
The KafkaToMqttInitInput interface provides context for the set up of a KafkaToMqttTransformer and is used to call the associated KafkaCluster and KafkaTopicService of the selected transformer during extension start.
| Method | Information |
|---|---|
|
Metric registry of the HiveMQ node. The registry can be used to add custom metrics that fulfil the monitoring needs of your specific business logic. |
@Override
public void init(@NotNull final KafkaToMqttInitInput input) {
this.metricRegistry = input.getMetricRegistry();
// Build custom metrics based on your business logic and needs
this.successCounter = metricRegistry.counter("com.hivemq.hello-world-example.success.count");
}KafkaToMqttInput
The KafkaToMqttInput object is the input parameter of the KafkaToMqttTransformer. The KafkaToMqttInput object contains the information of the KafkaRecord to which the transformation is applied and allows access to the KafkaCluster of the Kafka cluster the transformer references:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
|
The Kafka record that triggers this transformer call |
|
Kafka cluster that is configured to the MQTT to Kafka transformer |
@Override
public void transformKafkaToMqtt(@NotNull final KafkaToMqttInput kafkaToMqttInput,
@NotNull final KafkaToMqttOutput kafkaToMqttOutput) {
final KafkaCluster kafkaCluster = kafkaToMqttInput.getKafkaCluster();
final KafkaRecord kafkaRecord = kafkaToMqttInput.getKafkaRecord();
}KafkaToMqttOutput
The KafkaToMqttOutput object is the output parameter of the KafkaToMqttTransformer. The KafkaToMqttOutput object allows access to the MQTT PublishBuilder. After the KafkaToMqttTransformer transforms the KafkaToMqttInput, HiveMQ publishes this output in an MQTT message.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
|
Returns a new |
|
Defines the MQTT publish messages that HiveMQ publishes once the transformation is complete. Each call of the
|
|
If a publish or any element of a publish is null, a NullPointerException displays. If a publish contains any element that is not created via a PublishBuilder, an IllegalArgumentException displays.If the publishes list is empty, HiveMQ does not publish any MQTT message from the Kafka record.
|
@Override
public void transformKafkaToMqtt(@NotNull final KafkaToMqttInput kafkaToMqttInput,
@NotNull final KafkaToMqttOutput kafkaToMqttOutput) {
final KafkaRecord kafkaRecord = kafkaToMqttInput.getKafkaRecord();
final PublishBuilder publishBuilder = kafkaToMqttOutput.newPublishBuilder().topic(kafkaRecord.getTopic());
kafkaRecord.getValue().ifPresent(publishBuilder::payload);
kafkaToMqttOutput.setPublishes(List.of(publishBuilder.build()));
}Customization Use Cases
MQTT to Kafka Customization Use Case Examples
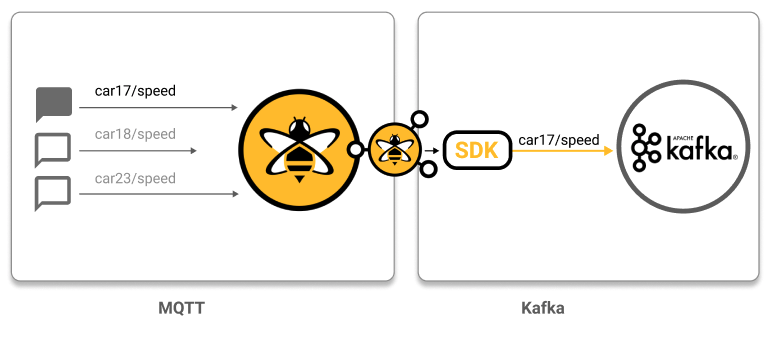
Build and send custom Kafka records in response to received MQTT messages: In this use case, the goal is to transform MQTT messages based on a defined business logic and output a customized Kafka record.
