HiveMQ Edge Protocol Adapters
HiveMQ Edge protocol adapters facilitate communication between systems, devices, or networks that use different proprietary or incompatible communication protocol formats. Once connected, the protocol adapter converts received data into open standards MQTT messages that are published to your local MQTT broker.
HiveMQ Edge offers numerous pre-built protocol adapters and the ability to create custom protocol adapters to suit your business needs.
The following HiveMQ Edge protocol adapters sre currently available:
Additional HiveMQ Edge protocol adapters will be added to the project over time.
Tags in Protocol Adapters
The functionality and configuration of industry protocols differ significantly. HiveMQ Edge enables the use of protocol tags to minimize configuration complexity to simplify integration and enhance ease of use. The tag abstracts the usages of the data points a protocol adapter provides. Instead of dealing complex protocol-specific identifiers, users can interact with human-readable tags. For example, although configuring Modbus registers is very different from setting up node IDs in OPC UA, all HiveMQ Edge protocol adapters use MQTT destination topics as a common endpoint for data routing.
Managing Tags
To define a tag on the HiveMQ Edge workspace, simply select a device:
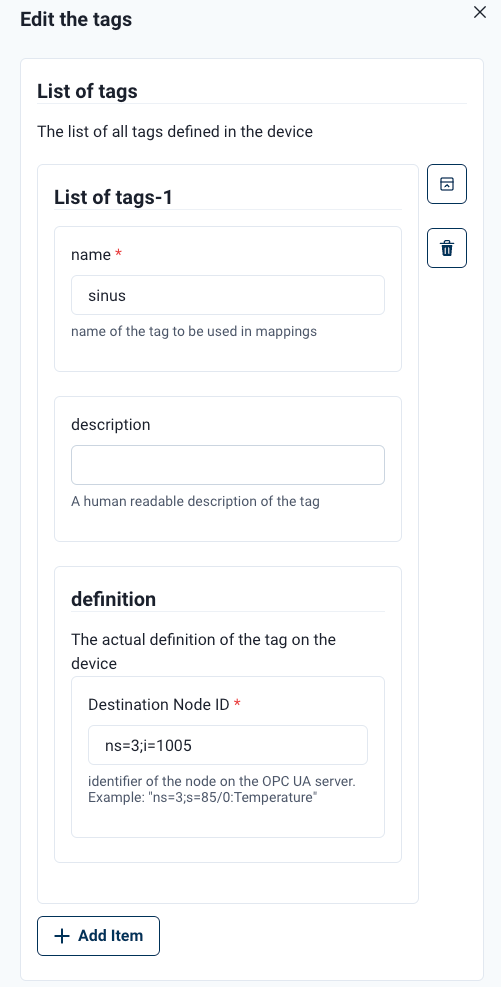
A standardized dialog that is similar for every protocol adapter opens. The first part of the tag definition includes the name of the tag and a description. The tag name must be unique across the HiveMQ Edge deployment. The definition part of the tag varies based on the protocol adapter type. For example, a OPC UA tag:
Northbound
In edge computing, northbound refers to the flow of data or communication from edge devices or lower layers of infrastructure to higher layers in a computing or network hierarchy. Northbound communication typically involves sending processed data, insights, or alerts from the edge layer to centralized systems for storage, further analysis, or integration with other systems.
-
northboundMappingsparameters
Property Name |
Default |
Mandatory |
Description |
Format |
tagName |
The tag name. |
String (Tags). For example, |
||
topic |
The MQTT topic. |
String. For example, |
||
maxQos |
1 |
The maximum MQTT QoS for the outgoing messages. |
Possible values are |
|
includeTagNames |
false |
Include the tag name in the MQTT payload. |
Boolean. |
|
includeTimestamp |
true |
Include a timestamp in the MQTT payload. |
Boolean. |
|
messageExpiryInterval |
no expiry |
The message expiry interval in seconds for MQTT 5 messages. |
Long > 0. |
|
mqttUserProperties |
List of user properties to include in the MQTT message. |
List of MQTT user properties. |
Southbound
In edge computing, southbound refers the flow of data or communication from higher layers of infrastructure down to components that are located closer to the edge of the network. Southbound communication is typically used to send commands, configurations, policies, updates, or control signals from a centralized system.
