HiveMQ Cloud Authentication and Authorization
HiveMQ Cloud provides advanced authentication and authorization mechanisms that help you safeguard your data, prevent unauthorized access, and maintain the overall security and integrity of your application.
Both authentication and authorization play important roles in ensuring secure communication between MQTT clients and the MQTT broker.
You manage authentication and authorization from the Access Management tab of your HiveMQ Cloud console.
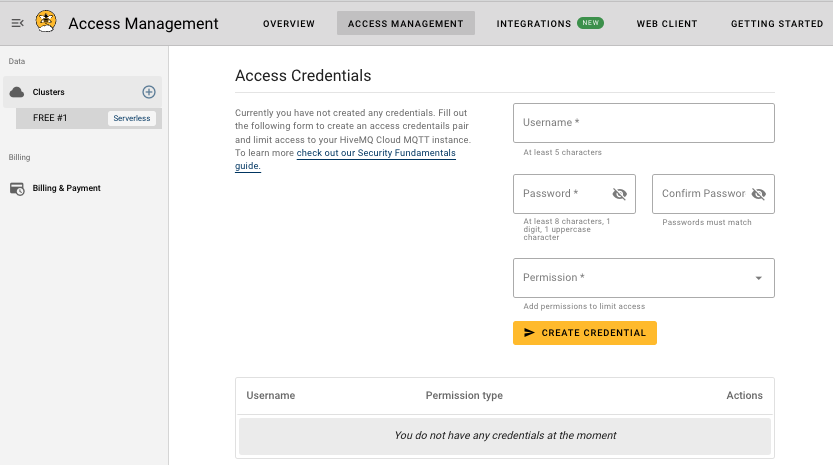
HiveMQ Cloud Access Management
HiveMQ Cloud access management offers various ways to authenticate and authorize the MQTT clients that access your cluster. The security configuration for your HiveMQ Starter plan cluster is divided into two sections:
Authentication: Defines the method HiveMQ Cloud uses to verify the identity of MQTT clients that connect to your HiveMQ Cloud broker. Authentication prevents unauthorized access and ensures that only trusted clients can perform actions on your cluster.
Authorization: Defines which actions an MQTT client is allowed to perform on your cluster. Authorization can be split into the concepts of roles and permissions.
To configure access to your broker, navigate to the HiveMQ Cloud console, select the cluster you want to configure, and select Access Management.
Authentication
To connect an MQTT client to your cluster, you need to define the authentication method that allows the client to access the cluster. Depending on the subscribed plan, HiveMQ Cloud offers three ways to ensure that only authorized devices can connect to your MQTT broker:
-
Access Credentials
-
Client Certificate
-
JSON Web Tokens
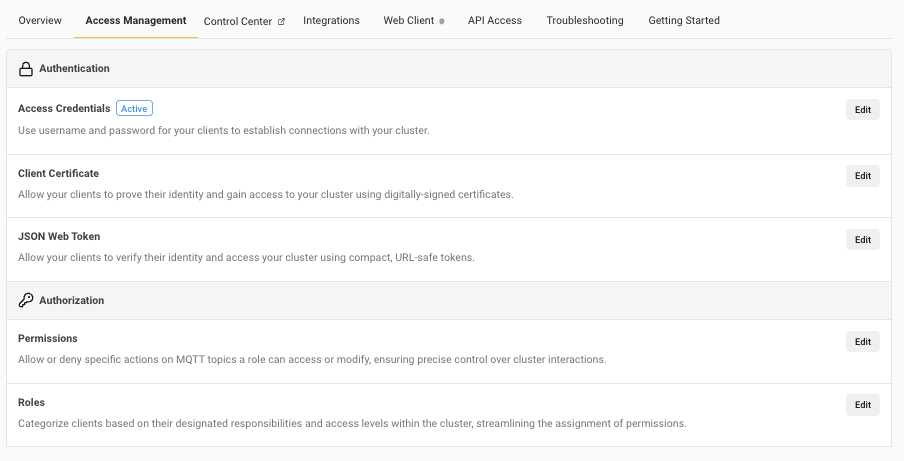
Only clients that present a known access credential, client certificate, or JSON Web Token are allowed to connect and perform actions on the selected cluster. You can choose the authentication method that fits your individual business needs.
