Getting Started with HiveMQ
HiveMQ is an MQTT-based messaging platform designed for fast, efficient, and reliable data movement to and from connected IoT devices. HiveMQ fully supports all standard MQTT features and delivers extended functionality such as high-availability clustering, enterprise-grade security, and deep integration into your existing systems.
Find the HiveMQ option that is right for you
HiveMQ is available in commercial and open source editions. For a complete overview of all available features, see the HiveMQ comparison chart.
The HiveMQ Enterprise MQTT Broker is the top commercial edition of HiveMQ. We offer a trial version of our enterprise broker so you can explore and test
all of the features our commercial edition provides.
HiveMQ trials are offered at no cost or obligation with the following limitations:
-
Your HiveMQ trial is for evaluation and testing purposes only. Production usage without a valid production license is strictly prohibited.
-
Our standard trial supports 25 connections. If your evaluation requires more connections, please contact us.
-
After download, you can test and evaluate HiveMQ without charge for up to 6 months.
The HiveMQ Community Edition is the open-source edition of HiveMQ. HiveMQ CE is a good choice for developers who need a basic Java-based MQTT broker that fully supports MQTT 3.x and MQTT 5. You can download HiveMQ CE on GitHub.
We make it easy for you try HiveMQ
-
Install and run your trial of the HiveMQ Enterprise MQTT Broker on a server or computer of your choice
-
Build and test a proof of concept for your HiveMQ use case
-
Take advantage of the powerful HiveMQ extension system to explore possible integrations with your application and IT infrastructure
First, select how you would like to get HiveMQ:
ZIP Download Package
Use this option to begin your HiveMQ trial from a convenient ZIP download package.
Pre-installation Requirements
-
Windows, Linux, or macOS with Java Runtime Environment 11 or higher.
For a more detailed list of requirements, see HiveMQ System Requirements.
-
Install HiveMQ
-
Unpack and run on Linux/macOS
-
Open a terminal window, go to the directory where you placed the download and unpack the ZIP archive:
cd <hivemq_install_directory> unzip hivemq-<version>.zip -
Go to the bin folder in your install directory and set permissions (the typical location is /opt/hivemq/). The
chmod 775command gives the user/owner and groups read, write, and execute rights. All others have read only access:cd <hivemq_install_directory>/bin chmod 755 run.sh -
To run the shell script and get HiveMQ started, enter:
./run.sh
-
-
Unpack and run on Windows
-
Use your file browser to extract the ZIP archive to the directory of your choice.
-
To start the batch file, open the bin folder and double-click run.bat.
-
-
| By default, the HiveMQ broker starts on localhost IP address (127.0.0.1) and listens on port 1883. |
-
Verify that HiveMQ is running
-
Navigate with your browser to http://localhost:8080. If you see the login dialog for the HiveMQ Control Center, you know that HiveMQ is up and running.
-
The HiveMQ Control Center is part of the standard HiveMQ distribution and is a web application that you can access from your browser. You do not need to install any additional software on your computer to use the control center. The default login credentials are: user: admin, password: hivemq.
-

Try out your newly-installed HiveMQ broker
The following steps show you how to get started with some MQTT basics:
-
Connect MQTT clients to your HiveMQ Enterprise MQTT broker
-
Start publishing MQTT messages and subscribing to MQTT topics
-
Monitor the activity of your MQTT clients on the HiveMQ Control Center
Once HiveMQ is running, you can use any MQTT client to connect to your MQTT broker on port 1883.
In the following procedure, we use the MQTT CLI to connect MQTT clients and test the HiveMQ broker. The MQTT CLI is an open-source, Java-based MQTT client tool that enables you to interact quickly and easily with any MQTT broker in various ways. The MQTT CLI is included in the tools directory of HiveMQ version 4.4.0 or higher.
Preparation
-
Make sure your HiveMQ instance is currently running.
-
If desired, review the introductory tutorial for the MQTT CLI on YouTube.
| The following instructions assume that HiveMQ and the MQTT clients run on the same machine. If the MQTT clients and the HiveMQ broker run on separate systems, replace 'localhost' with the address of your broker in the example commands. |
Connect MQTT Clients to HiveMQ
-
Open a terminal window and go to the
toolsdirectory of your HiveMQ 4.4 or higher installation. In thetoolsdirectory, go to themqtt-cli/binfolder and enter mqtt sh to start the MQTT CLI in shell mode.
