HiveMQ Edge MQTT Bridges
HiveMQ Edge offers bidirectional MQTT bridge functionality to connect it to enterprise MQTT brokers and forward messages or receive messages from upstream.
You can configure bridges on the HiveMQ Edge UI or in your HiveMQ Edge configuration file.
<hivemq>
...
<mqtt-bridges>
<mqtt-bridge>
<id>my-hivemq-cloud-bridge</id>
<remote-broker>
<host>your.broker.host</host>
<port>1883</port>
</remote-broker>
<forwarded-topics>
<forwarded-topic>
<filters>
<mqtt-topic-filter>mytopic/#</mqtt-topic-filter>
</filters>
</forwarded-topic>
</forwarded-topics>
<remote-subscriptions>
<remote-subscription>
<filters>
<mqtt-topic-filter>myothertopic/#</mqtt-topic-filter>
</filters>
</remote-subscription>
</remote-subscriptions>
</mqtt-bridge>
</mqtt-bridges>
...
</hivemq>| Name | Default | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Unique identifier for this bridge. |
|
|
|
Connection information for the remote broker. For more information, see remote-broker. |
|
|
|
Forwarded topics. |
|
|
|
Remote subscriptions. |
|
|
|
|
Optional setting to reduce the possibility of unintentional message loops with MQTT bridging. For more information, see loop-prevention. |
Bridge Remote Broker Configuration
The remote broker configuration contains all configurations about the MQTT connection/session to the remote broker.
Example bridge configuration with all remote broker settings:
<hivemq>
...
<mqtt-bridges>
<mqtt-bridge>
<id>my-hivemq-cloud-bridge</id>
<remote-broker>
<host>my.broker.url</host>
<port>1883</port>
<authentication>
<mqtt-simple-authentication>
<username>user1</username>
<password>pass1</password>
</mqtt-simple-authentication>
</authentication>
<tls>
<enabled>true</enabled>
<keystore>
<path>/path/to/keystore.jks</path>
<password>pass2</password>
<private-key-password>pass3</private-key-password>
</keystore>
<truststore>
<path>/path/to/truststore.jks</path>
<password>pass4</password>
</truststore>
<cipher-suites>
<cipher-suite>TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256</cipher-suite>
<cipher-suite>TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384</cipher-suite>
<cipher-suite>TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA</cipher-suite>
<cipher-suite>TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA</cipher-suite>
</cipher-suites>
<protocols>
<protocol>TLSv1.2</protocol>
<protocol>TLSv1.3</protocol>
</protocols>
<handshake-timeout>10</handshake-timeout>
<verify-hostname>true</verify-hostname>
</tls>
<mqtt>
<clean-start>true</clean-start>
<client-id>my-custom-mqtt-client-identifier</client-id>
<keep-alive>60</keep-alive>
<session-expiry>3600</session-expiry>
</mqtt>
</remote-broker>
...
</mqtt-bridge>
</mqtt-bridges>
...
</hivemq>| Name | Default | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Unique identifier for this bridge. |
|
|
|
|
Unique identifier for this bridge. |
|
|
|
Connection information for the remote broker, see remote-broker |
|
|
|
Forwarded topics, see forwarded-topics |
|
|
Remote subscriptions, see remote-subscriptions |
Authentication configuration
HiveMQ Edge bridges support MQTT username/password based authentication.
<hivemq>
...
<mqtt-bridges>
<mqtt-bridge>
...
<remote-broker>
<authentication>
<mqtt-simple-authentication>
<username>user1</username>
<password>pass1</password>
</mqtt-simple-authentication>
</authentication>
</remote-broker>
...
</mqtt-bridge>
</mqtt-bridges>
...
</hivemq>| Name | Default | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Username |
|
|
|
Password |
TLS configuration
Secured connections can be configured with the tls configuration section.
<hivemq>
...