| Property Name | Default | Mandatory | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The tag name |
String (Tags). For example, |
||
|
The MQTT topic filter to read from |
String. For example, |
Topic Filters
MQTT topic filters are used to read data that is subsequently written to a tag. To ensure reliable operation, the topic filter must have a data schema.
| Currently, only JSON schemas are supported. |
Topic filters can be defined on the HiveMQ Edge workspace:
A dialog to create topic filters and associate a schema automatically opens:
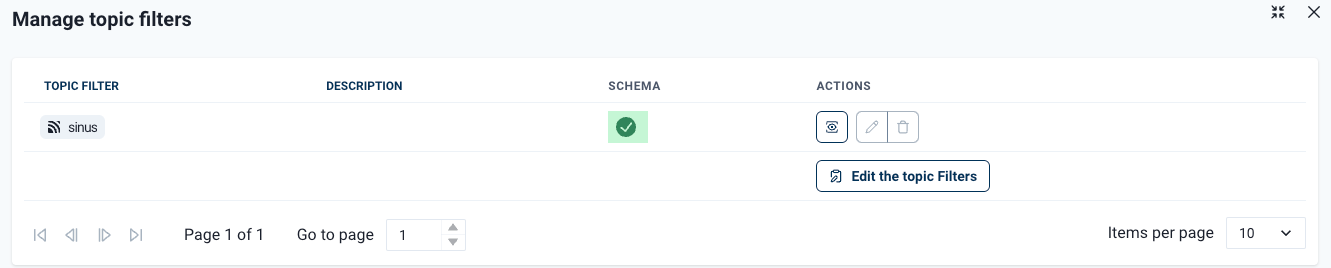
Once a topic filter is created, there are two ways to assign a schema:
-
If you are already sending data to a topic that is included in the topic filter, the topic filter dialog gives you the option to infer a schema from existing traffic.
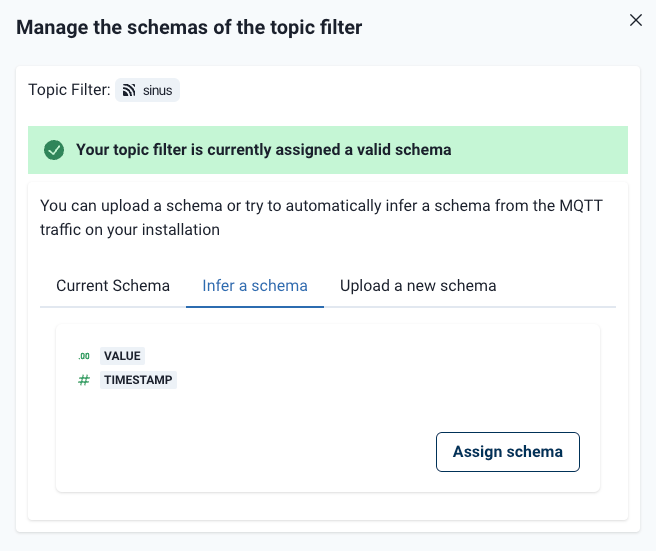
-
Upload a JSON Schema file to HiveMQ Edge that defines the schema of the incoming data.
The JSON Schema must include at least a properties definition.
For more information, see JSON Schema definition.
|
{
"title": "The schemas defines the data structure for controlling speed",
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"speed": {
"type": "number",
"minimum": 0,
"maximum": 100
}
},
"required": [ "speed" ]
}The example JSON Schema includes a speed property that is an integer and ranges from 0 to 100.
{
"speed": 50
}HiveMQ Edge makes sure that the incoming MQTT traffic is continuously checked against the defined schema before it
writes to the tag and eventually to the device.