The MQTT CLI starts and lists useful options and commands. -
To connect your first MQTT client to your HiveMQ broker on localhost and give it a custom identifier,
enter con -h localhost -i testClient1
This command creates the first MQTT client with the custom identifier testClient1 and connects the client to your MQTT broker on localhost. -
To connect another MQTT client that you can use to test your installation, open a second terminal window and
enter mqtt sh (keep your original terminal window open). -
In the second terminal window, enter con -h localhost -i testClient2
This command creates a second MQTT client with the custome identifier testClient2 and connects the client to your MQTT broker on localhost.
Publish an MQTT Message / Subscribe to an MQTT Topic
-
In the terminal window of the second MQTT client (testClient2), enter sub -t testTopic -s.
This command subscribes testClient2 to all messages that are published with the topic testTopic. -
In the terminal window of the first MQTT client (testClient1), enter pub -t testTopic -m Hello.
This command publishes the message Hello from testClient1 with the topic testTopic.
The message Hello appears immediately in the terminal window of testClient2.
| In shell mode adding the command -s blocks the MQTT CLI console so that the incoming messages are printed out to the user. |
Monitor Your Client Activity on the HiveMQ Control Center
The HiveMQ Control Center provides a wide range of metrics that help you manage and analyze your HiveMQ installation. The detailed information the control center provides helps you maintain a clear overview of your HiveMQ installation and quickly identify irregular client behavior.
-
To view the client activity that you just created, navigate with your browser to http://localhost:8080 and log in to the control center with the default credentials: user: admin, password: hivemq.
The control center Dashboard opens and shows you the current status of your HiveMQ installation (including notifications, license information, and key metrics):
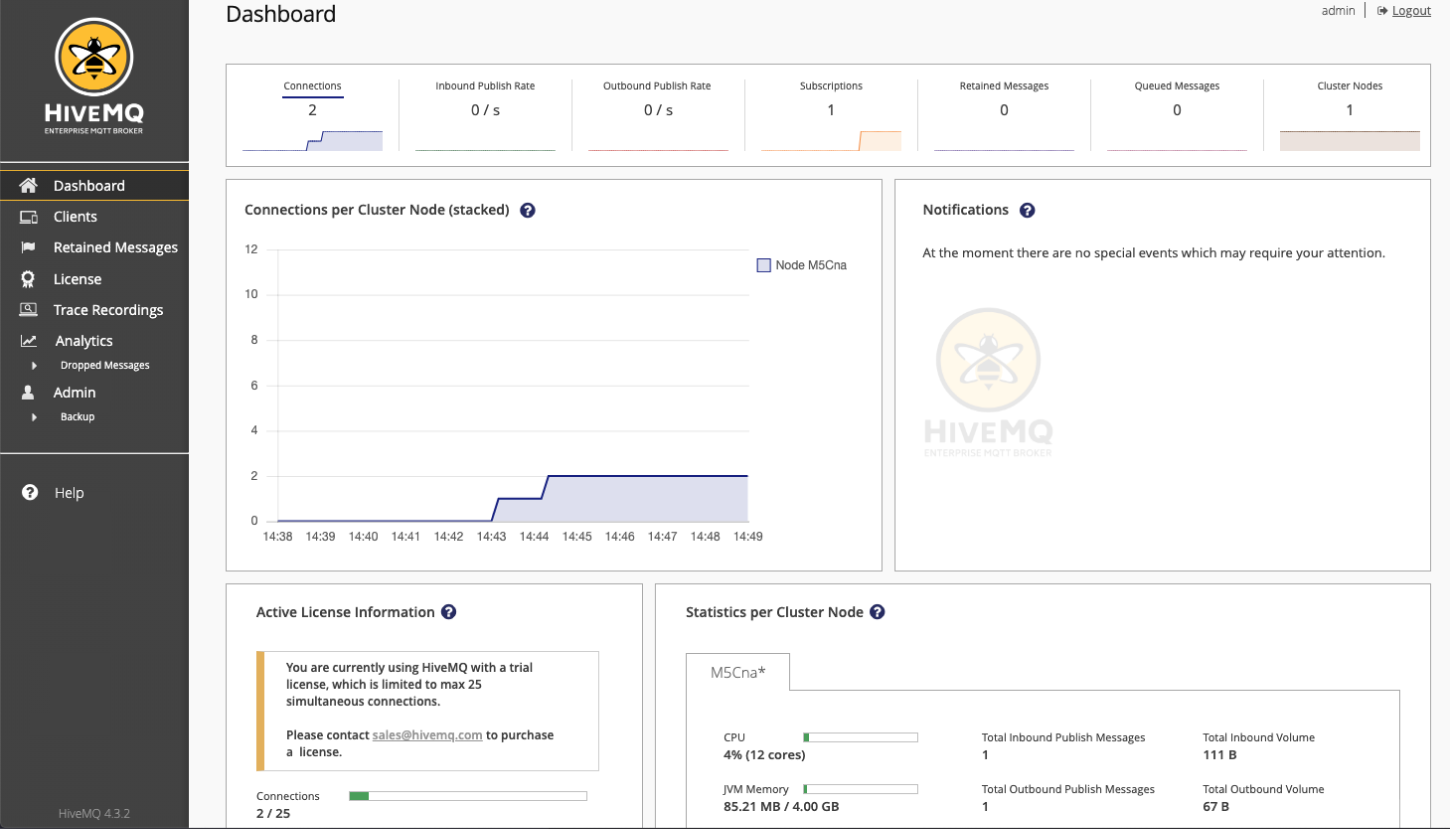
-
To view more information on the two MQTT clients that you just connected, switch to the Clients overview:
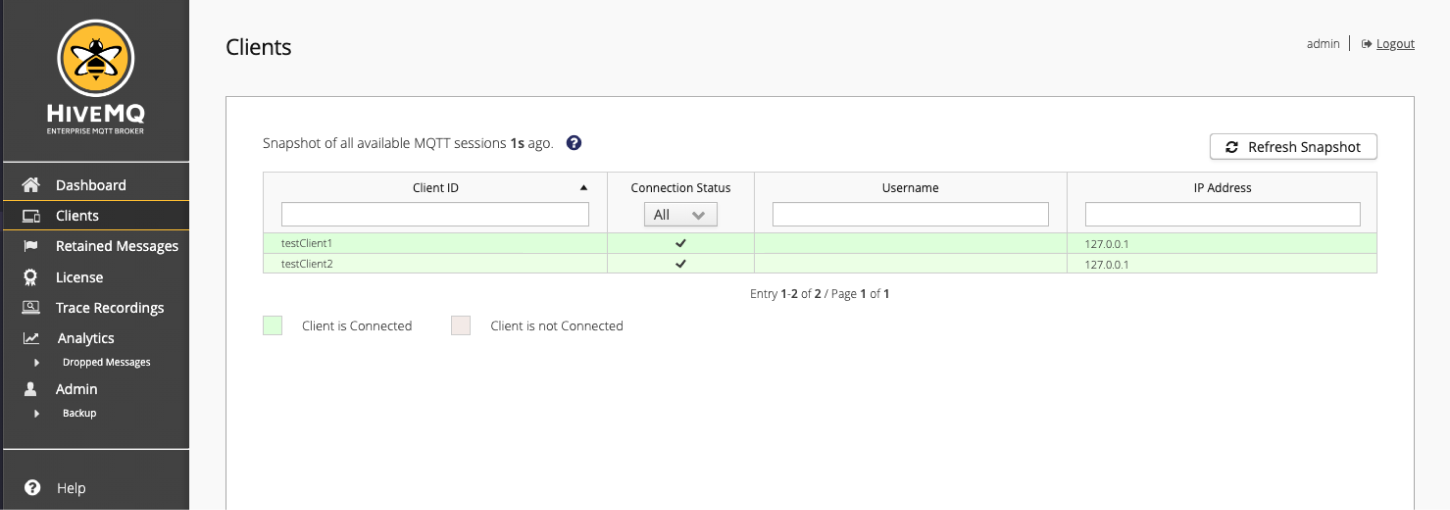
-
To learn more about all the information that the HiveMQ Control Center provides, see the Available Information.
HiveMQ Docker Installation
Running your HiveMQ trial with Docker is one of the simplest way to experiment with HiveMQ and MQTT.