public class BusinessLogicTransformer implements MqttToKafkaTransformer {
@Override
public void transformMqttToKafka(@NotNull final MqttToKafkaInput input,
@NotNull final MqttToKafkaOutput output) {
// Get MQTT payload
final ByteBuffer mqttPayload= input.getPublishPacket().getPayload().orElse(ByteBuffer.allocate(0));
// Manipulate the MQTT payload according to your business logic
// For example, deserialize or add fields
byte[] recordValue = ownBusinessLogic(mqttPayload);
final KafkaRecord kafkaRecord = output.newKafkaRecordBuilder()
.topic(input.getPublishPacket().getTopic())
.key(input.getPublishPacket().getResponseTopic().orElse("unknown"))
.value(recordValue)
.build();
// Set Record as output
output.setKafkaRecords(List.of(kafkaRecord));
}
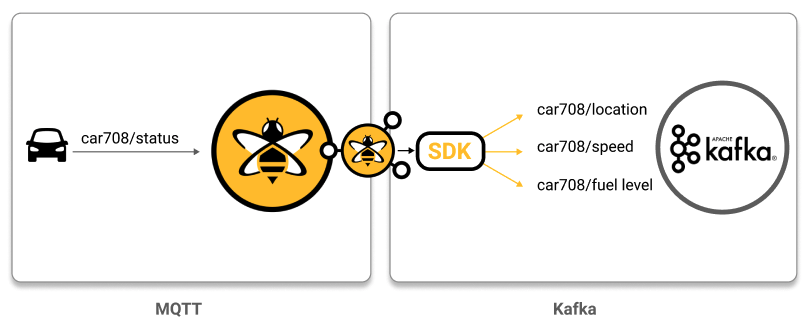
}Multicast one MQTT message to multiple Kafka topics: In this use case, the goal is to transform one MQTT message into multiple customized Kafka records that each contain a specific part of the information from the original MQTT message:
public class MulticastTransformer implements MqttToKafkaTransformer {
private static final String KAFKA_TOPIC_LOCATION_SERVICE = "location-service";
private static final String KAFKA_TOPIC_SPEED_SERVICE = "speed-control-service";
private static final String KAFKA_TOPIC_FUEL_SERVICE = "fuel-control-service";
@Override
public void transformMqttToKafka(@NotNull final MqttToKafkaInput input,
@NotNull final MqttToKafkaOutput output) {
// Get MQTT payload
final ByteBuffer mqttPayload = input.getPublishPacket().getPayload().get();
// Extract information from MQTT payload
byte[] location = extractLocation(mqttPayload);
// Create record for the location information
final KafkaRecord locationRecord = output.newKafkaRecordBuilder()
.topic(KAFKA_TOPIC_LOCATION_SERVICE)
.key(input.getPublishPacket().getTopic())
.value(location)
.build();
// Create record for the speed information
byte[] speed = extractSpeed(mqttPayload);
final KafkaRecord speedRecord = output.newKafkaRecordBuilder()
.topic(KAFKA_TOPIC_SPEED_SERVICE)
.key(input.getPublishPacket().getTopic())
.value(speed)
.build();
// Create record for the fuel information
byte[] fuel = extractFuel(mqttPayload);
final KafkaRecord fuelRecord = output.newKafkaRecordBuilder()
.topic(KAFKA_TOPIC_FUEL_SERVICE)
.key(input.getPublishPacket().getTopic())
.value(fuel)
.build();
// Set the 3 Kafka records as output
output.setKafkaRecords(List.of(locationRecord, speedRecord, fuelRecord));
}
private byte[] extractFuel(final @NotNull ByteBuffer mqttPayload) {
// Pseudo-implementation, add custom code
return null;
}
private byte[] extractSpeed(final @NotNull ByteBuffer mqttPayload) {
// Pseudo-implementation, add custom code
return null;
}
private byte[] extractLocation(final @NotNull ByteBuffer mqttPayload) {
// Pseudo-implementation, add custom code
return null;
}
}Use custom logic to drop specific MQTT messages: In this use case, the goal is to filter out received MQTT messages that have empty message payloads and to create Kafka records only for received MQTT messages with message payloads that contain data.