All invalid messages are re-routed to the $invalid topic.
HiveMQ Edge Protocol Adapter Configuration
Adapter instances can be added to the system using the HiveMQ Edge API, user interface, or a static configuration.
All three methods result in the main config.xml file being updated with a new element within the <protocol-adapters> element.
Each adapter type has its own element name that matches the adapter type name in the ProtocolAdapterFactory.
For example, the Simulation protocol has a type of simulation and a <simulation></simulation> configuration element.
In the adapter configuration, each adapter instance much be identified with a unique <id> element .
| The HiveMQ Edge UI and API automatically validate the uniqueness of the instance. |
Simulation Adapter
The simulation adapter enables the system to be configured to publish messages with random values through the protocol adapter layer at a specific interval. This functionality gives you the ability to test and observe the behavior of adapters in your system without requiring actual hardware or external data sources.
The adapter supports the following capability:
-
Read (Northbound): Generate simulated data and publish to MQTT topics.
The example configuration publishes random data with MQTT quality of service level 1 to the destination topic called 'topic'.
<protocol-adapters>
<protocol-adapter>
<adapterId>sim</adapterId>
<protocolId>simulation</protocolId>
<config>
<minDelay>0</minDelay>
<maxDelay>0</maxDelay>
<minValue>0</minValue>
<maxValue>1000</maxValue>
<simulationToMqtt>
<pollingIntervalMillis>100</pollingIntervalMillis>
<maxPollingErrorsBeforeRemoval>-1</maxPollingErrorsBeforeRemoval>
</simulationToMqtt>
</config>
<northboundMappings>
<northboundMapping>
<topic>sim</topic>
<includeTagNames>false</includeTagNames>
<includeTimestamp>true</includeTimestamp>
<maxQos>0</maxQos>
<tagName>t1</tagName>
</northboundMapping>
</northboundMappings>
</protocol-adapter>
</protocol-adapters>Simulation Adapter Properties
| Property Name | Default | Mandatory | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The unique identifier of the selected adapter instance. |
String [a-zA-Z0-9-_] |
||
|
|
Minimum limit for the randomly generated values (inclusive). |
Integer >= 0 |
|
|
|
Maximum limit for the randomly generated values (exclusive). |
Integer |
|
|
|
Minimum artificial delay in milliseconds before the polling method generates a value. Must not exceed maxDelay. |
Integer >= 0 |
|
|
|
Maximum artificial delay in milliseconds before the polling method generates a value. When minDelay equals maxDelay, the delay is fixed; otherwise, a random delay between minDelay and maxDelay is used. |
Integer >= 0 |
|
|
Configuration for polling and MQTT publishing |
| Property Name | Default | Mandatory | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Time in milliseconds between polling cycles. Each cycle generates new random values for all configured tags. |
Integer >= 1 |
|
|
|
Maximum number of consecutive polling errors before the adapter stops. Set to -1 for unlimited retries. |
Integer >= -1 |
| Property Name | Default | Mandatory | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Common configurations |
{
"timestamp": 1730707250320,
"value": 729.6615064364747
}The payload includes:
-
timestamp: Unix timestamp in milliseconds when the value was generated (only present ifincludeTimestampis true). -
value: Randomly generated double-precision floating-point number betweenminValue(inclusive) andmaxValue(exclusive).
| The Simulation adapter publishes a new value on every polling cycle. Unlike some other adapters, there is no option to publish only when the value changes, as the adapter generates new random values each time. |
ModBus (TCP) Adapter
The ModBus adapter enables connections to ModBus slaves via TCP. The adapter supports reading from coils, discrete inputs, input registers, and holding registers in the address range 0-65534 (incl).
The adapter supports the following capabilities:
-
Read (Northbound): Poll Modbus registers and publish data to MQTT topics.
The connection samples the ModBus slave on the sampling time specified in the configuration.