-
To download and start a single HiveMQ trial node, enter:
$ docker run -p 8080:8080 -p 1883:1883 hivemq/hivemq4
(Make sure Docker is installed and running before you execute this command). -
Navigate with your browser to http://localhost:8080. If you see the login dialog for the HiveMQ Control Center, you know that HiveMQ is up and running.

The HiveMQ Control Center is part of the standard HiveMQ distribution and is a web application that you can access from your browser.
You do not need to install any additional software on your computer to use the control center.
To log in, use the default credentials: user: admin, password: hivemq.
Next Steps
Once the HiveMQ MQTT broker is running, you can use any MQTT client to connect to your HiveMQ MQTT broker on port 1883.
-
To learn more about HiveMQ clustering with Docker and using Docker and HiveMQ in production, see HiveMQ on Docker Hub and the HiveMQ User Guide.
Kubernetes and Openshift are supported as well.
| The standard trial of HiveMQ does not require a license and is limited to 25 connections. To try out HiveMQ on Docker without limitations, contact us and request an evaluation license. |
HiveMQ AWS Deployment
Quick-Launch AWS EC2 Installation for HiveMQ
Our pre-built Amazon Machine Images (AMI) let you deploy a HiveMQ trial instance on AWS EC2 with ease.
The HiveMQ Quick-Launch installation sets up a fully operational HiveMQ AWS EC2 instance with the sizing of your choice on your AWS account.