| Currently, you can use only one authentication at a time. When you configure a method, all others are automatically disabled for your MQTT clients. The authentication method in use displays an active symbol. |
Username and Password Authentication
Username and password authentication is the default method for securing MQTT clients on HiveMQ Cloud. When this authentication method is active, clients must present credentials in the CONNECT packet to establish a connection with the MQTT broker. You can define and manage access credentials from your HiveMQ Cloud console. Each set of credentials contains a username, password, and permissions. HiveMQ securely stores the credentials and verifies client identities during connection attempts.
Access Credentials
In HiveMQ Cloud, only MQTT clients that successfully authenticate with known credentials are allowed to connect and perform actions on your cluster.
Create Access Credentials for MQTT Clients
To create a credential, go to the Access Credentials area of the Access Management tab on your running HiveMQ Cloud cluster.
| To locate the Access Credentials area, go to Clusters Overview and select Manage Cluster for the desired cluster and switch to the Access Management tab. |
When you create an access credential for HiveMQ Cloud, you define a username, a password, and assign a permission or role to the credential.
| The way permissions are assigned to a credential varies based on your HiveMQ Cloud plan. The Serverless plan ties the permission to a username. The Starter plan ties permissions to roles. To assign multiple roles and associated permissions to a single credential, you need to use the HiveMQ Cloud Starter plan or above. |
-
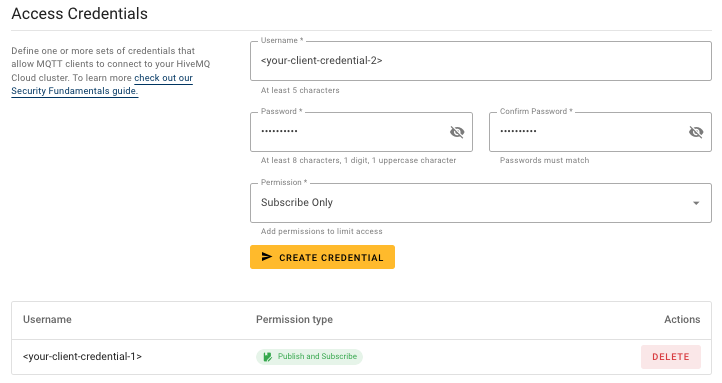
To create a credential on the Serverless plan, enter a Username and Password, and select the Permission level you want to associate with the credential. To create the Serverless credential, select Create Credential.
-
To create a credential on the Starter plan, enter a Username and Password, and select the Role you want to associate with the credential. To create the Starter credential, select Create Credential.
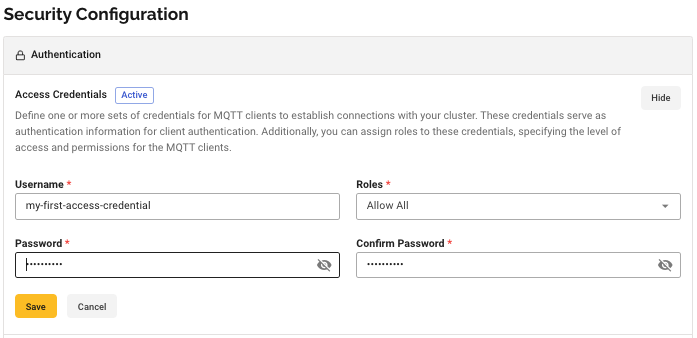
| The credential username must be unique within the HiveMQ Cloud cluster. Multiple MQTT clients can share the same credential, or you can create dedicated credentials for each MQTT client. |
The permissions or roles that you assign to a credential control the type of actions MQTT clients that connect with the credential can perform. You can use the predefined default permissions and role that HiveMQ Cloud provides or create custom permissions and roles as needed to fulfill your individual use case. For more information, see Permission Management.