<mqtt-bridges>
<mqtt-bridge>
<remote-broker>
<tls>
<enabled>true</enabled>
<keystore>
<path>/path/to/keystore.jks</path>
<password>pass2</password>
<private-key-password>pass3</private-key-password>
</keystore>
<truststore>
<path>/path/to/truststore.jks</path>
<password>pass4</password>
</truststore>
<cipher-suites>
<cipher-suite>TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256</cipher-suite>
<cipher-suite>TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384</cipher-suite>
<cipher-suite>TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA</cipher-suite>
<cipher-suite>TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA</cipher-suite>
</cipher-suites>
<protocols>
<protocol>TLSv1.2</protocol>
<protocol>TLSv1.3</protocol>
</protocols>
<handshake-timeout>10</handshake-timeout>
<verify-hostname>true</verify-hostname>
</tls>
...
</remote-broker>
...
</mqtt-bridge>
</mqtt-bridges>
...
</hivemq>Mutual TLS (using client certificate) is automatically enabled if the keystore is set.
| Name | Default | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Specifies whether TLS is enabled. |
|
|
The keystore that contains the client certificate and private key to use for mTLS. If not set mTLS will not be used. |
|
|
|
|
The truststore containing the trusted certificates. If no truststore is set, the default system truststore is used. |
|
|
A list of cipher suites to support. |
|
|
|
A list of protocols to support. |
|
|
|
|
The duration of the TLS handshake timeout in seconds. |
|
|
|
Specifies whether the server certificate hostname is verified. |
<hivemq>
...
<mqtt-bridges>
<mqtt-bridge>
<remote-broker>
<tls>
<keystore>
<path>/path/to/keystore.jks</path>
<password>pass2</password>
<private-key-password>pass3</private-key-password>
</keystore>
...
</tls>
...
</remote-broker>
...
</mqtt-bridge>
</mqtt-bridges>
...
</hivemq>| Name | Default | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
The path on the local filesystem to the JKS keystore. |
|
|
The password for the keystore. |
|
|
|
The password for the private key in the keystore. |
<hivemq>
...
<mqtt-bridges>
<mqtt-bridge>
<remote-broker>
<tls>
<truststore>
<path>/path/to/truststore.jks</path>
<password>pass4</password>
</truststore>
...
</tls>
...
</remote-broker>
...
</mqtt-bridge>
</mqtt-bridges>
...
</hivemq>| Name | Default | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
The path on the local filesystem to the JKS truststore. |
|
|
the password for the truststore. |
Remote broker MQTT connection configuration
<hivemq>
...
<mqtt-bridges>
<mqtt-bridge>
<id>my-hivemq-cloud-bridge</id>
<remote-broker>
<mqtt>
<clean-start>true</clean-start>
<client-id>my-custom-mqtt-client-identifier</client-id>
<keep-alive>60</keep-alive>
<session-expiry>3600</session-expiry>
</mqtt>
...
</remote-broker>
...
</mqtt-bridge>
</mqtt-bridges>
...
</hivemq>| Name | Default | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Defines whether the client wants to start a new session upon reconnection (clean-start = true) or resume a previous session if present (clean-start = false).
The default setting is |
|
|
|
Specifies the client identifier of the bridge MQTT client. If no client identifier is set, the identifier of the bridge is used. |
|
|
|
The time in seconds that the broker permits between when a bridge MQTT client finishes sending one MQTT packet and starts to send the next. The broker must disconnect a client that does not send a message or a PINGREQ packet in one and a half times the stated keep alive interval. The default setting is 60 seconds. |
|
|
|
The time in seconds until the session of the bridge MQTT client expires after the connection is lost or closed. The default setting is 3600 seconds (one hour). Session expiry is only available for MQTT 5 remote brokers. |
Loop prevention
It is possible to create infinite message loops with MQTT bridging. Unintentional message loops can increase the load on your MQTT brokers significantly. To mitigate the possibility of overload due to uncontrolled message loops, HiveMQ Edge enables basic loop-prevention by default.