You do not need to provide any AWS credentials for this installation. A standard EC2 AWS web console dialog in your web browser is used and
no data is transmitted to us.
Select Your AMI
The AMI that you select determines the AWS region where your HiveMQ instance is deployed:
| AWS Region | Description | Action |
|---|---|---|
EU Central 1 (Frankfurt) |
Deploys HiveMQ on the AWS |
|
EU West 1 (Ireland) |
Deploys HiveMQ on the AWS |
|
EU West 2 (London) |
Deploys HiveMQ on the AWS |
|
EU West 3 (Paris) |
Deploys HiveMQ on the AWS |
|
US East 1 (N. Virginia) |
Deploys HiveMQ on the AWS |
|
US East 2 (Ohio) |
Deploys HiveMQ on the AWS |
|
US West 1 (N. California) |
Deploys HiveMQ on the AWS |
|
US West 2 (Oregon) |
Deploys HiveMQ on the AWS |
|
Canada (Central) |
Deploys HiveMQ on the AWS |
|
Asia-Pacific (Tokyo) |
Deploys HiveMQ on the AWS |
|
Asia-Pacific (Seoul) |
Deploys HiveMQ on the AWS |
|
Asia-Pacific (Singapore) |
Deploys HiveMQ on the AWS |
|
Asia-Pacific (Sydney) |
Deploys HiveMQ on the AWS |
|
South America (São Paulo) |
Deploys HiveMQ on the AWS |
Select an Instance Type
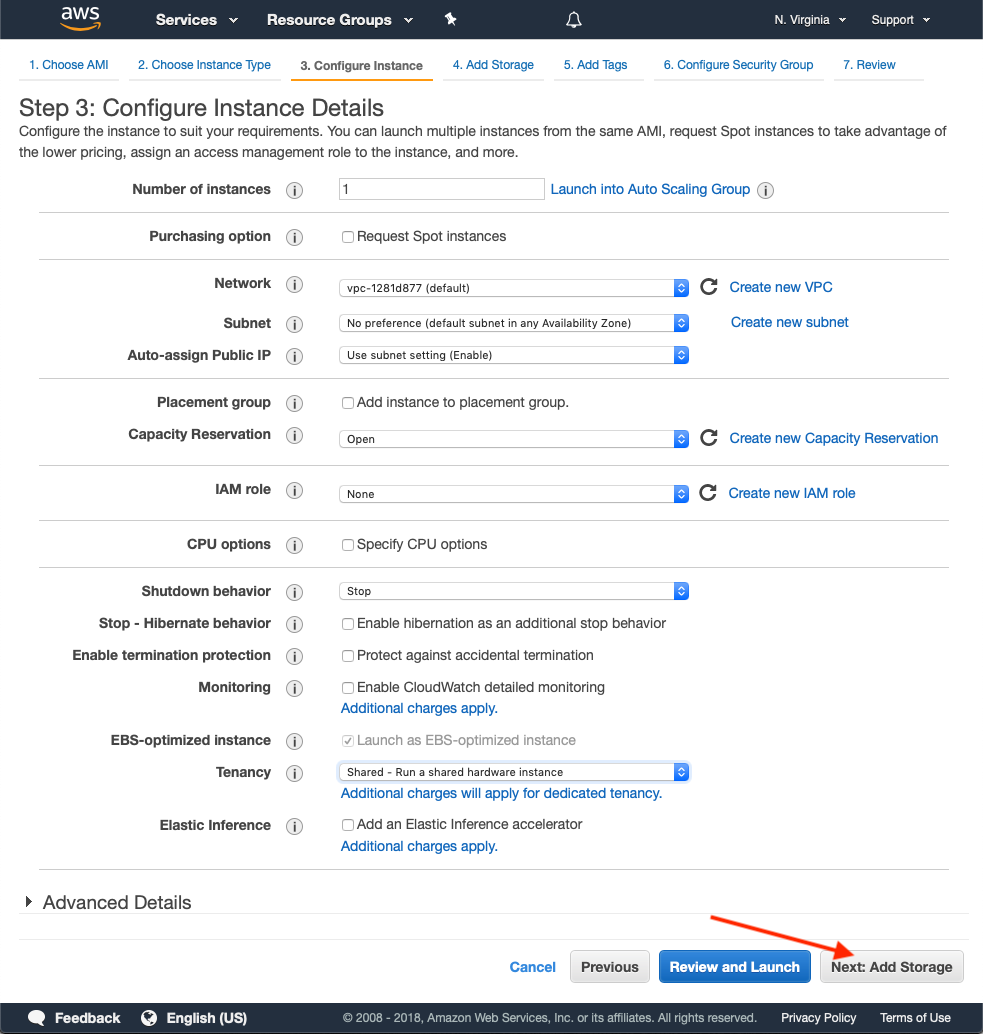
Define an appropriate instance size for your EC2 instance. To fulfill the minimum requirements for HiveMQ, use a m5.xlarge or c5.xlarge instance.
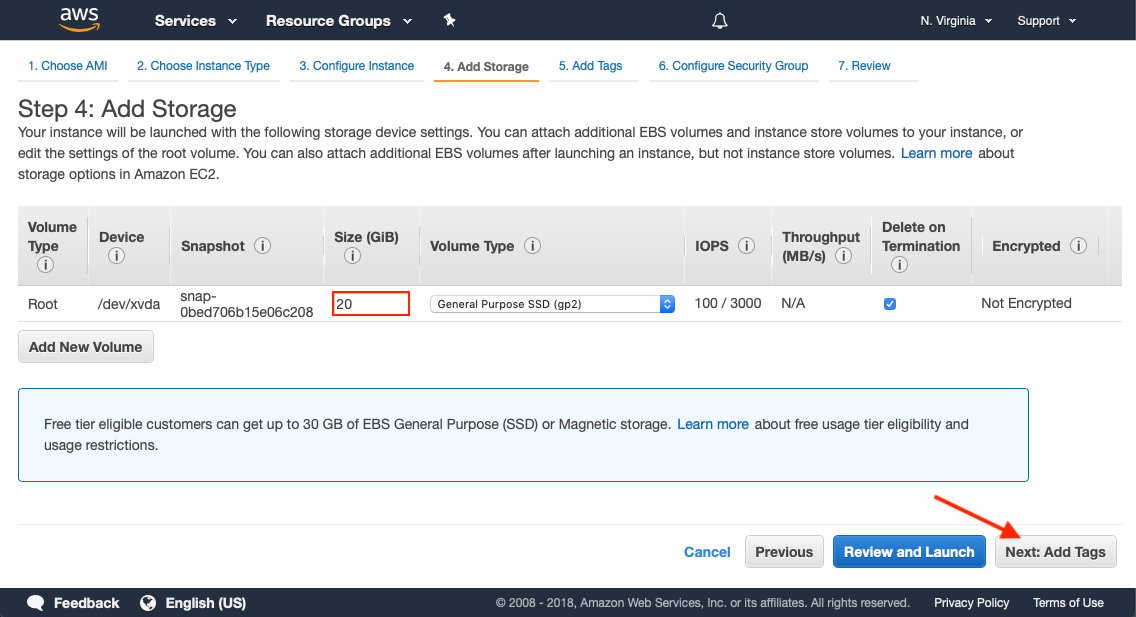
Add Storage
The minimum recommended amount of storage is 20 GB. For production deployments, we recommend 100 GB or more.