public class DroppingTransformer implements MqttToKafkaTransformer {
@Override
public void transformMqttToKafka(@NotNull final MqttToKafkaInput input,
@NotNull final MqttToKafkaOutput output) {
// If no payload is set, drop message
if (input.getPublishPacket().getPayload().isEmpty()) {
output.setKafkaRecords(List.of());
return;
}
// Create simple Kafka record
final KafkaRecord kafkaRecord = output.newKafkaRecordBuilder()
.topic(input.getPublishPacket().getTopic())
.key(input.getPublishPacket().getResponseTopic().orElse("unknown"))
.value(input.getPublishPacket().getPayload().get())
.build();
// Set Record as output
output.setKafkaRecords(List.of(kafkaRecord));
}
}Manage your Kafka topics: In this use case, the goal is to check whether a target Kafka topic exists and, if the topic does not yet exist, to create the topic programmatically and complete the MQTT to Kafka transformation.
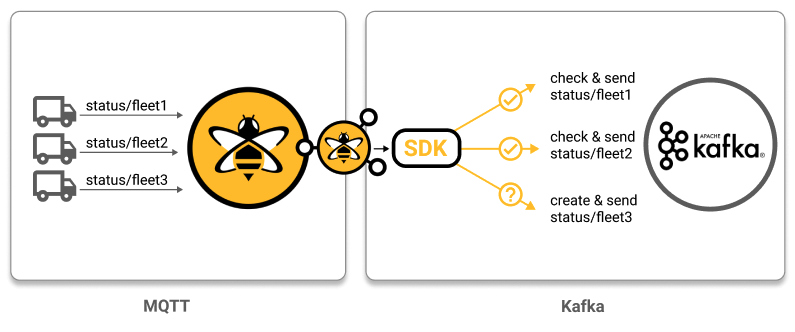
public class CreateTopicsTransformer implements MqttToKafkaTransformer {
private static final @NotNull Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CreateTopicsTransformer.class);
public static final String KAFKA_TOPIC = "example-topic";
@Override
public void init(@NotNull MqttToKafkaInitInput input) {
// Get the service for Kafka topic
final KafkaTopicService kafkaTopicService = input.getKafkaTopicService();
// See if Kafka topics exist
final KafkaTopicService.KafkaTopicState topicState = kafkaTopicService.getKafkaTopicState(KAFKA_TOPIC);
if (topicState== KafkaTopicService.KafkaTopicState.MISSING) {
final KafkaTopicService.KafkaTopicState result = kafkaTopicService.createKafkaTopic(KAFKA_TOPIC);
if (result == KafkaTopicService.KafkaTopicState.CREATED) {
log.info("Topic '{}' was created successfully", KAFKA_TOPIC);
} else {
log.warn("Topic '{}' could not be created", KAFKA_TOPIC);
}
} else if (topicState == KafkaTopicService.KafkaTopicState.FAILURE) {
// The query on the topic failed (handle this error by logging or custom logic)
}
}
@Override
public void transformMqttToKafka(@NotNull final MqttToKafkaInput input,
@NotNull final MqttToKafkaOutput output) {
// Get MQTT payload
final ByteBuffer mqttPayload= input.getPublishPacket().getPayload().orElse(ByteBuffer.allocate(0));
final KafkaRecord kafkaRecord = output.newKafkaRecordBuilder()
.topic(KAFKA_TOPIC)
.key(input.getPublishPacket().getTopic())
.value(mqttPayload)
.build();
// Set Record as output
output.setKafkaRecords(List.of(kafkaRecord));
}
}Kafka to MQTT Customization Use Case Examples
Build custom MQTT topic from incoming Kafka records: In this use case, the goal is to extract selected information from an incoming Kafka record and publish this information to a specific MQTT topic based on your own custom business logic.