The loop-prevention configuration utilizes an MQTT 5 user property to set duplication limits for PUBLISH messages.
|
Hop Counting
The bridge tracks the movement (hops) of PUBLISH messages within the bridge and stores the count in the hmq-bridge-hop-count user property of the message.
The hop count is incremented at the moment the PUBLISH message enters the bridge.
If the bridge registers an increment in the hmq-bridge-hop-count user property of a PUBLISH message that exceeds the hop-count-limit in your loop-prevention configuration, the bridge discards the message.
Hop counting provides a simple way to avoid potential loop-creation without the need for complex topic naming configurations.
When you use the default hop-count-limit of 1, no duplicate messages are possible.
If you configure the hop-count-limit to a value that is greater than 1, a fixed number of duplicate messages are possible, but no loops can form.
| Duplicates can also be prevented through correct configuration with a proper topic structure. |
...
<mqtt-bridges>
<mqtt-bridge>
...
<loop-prevention>
<enabled>true</enabled>
<hop-count-limit>1</hop-count-limit>
</loop-prevention>
...
</mqtt-bridge>
</mqtt-bridges>
...Topic Mapping
Topic mapping filters the messaging flow from the source topics to the destination topics. Each topic can consist of one or more topic levels. Topic levels are separated by a forward slash (topic level separator).
| Topic mapping functions are bidirectional. |
| Topic Filter Setting | Description |
|---|---|
|
Defines which messages the bridge processes. |
|
Defines a subset of topics from the topic |
|
Modifies the selected topic to map to a different topic at the local or remote broker. This modification is executed before the message is published. |
|
Defines whether the retained message flags of retained messages in the selected data stream are kept. |
|
Adds custom static user properties to the messages processed by the bridge. |
<forwarded-topic>
<filters>
<mqtt-topic-filter>topicA/#</mqtt-topic-filter>
<mqtt-topic-filter>house/#/temperature</mqtt-topic-filter>
</filters>
<destination>{#}</destination>
<excludes>
<mqtt-topic-filter>topicA/not-this</mqtt-topic-filter>
</excludes>
<preserve-retain>false</preserve-retain>
<max-qos>2</max-qos>
<custom-user-properties>
<user-property>
<key>my-key</key>
<value>my-value</value>
</user-property>
</custom-user-properties>
</forwarded-topic><remote-subscription>
<filters>
<mqtt-topic-filter>topicA/#</mqtt-topic-filter>
<mqtt-topic-filter>house/#/temperature</mqtt-topic-filter>
</filters>
<destination>remote/topic</destination>
<custom-user-properties>
<user-property>
<key>my-key</key>
<value>my-value</value>
</user-property>
</custom-user-properties>
</remote-subscription>Modifications of destination tag based on a topic filter:
-
Variables can be used inside the
destinationandexcludestags -
Each topic level can be addressed by number, starting with 1
-
Static text can be added
-
A prefix and postfix can be used
Topic Filter Configuration Examples
Forward to a Static Remote Topic Example
<filters>
<mqtt-topic-filter>+/status</mqtt-topic-filter>
</filters>
<destination>remote/data</destination>Original topic: machine/status
Resulting topic: remote/data
Exclude Specific Topics Example
<filters>
<mqtt-topic-filter>clients/+/+</mqtt-topic-filter>
</filters>
<excludes>
<mqtt-topic-filter>clients/id1/status</topic-filter>
</excludes>Original topic: clients/id1/status
Resulting topic: <not forwarded>
-
The bridge consumes all topics that match the filter and forwards messages other than messages to the excluded topics to the destination topic.
Add Prefix and Postfix as Destination Example
<filters>
<mqtt-topic-filter>+/status</mqtt-topic-filter>
</filters>
<destination>prefix/{#}/data</destination>Original topic: machine/status
Resulting topic: prefix/machine/status/data
-
The bridge consumes all topics that match the filter and uses the full MQTT topic from the client as the destination topic at the remote broker with a prefix and a postfix.