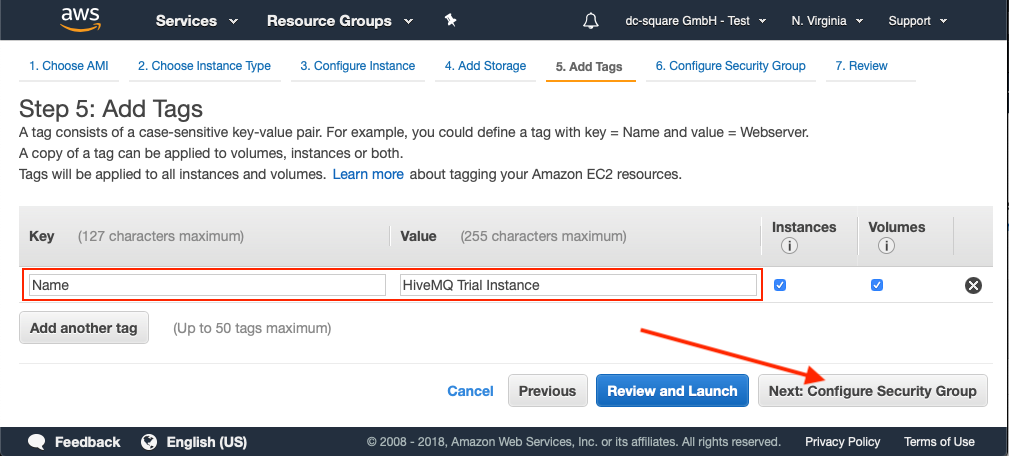
Add Tags
Optional tags are useful for adding metadata to your instance. To make it easier to identify the launched instance on your AWS web console, add a Name tag.
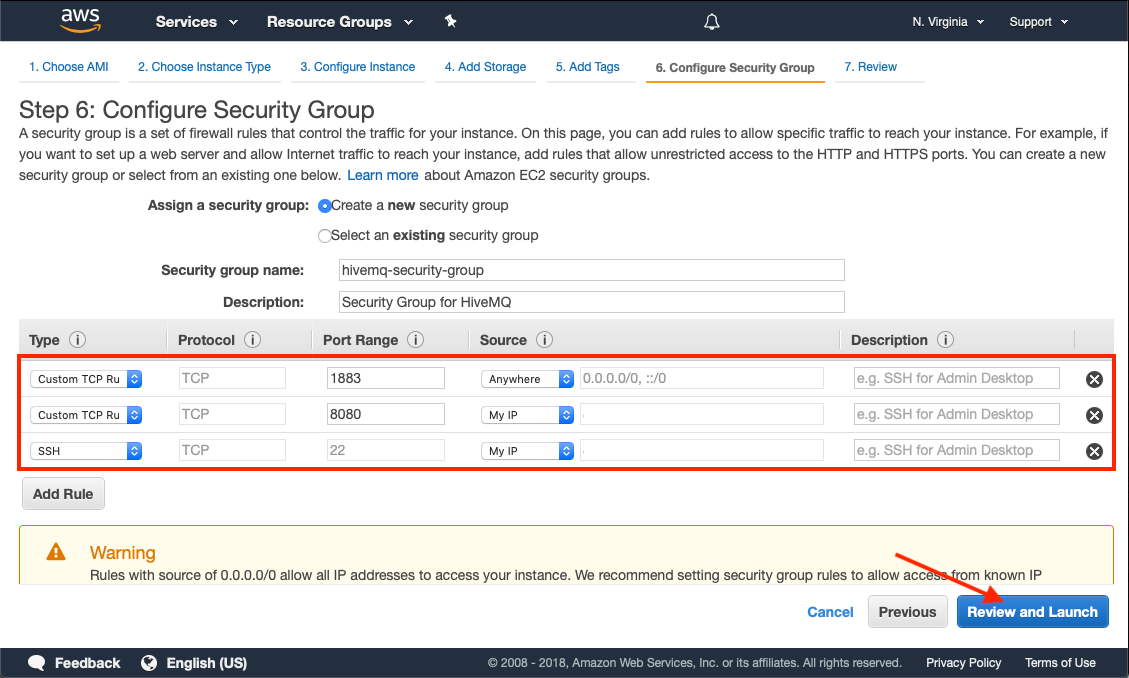
Configure Security Groups
To make your HiveMQ instance accessible to your MQTT clients, you must expose port 1883. If you want your instance to be accessible over the Internet, select anywhere as the Source.