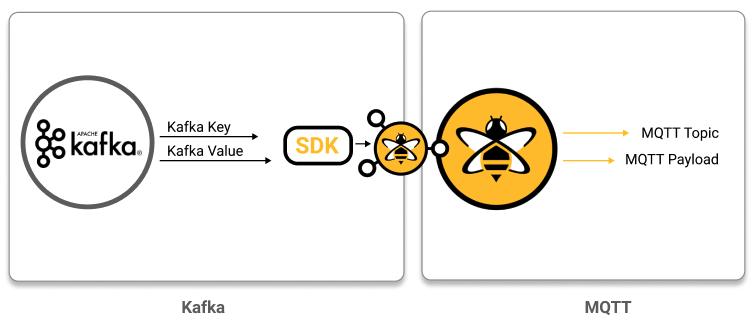
public class CustomTransformer implements KafkaToMqttTransformer {
@Override
public void transformKafkaToMqtt(@NotNull final KafkaToMqttInput input, @NotNull final KafkaToMqttOutput output) {
// Get the Kafka record
final KafkaRecord kafkaRecord = input.getKafkaRecord();
// Get value of Kafka record and use it to build MQTT payload according to custom business logic
final byte[] kafkaValue = kafkaRecord.getValueAsByteArray().orElse(new byte[0]);
final byte[] mqttPayload = ownBusinessLogic(kafkaValue);
// Get the Kafka key and use it as the MQTT topic
final byte[] kafkaKey = kafkaRecord.getKeyAsByteArray().orElse("unknown".getBytes());
String mqttTopic = new String(kafkaKey);
// Build MQTT publish
final Publish publish = output.newPublishBuilder()
.topic(mqttTopic)
.qos(Qos.AT_LEAST_ONCE)
.payload(ByteBuffer.wrap(mqttPayload))
.build();
// Set MQTT publish as output
output.setPublishes(List.of(publish));
}
private byte[] ownBusinessLogic(byte[] mqttPayload) {
// Insert your own business logic
return mqttPayload;
}
}Use custom logic to skip specific Kafka records: In this use case, the goal is to filter out incoming Kafka records that have an empty Kafka Key or Kafka Value and to create MQTT messages only for received Kafka records that have data in those fields.
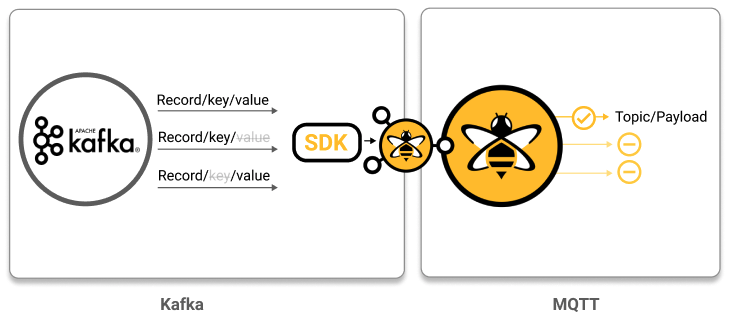
public class SkippingTransformer implements KafkaToMqttTransformer {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SkippingTransformer.class);
@Override
public void transformKafkaToMqtt(@NotNull final KafkaToMqttInput input, @NotNull final KafkaToMqttOutput output) {
// Get the Kafka record
final KafkaRecord kafkaRecord = input.getKafkaRecord();
// Skip the Kafka record if the key or value are missing
if (kafkaRecord.getKey().isEmpty() || kafkaRecord.getValue().isEmpty()) {
log.warn("Value or Key were empty, skipping Kafka record");
output.setPublishes(List.of());
return;
}
// Get value of Kafka record and use it to build MQTT payload according to custom business logic
final byte[] mqttPayload = kafkaRecord.getValueAsByteArray().orElse(new byte[0]);
// Get the Kafka key and use it as the MQTT topic
final byte[] kafkaKey = kafkaRecord.getKeyAsByteArray().orElse("unknown".getBytes());
String mqttTopic = new String(kafkaKey);
// Build MQTT publish
final Publish publish = output.newPublishBuilder()
.topic(mqttTopic)
.qos(Qos.AT_LEAST_ONCE)
.payload(ByteBuffer.wrap(mqttPayload))
.build();
// Set MQTT Publish as output
output.setPublishes(List.of(publish));
output.setPublishes(List.of(publish));
}
}-
Transform incoming Kafka records to build custom MQTT topics that are enriched from third-party sources: In this use case, the goal is to build MQTT messages from the information in incoming Kafka records and to enrich the payload of the resulting MQTT messages with information from a third-party system.