HiveMQ Cloud has three default permissions: * Publish and subscribe * Subscribe only * Publish only
For more information, see Default Permissions.
HiveMQ Cloud Starter plan and up provides one default role that includes all three default permissions. For more information, see Default Role.
You can add and delete as many MQTT credentials for your HiveMQ Cloud cluster as needed. When you add or delete a credential, the Access Credentials area automatically adjusts to list only credentials that are currently available for the selected cluster.
| When you remove credentials, clients that are currently connected with the credentials remain connected. During the next reconnect, the clients will no longer be able to connect to the cluster with the old credentials. |
| Credentials are briefly cached. When you update credentials, your changes can take up to 1 minute to become active. To ensure only clients that use the updated credentials are connected, use the HiveMQ Control Center or API to force reconnection. |
Client Certificate Authentication
HiveMQ Cloud Starter plan and above support MQTT client authentication with client certificates. Client certificate authentication is a secure method for connecting MQTT clients to an MQTT broker. This method ensures that only trusted clients with valid certificates can establish a connection.
To authenticate the client at the broker using certificates, once the server certificate is validated, the client presents its certificate (which includes the public key of the client) as part of the TLS handshake. The broker then verifies the identity of the client based on the presented certificate and can terminate the handshake if the verification fails.
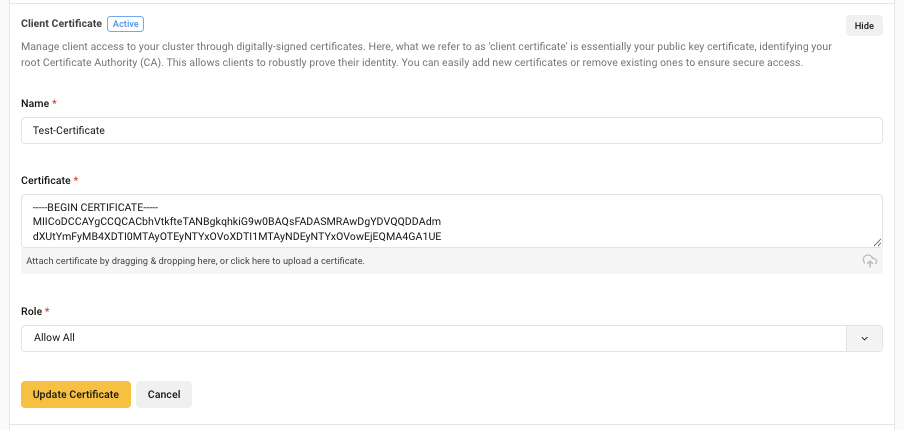
In the expanded Client Certificate area, enter a Name for the client certificate. Drag and drop or upload your public key certificate to the Key field. Assign a role from the Role drop-down list to set the level of access and permissions the client certificate allows. Select Save to enable the client certificate authentication method.
You can add and remove client certificates as needed to ensure secure access.
| When you change your authentication method, your previously selected authentication method is overridden. Currently-connected clients can be disconnected and could need to be reconfigured. |
JWT Authentication
HiveMQ Cloud Starter plan and above support the use of JSON Web Tokens (JWT) to authenticate MQTT clients. JWT authentication provides a secure and scalable way to authenticate MQTT clients without requiring traditional username-password credentials or certificates. JWT authentication uses a compact URL-safe token to confirm the identity of the MQTT client. The authentication server signs the token with a private key to ensure its integrity and authenticity. HiveMQ Cloud uses the corresponding public key to verify the signature of the JWT.