To access the HiveMQ Control Center, configure port 8080 in your security group. If you want SSH access to your machine, you must add an SSH rule.
Make sure that the HiveMQ Control Center port 8080 and port 22 are only accessible from your IP address or trusted IP addresses. Do not allow access to these ports over the Internet.
Launch the AMI
To launch the AMI, select Launch and wait for the EC2 instance to launch. This process usually takes a few minutes.
Navigate to your EC2 Instance Overview and go to the address of your newly spawned EC2 instance with HiveMQ:
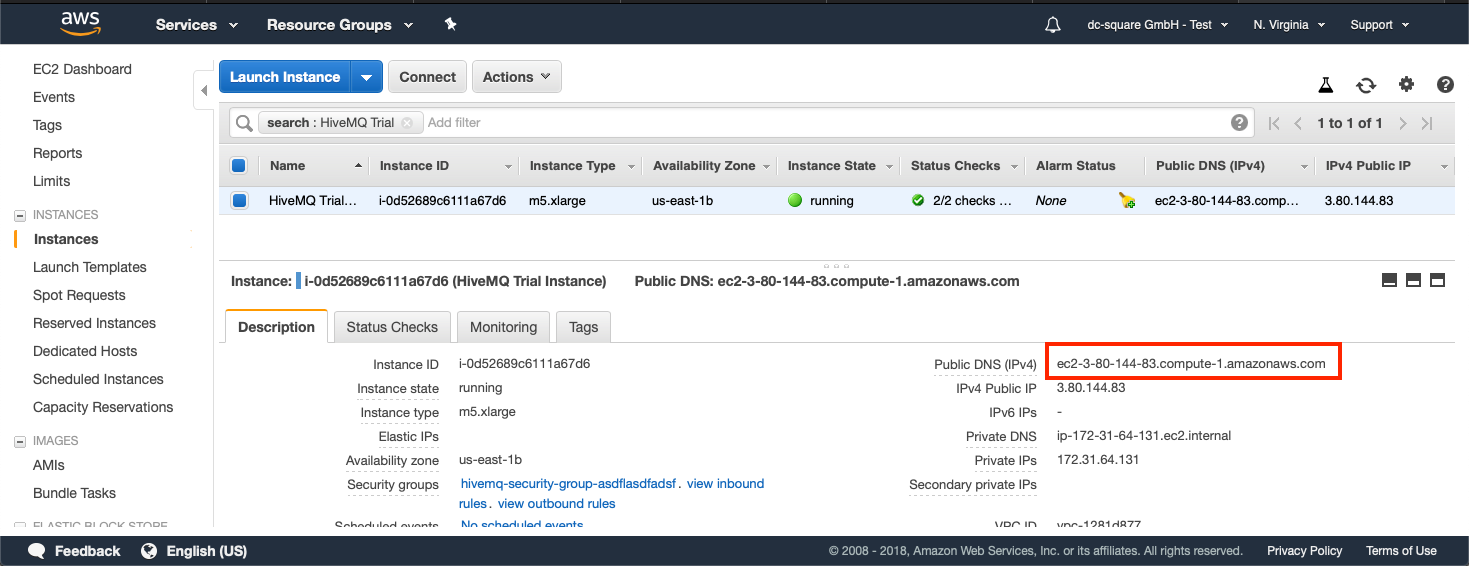
Navigate with your browser to http://<your-IP-address:8080> (use the address you located in the EC2 Instance Overview) and open the HiveMQ Control Center.
If the HiveMQ Control Center is available, HiveMQ is up and running.

You can log in with the default credentials, user: admin password: hivemq.
Once the HiveMQ MQTT broker is running, you can use any MQTT client to connect to your HiveMQ MQTT broker on port 1883.
Next Steps
The standard trial of HiveMQ does not require a license and is limited to 25 connections.
If you want to try out HiveMQ on AWS without limitations, contact us and request an evaluation license. We are happy to talk with you about setting up HiveMQ in production.