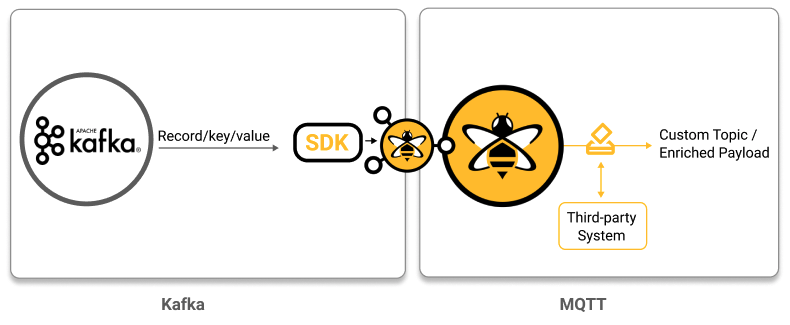
public class ThirdPartyDataTransformer implements KafkaToMqttTransformer {
@Override
public void transformKafkaToMqtt(@NotNull final KafkaToMqttInput input, @NotNull final KafkaToMqttOutput output) {
// Get the Kafka record to get value und key
final KafkaRecord kafkaRecord = input.getKafkaRecord();
final byte[] kafkaKey = kafkaRecord.getKeyAsByteArray().get();
final byte[] kafkaValue = kafkaRecord.getValueAsByteArray().get();
// Use the key and value of the Kafka Record to load information from another source and use it as MQTT Payload
byte[] mqttPayload = enrichKafkaValue(kafkaKey, kafkaValue);
// Build MQTT publish
final Publish publish = output.newPublishBuilder()
.topic(kafkaRecord.getTopic())
.qos(Qos.AT_LEAST_ONCE)
.payload(ByteBuffer.wrap(mqttPayload))
.build();
// Set MQTT Publish as output
output.setPublishes(List.of(publish));
}
private byte[] enrichKafkaValue(byte[] kafkaKey, byte[] kafkaValue) {
// Open files/db or contact other systems here and build MQTT payload or other information
byte[] mqttPayload = new byte[0];
return mqttPayload;
}
}Deploy Customization
You can deploy your customization with three simple steps:
-
Configure your
kafka-configuration.xmlto add the MQTT to Kafka transformer. -
Run the
./gradlew jartask from your Gradle project to build your customization. For example, the task from the Hello World project. -
Move the jar file from your local
build/libs/folder to theHIVEMQ_HOME/extensions/hivemq-kafka-extension/customizationsdirectory of your HiveMQ installation.
Metrics
When you implement a transformer, The HiveMQ Kafka Extension Customization SDK adds useful metrics to your HiveMQ Enterprise Extension for Kafka. Monitor the metrics to gain valuable insights into the behavior of your applications over time.
For more information, see Kafka Extension Customization SDK Metrics.
In addition to the default metrics, the Metric Registry that the Kafka Extension Customization SDK exposes gives you the ability to create your own metrics to measure specific business aspects of your individual use case.
For more information, see KafkaToMqttInitInput.