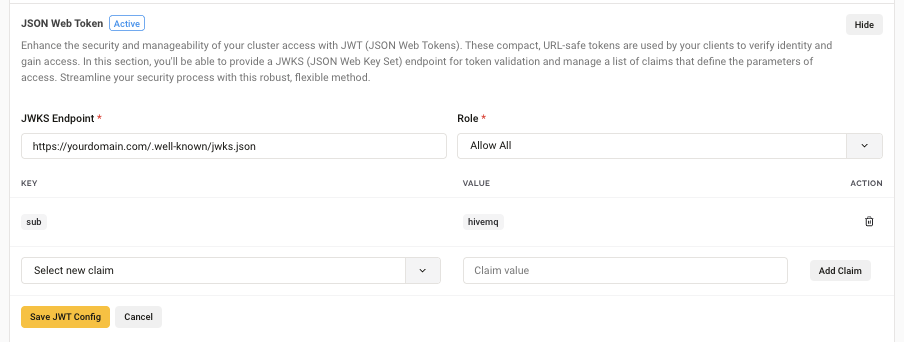
In the JSON Web Token section, you can provide a JSON Web Key Set (JWKS) endpoint for token validation and manage a list of claims that define the parameters of access.
To set up JSON Web Token authentication, select Edit in the JSON Web Token area of your Security Configuration. In the expanded JSON Web Token area, select Add JSON Web Token and enter a JWKS Endpoint. In the Claims area, enter one or more Key and Value pairs. Claims are key-value pairs within the JWT payload that carry information about the MQTT client used to verify and authorize the client at the broker. Assign a role from the Role drop-down list to set the level of access and permissions the JWT allows.
| The Starter plan only supports the registered claims iss, sub, aud, iat, exp, scope. |
| When you change your authentication method, your previously selected authentication method is overridden. Currently connected clients can be disconnected and could need to be reconfigured. |
Authorization
In MQTT, authorization controls what actions a client can perform once authenticated. HiveMQ Cloud provides different authorization mechanisms based on the selected plan. Access to the broker is defined with permissions that specify what the MQTT client is allowed to do. In HiveMQ Cloud Starter plan and above, permissions are grouped into roles, so a collection of permissions can be assigned to one or multiple clients.
Permission Management
In HiveMQ Cloud, you assign different permissions to set the activity level of an MQTT client on your cluster. A permission is a rule that defines a specific action an MQTT client is allowed to perform at the broker. Each permission is tied to an MQTT topic filter. For more information, see Topic Filters. The available granularity of a permission depends on the HiveMQ Cloud plan.
Default Permissions
For your convenience, HiveMQ Cloud provides several default permissions that you can use to authorize your MQTT clients. All default permissions use multi-level wildcard topic filters (#). The multi-level wildcard topic filter specifies that the activity the default permission allows applies to all available MQTT topics.
The default permissions cannot be modified or removed from the system.
| To limit a permission to specific MQTT topics, create a custom permission. You can create as many custom permissions as your use case requires. For more information, see Custom Permissions. |
| Permission name | Description |
|---|---|
Subscribe Only |
Clients that authenticate with credentials that include Subscribe Only permission are allowed to receive MQTT messages on all MQTT topics but are not allowed to publish MQTT messages. The permission includes a multi-level wildcard topic filter (#) specifies that subscriptions to all MQTT topics are allowed. Publishes are not allowed with this permission. |
Publish Only |
Clients that authenticate with credentials that include Publish Only permission are allowed to publish to available MQTT topics but are not allowed to subscribe to MQTT topics. |
Publish and Subscribe |
Clients that authenticate with credentials that include Publish and Subscribe permission are allowed to publish and subscribe to all available MQTT topics. |
The HiveMQ Cloud Serverless plan supports the selection of one permission per credential. In the Serverless plan, permissions are tied to a username. The default permissions are available for selection in the dropdown menu of the Permissions field:
In the HiveMQ Cloud Starter plan, permissions are tied to roles. Each role can include one or more permissions, and you can assign multiple roles per credential. For your convenience, the Starter plan provides one default role that includes all three default permissions:
| When you create custom permissions in the Serverless plan, the new permissions are automatically added to the list of available permissions in the Permissions field of the Access Credentials area. When you create custom permissions in the Starter plan, the new permissions are automatically added to the list of available permissions in the Permissions field of the Roles area. When you create additional roles, the new roles are automatically added to the list of available roles in the Roles field of the Access Credentials area. |
Custom Permissions
For some use cases, the default HiveMQ Cloud permissions are too generic. The ability to define custom permissions allows you to implement sophisticated topic-based access rights that match your business needs and facilitate permission management.