Topic Level Configuration Examples
Parts of Topic Filter as Destination Example
<filters>
<mqtt-topic-filter>+/+/+/+</mqtt-topic-filter>
</filters>
<destination>prefix/{1-3}/data</destination>Original topic: a/b/c/d
Resulting topic: prefix/a/b/c/data
-
This example uses a four-level incoming filter. The bridge forwards all publish topics that match the pattern.
-
For the destination topic at the remote broker, only the first three parts of the local publish topic are used and a prefix and a postfix are added.
Prefix, Postfix, and Topic Filter Parts as Destination Example I
<filters>
<mqtt-topic-filter>a/+/+/+</mqtt-topic-filter>
</filters>
<excludes>
<mqtt-topic-filter>+/client2/#</topic-filter>
</excludes>
<destination>prefix/{2-3}/data</destination>Original topic: a/b/c/d
Resulting topic: prefix/b/c/data
Original topic: a/client2/c/d
Resulting topic: <not forwarded>
-
This example uses a four-level incoming filter. The bridge forwards all publish topics that match the pattern.
-
For the destination topic at the remote broker, only the second and third parts of the local publish topic are used and a prefix (prefix) and postfix (allData) are added.
-
Messages that have the string client2 at the second level are not forwarded.
Prefix, Postfix, and Topic Filter Parts as Destination Example II
<filters>
<mqtt-topic-filter>+/+/+/+</mqtt-topic-filter>
</filters>
<destination>prefix/{2}/NEU/{4}/data</destination>Original topic: a/b/c/d
Resulting topic: prefix/b/NEU/d/data
-
This example uses a four-level incoming filter. The bridge forwards all publish topics that match the pattern.
-
For the destination topic at the remote broker, only the second and fourth level from the incoming topic are used. The third level is replaced with a constant and a prefix is added.
Additional Topic Level Addressing Examples
-
{2}: Topic filter level 2 -
{2 - #}: Topic filter level 2 and all following levels -
{#}: Whole topic filter -
prefix/{#}/postfix: Whole topic filter inside prefix and postfix -
{1}/A/{2}/B: Level 1 + "/A" + level 2 + "/B" -
{#}/{1-3): Whole topic filter + level 1, 2, and 3
Connecting HiveMQ Edge to HiveMQ Cloud