Permission Name
HiveMQ Cloud uses the permission name to identify the permission within the system. Since the name is used as an identifier, each permission on your HiveMQ Cloud cluster must have a unique name. When you create a custom permission, HiveMQ Cloud alerts you if the permission name is already in use and prevents the creation of a permission with a duplicate name.
To configure a custom permission, select Create new permission in the Permissions area of the Authorization section.
In addition to a unique name, each custom permission includes a Description field where you can add information that helps identify the purpose of the permission.
After you create a custom permission, the name of the permission appears in the list of permissions you can assign during access credential creation.
| In the Serverless plan, permissions are tied to a username. In the Starter plan and above, permissions are associated with a role. Currently, the Starter plan does not support mapping permissions to a username. |
Permission Topic Filters
In a HiveMQ Cloud permission, the Topic Filter defines to which topics the permission applies. All valid MQTT topic filters, including wildcards (+,#) are supported. When you create a custom permission, the activity the permission allows applies only to the topics you define in the Topic Filter field.
Dynamic Variables in MQTT Topics
HiveMQ Cloud Starter plan gives you the ability to dynamically customize your MQTT topics with variables based on your authentication method. The use of dynamic variables allows for more flexible and personalized data routing.
| Authentication Method | Variables | Description |
|---|---|---|
Access Credentials |
${mqtt-username} |
Apply for user-specific topics |
JWT Claims |
${string-sub}, ${string-aud}, ${string-iss}, ${string-scope} |
Apply for the audience, issuer, and scope respectively |
x509 Certificate |
${string-subject-common-name}, ${string-issuer-common-name} |
Apply for detailed certificate identification |
Universal |
${mqtt-clientid} |
Apply to all authentication methods for client identification |
| Keep in mind that MQTT special characters such as # (multi-level wildcard) and + have unique functionalities in topic filters. For more information, see MQTT Topics, Wildcards, & Best Practices. |
Create Permissions (Serverless plan)
In the HiveMQ Cloud Serverless plan, you select permissions in the Permissions field of the Access Credentials area. To add a permission to the list of permissions that are available to assign to a credential, define a permission in the Permissions area of the Access Management tab:
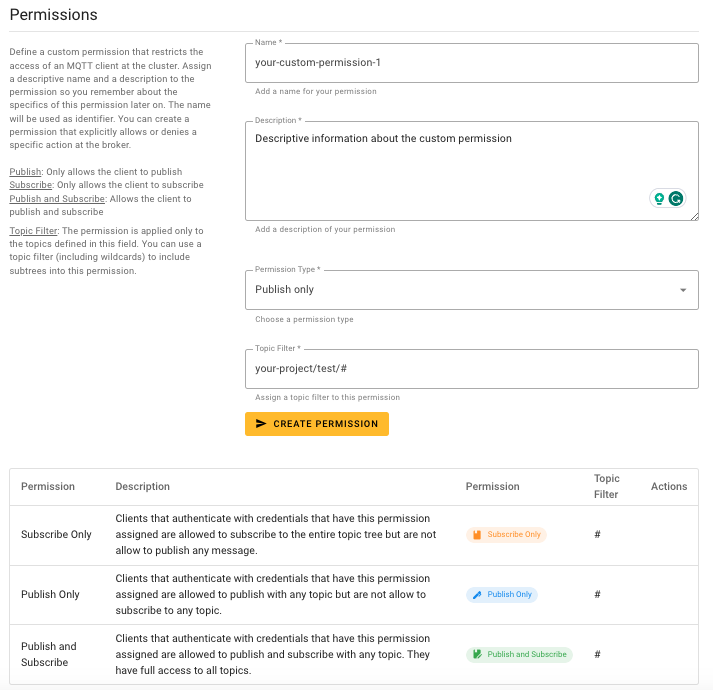
After you create a permission in the Serverless plan, the name of the permission appears in the list of permissions you can assign to a credential.
Create Permissions (Starter plan and up)
In the HiveMQ Cloud Starter plan and above, you can define and attach one or more permissions to a role. To add permissions to the list of permissions that are available to assign to a role, define a permission in the Permissions area of the Access Management tab:
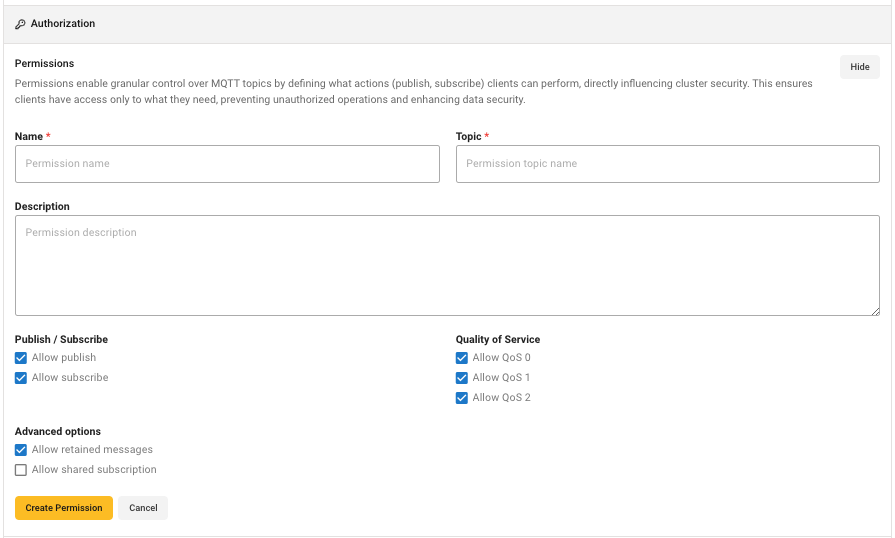
Permissions in the Starter plan and above include the following options to allow specific actions:
-
Topic Filter: Defines the topic filter to which the permission applies. All valid MQTT topic filters, including wildcards (+,#) are supported. This field is required.
-
Publish/Subscribe: Defines the activity that the permission allows. You can apply the permission for Publishes, Subscriptions, or both. Select the checkboxes for all activities you want the permission to allow.
-
Quality of Service level (QoS): Defines the QoS levels to which the permission applies. You can select one or more available QoS levels: QoS 0, QoS 1, and QoS 2. Select the checkboxes for all QoS levels for which you want the permission to apply.
-
Retained messages: Specifies whether the client is allowed to publish a message as a retained message. This option is only applicable for permissions that allow publishing.
-
Shared group: Specifies whether the client is allowed to subscribe to a shared subscription. If this option is selected, you must input a valid shared group name to which the client is allowed to subscribe. Enter the shared group name without
$share/or enter#to match all shared groups.
| The HiveMQ Cloud broker uses explicit whitelisting functionality. If an action is not explicitly allowed, it is denied. |
Each custom permission you create is added to the list of available permissions along with the predefined default permissions. To delete a custom permission from the list of available permissions, select Delete.
| A permission can only be deleted if it is not used to authenticate an MQTT client or used by a role. Before you delete a permission, you must remove all credentials and roles that use the permission. The default HiveMQ Cloud permissions cannot be removed from the system. |
| Permissions are cached for 5 minutes. When you update a permission, your changes can take up to 5 minutes to become active. To ensure only clients that use updated permissions are connected, delete the old permission and create a new permission. |
Role-Based Access Control for MQTT Clients
HiveMQ Cloud Starter plans and above support Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) for your MQTT clients. RBAC gives you the ability to group permissions into various roles. When you assign roles to a credential, client certificate, or JWT authentication, clients that access your cluster can perform all activities that permissions associated with the roles allow.