To connect HiveMQ Edge with HiveMQ Cloud for free, you can log in to HiveMQ Cloud, Start a free cluster and enter your credentials either into the HiveMQ Edge UI or into your configuration file.
MQTT Bridge Configuration on the HiveMQ Edge User Interface
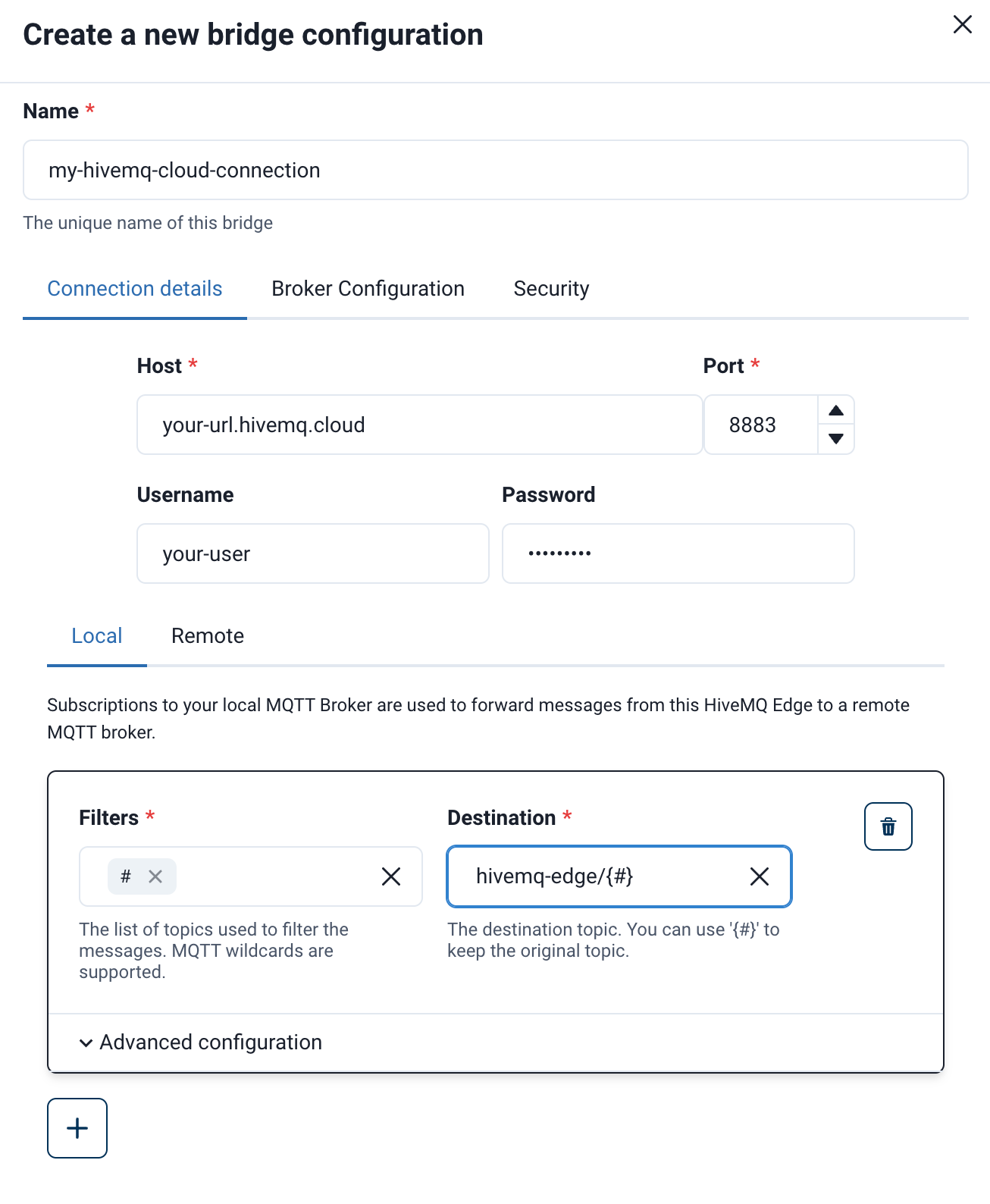
Go to MQTT Bridges → Add bridge connection and add the following values
-
Host ←
<your-cluster-url>.hivemq.cloud -
Port ←
8883 -
Username ←
<your-username>from Access Management in HiveMQ Cloud -
Password ←
<your-username>from Access Management in HiveMQ Cloud -
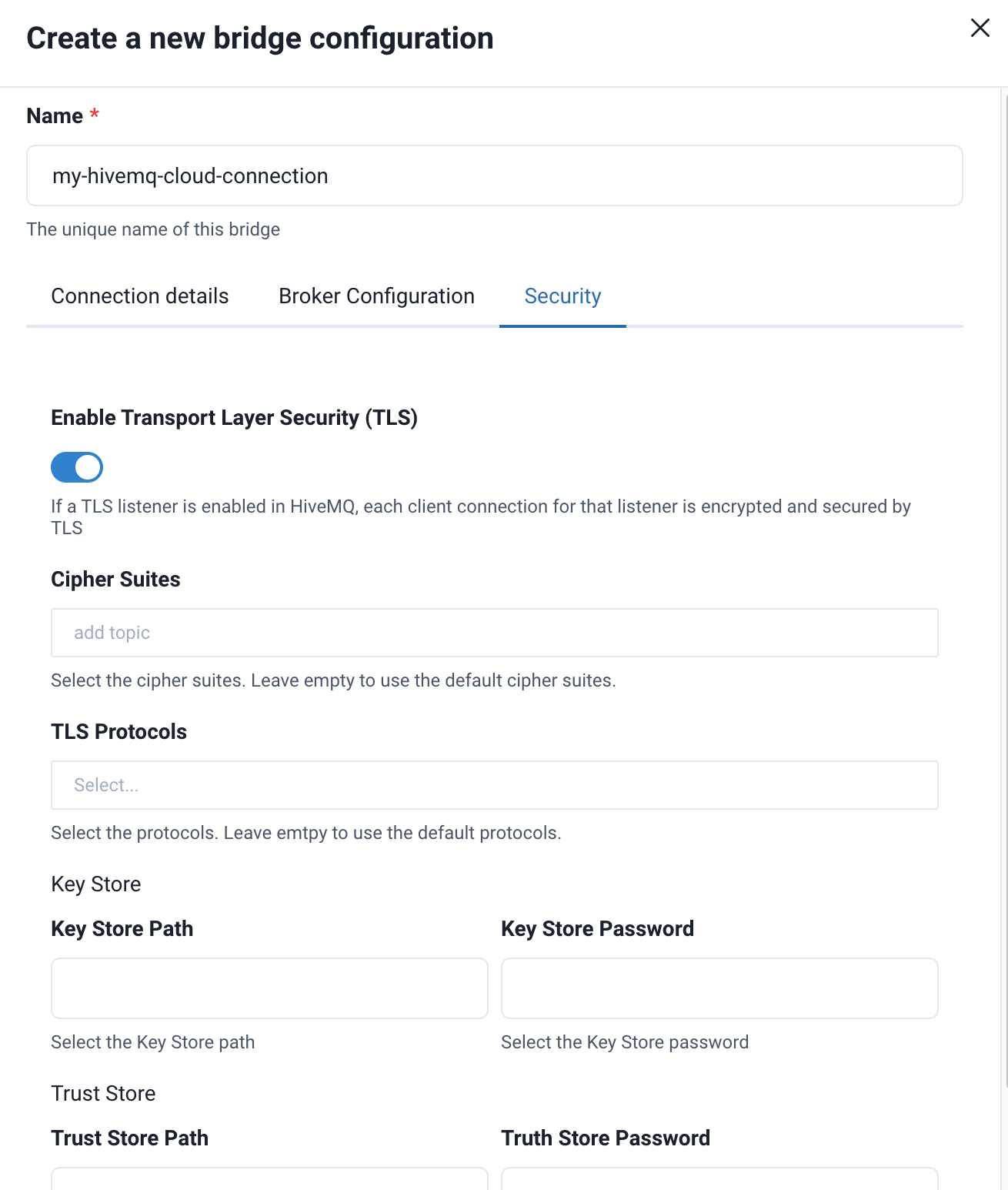
In the
SecurityTab in HiveMQ Edge enable Transport Layer Security (TLS) -
Add a local or remote subscription
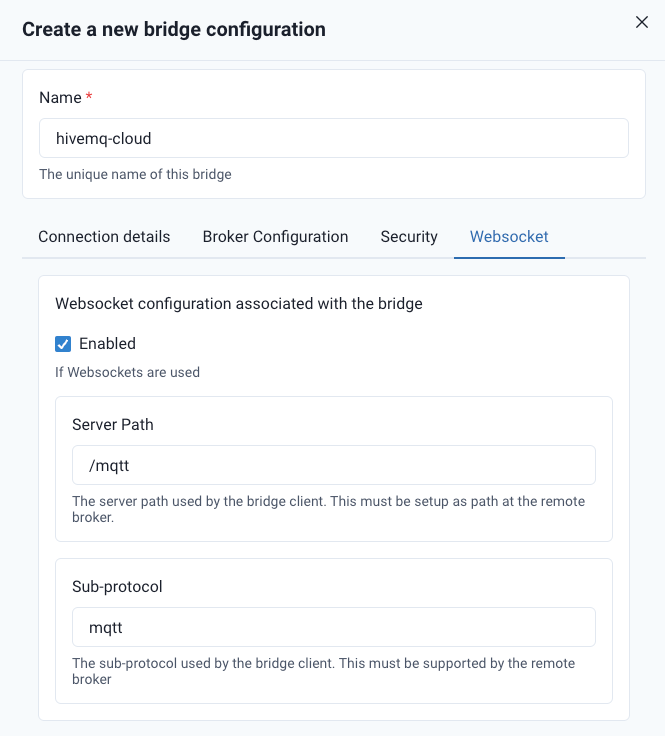
WebSocket Support
The HiveMQ Edge Bridge supports WebSocket connections. To configure WebSocket
use the common fields such as host and port from your remote broker in the bridge connection UI. To specifically activate a WebSocket connection
select the Enabled checkbox. To specify
the server path or sub-protocol, enter the necessary information in the Server Path and Sub-protocol fields.
Offline Buffering
Each bridge can be configured in such a way that MQTT traffic that is forwarded to a remote broker is persisted using the offline buffering functionality. For detailed configuration information, see Offline Buffering.
| The Offline Buffering feature requires a commercial license. To obtain a license, please contact our sales@hivemq.com to obtain a license. |
<mqtt-bridge>
...
<forwarded-topics>
<forwarded-topic>
<filters>
<mqtt-topic-filter>sourceTopic</mqtt-topic-filter>
</filters>
<destination>destinationTopic</destination>
<max-qos>1</max-qos>
</forwarded-topic>
</forwarded-topics>
...
<persist>true</persist>
</mqtt-bridge>In the example configuration, the persist flag is set to true, which means that the MQTT payloads HiveMQ Edge transmits over the bridge are buffered.
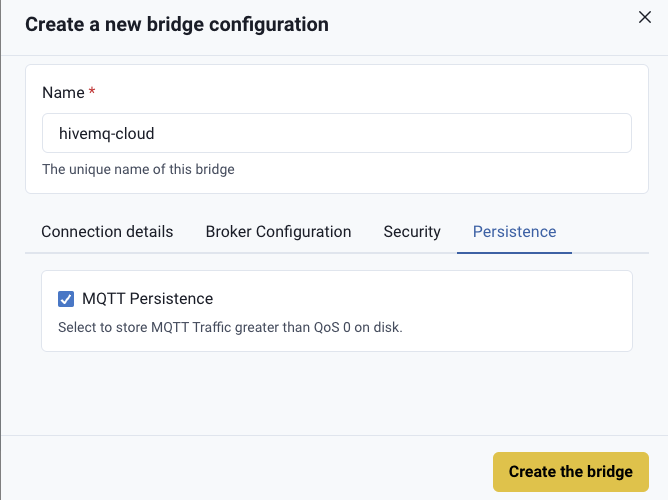
For your convenience, it is also possible to configure the persistence from the HiveMQ Edge UI:
Via configuration file
Add the following section to your configuration file <HIVEMQ_HOME>/conf/config.xml between the <hivemq> tags.
<mqtt-bridges>
<mqtt-bridge>
<id>my-hivemq-cloud-bridge</id>
<remote-broker>
<host>yoururl.hivemq.cloud</host>
<port>8883</port>
<authentication>
<mqtt-simple-authentication>
<!-- you can create these credentials in 'Access Management' in HiveMQ Cloud -->
<username>your-mqtt-username</username>
<password>your-mqtt-password</password>
</mqtt-simple-authentication>
</authentication>
<tls>
<enabled>true</enabled>
</tls>
</remote-broker>
<forwarded-topics>
<forwarded-topic>
<filters>
<mqtt-topic-filter>#</mqtt-topic-filter>
</filters>
<destination>hivemq-edge/{#}</destination>
</forwarded-topic>
</forwarded-topics>
<!-- add more forwarded topic or remote subscriptions here -->
</mqtt-bridge>
</mqtt-bridges>This will create a bridge to your HiveMQ Cloud cluster and forward every message originating from or published to HiveMQ Edge to your HiveMQ Cloud cluster and prefixes the topic with hivemq-edge/.