Grouping permissions into roles helps reduce the complexity of managing individual permissions for MQTT clients. As your use case grows, simplified permission management makes it easier to standardize the access rights of your MQTT clients. With RBAC, you can ensure that MQTT clients with similar responsibilities have consistent levels of access.
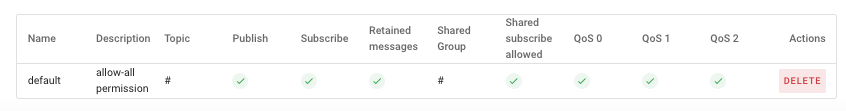
Default Role
For your convenience, the HiveMQ Starter plan provides a default role that you can use to assign permissions to your credentials. The default role includes all default permissions and several additional MQTT-specific permissions:
Custom Roles
Role-based access control for a HiveMQ Cloud cluster usually requires more roles than the default HiveMQ Cloud role. The ability to define custom roles with specifically selected permissions allows you to implement effective role-based access control for your MQTT clients to match your business needs.
Role Name
HiveMQ Cloud uses the name of the role to identify the role within the system. Since the name is used as an identifier, each role on your HiveMQ Cloud cluster must have a unique name. When you create a role, HiveMQ Cloud alerts you if the role name is already in use and prevents the creation of a role with a duplicate name.
In addition to a unique name, each role includes an optional Description field where you can add information that helps identify the purpose of the role.
After you create a role, the name of the role appears in the list of roles you can assign during access credential creation.
Every role in HiveMQ Cloud includes at least one permission that is associated with the role. For more information, see Permission Management.
Create Roles (Starter plan and above only)
In the HiveMQ Cloud Starter plan and above, you define roles to group permissions in ways that match your particular use case.
To add roles to the list of roles that are available to assign to a username when you create an access credential, define a role in the Roles area of the Access Management tab:
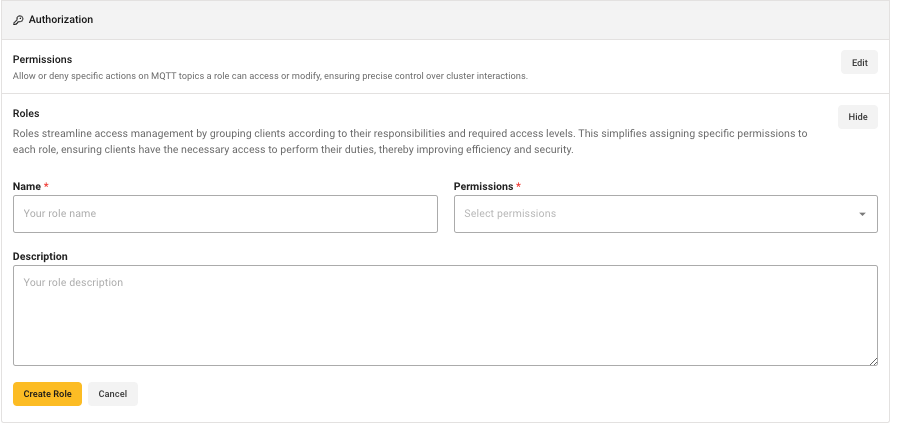
Each role can consist of an unlimited number of permissions. When you create a custom role, you can select the permissions you group together in the role to perform a specific task.
To create a role, enter a unique name, add a description of the role, and select one or more permissions from the list of available permissions in the Permissions field.
| The list automatically contains the predefined HiveMQ Cloud default permissions and all available custom permissions that you create. To add more permissions to the list of available permissions, see Create Permissions (Starter plan and up). |
To create the defined role, select Create role.
Each role you create is added to the list of available roles in the Roles field of the Access Credentials area along with the predefined default role.
To delete a role from the list of available roles, select Delete.
| A role can only be deleted if it is not used to authenticate an MQTT client. Before you delete a role, you must remove all credentials that use the role. |
| Roles are cached for 24 hours. When you update a role, your changes can take up to 1 day to become active. To ensure only clients that use the updated roles are connected, delete the old role and create a new role with the updated set of permissions. |