Each connection can be configured to only publish samples when changes in values are detected (publishChangedDataOnly).
<modbus>
<id>my-modbus-protocol-adapter</id>
<host>my.modbus-server.com</host>
<port>502</port>
<timeoutMillis>500</timeoutMillis>
<modbusToMqtt>
<pollingIntervalMillis>150</pollingIntervalMillis>
<maxPollingErrorsBeforeRemoval>5</maxPollingErrorsBeforeRemoval>
<publishChangedDataOnly>false</publishChangedDataOnly>
<modbusToMqttMappings>
<modbusToMqttMapping>
<mqttTopic>my/topic</mqttTopic>
<mqttQos>1</mqttQos>
<tagName>myTag</tagName>
<messageHandlingOptions>MQTTMessagePerSubscription</messageHandlingOptions>
<mqttUserProperties>
<mqttUserProperty>
<name>name</name>
<value>value1</value>
</mqttUserProperty>
<mqttUserProperty>
<name>name</name>
<value>value2</value>
</mqttUserProperty>
</mqttUserProperties>
<includeTagNames>true</includeTagNames>
<includeTimestamp>false</includeTimestamp>
</modbusToMqttMapping>
</modbusToMqttMappings>
</modbusToMqtt>
</modbus>myTag in the config above<tag>
<tagDefinition>
<unitId>0</unitId>
<startIdx>11</startIdx>
<readType>HOLDING_REGISTERS</readType>
<dataType>INT_64</dataType>
</tagDefinition>
<tagName>myTag</tagName>
</tag>ModBus (TCP) Adapter Properties
| Property Name | Default | Mandatory | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The unique identifier of the selected adapter instance. |
String [a-zA-Z0-9-_] |
||
|
The host or IPv4/IPv6 of the ModBus device. |
Hostname or IP |
||
|
The port to connect to. |
Integer 1-65535 |
||
|
|
Time in milliseconds to await a connection before the client gives up. |
Integer (1000-15000) |
|
|
Configuration for Modbus to MQTT data flow |
| Property Name | Default | Mandatory | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Time in milliseconds between polling cycles. |
Integer >= 1 |
|
|
|
Maximum number of consecutive polling errors before the adapter stops. Set to -1 for unlimited retries. |
Integer >= -1 |
|
|
|
When enabled, the adapter only publishes data when a value has changed since the last poll. This reduces MQTT traffic for slow-changing data. |
Boolean |
ModBus Tag Definition
Tags in the Modbus adapter define which registers to read from the device.
| Property Name | Default | Mandatory | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The starting address index (inclusive) of the register to read. |
Integer (0-65535) |
||
|
Type of Modbus register to read. |
COILS, DISCRETE_INPUTS, INPUT_REGISTERS, HOLDING_REGISTERS |
||
|
Id of the unit (slave) to access on the Modbus network. |
Integer |
||
|
|
Defines how the read registers are interpreted. |
See Data Types |
|
|
|
When enabled, registers are evaluated in reverse order. Some Modbus implementations write content as big endian but order registers as little endian. |
Boolean |
ModBus Data Types
| Type | Description | Size |
|---|---|---|
|
Boolean value |
1 bit / 1 register |
|
Signed 16-bit integer |
16 bit / 1 register |
|
Unsigned 16-bit integer |
16 bit / 1 register |
|
Signed 32-bit integer |
32 bit / 2 registers |
|
Unsigned 32-bit integer |
32 bit / 2 registers |
|
Signed 64-bit integer |
64 bit / 4 registers |
|
32-bit floating-point (IEEE 754 single precision) |
32 bit / 2 registers |
|
64-bit floating-point (IEEE 754 double precision) |
64 bit / 4 registers |
|
UTF-8 encoded string |
64 bit / 4 registers |
For multi-register data types (INT_32, INT_64, FLOAT_32, FLOAT_64, UTF_8), use the flipRegisters option if your device uses little-endian register ordering.
|
| Each sample is published as an array with each 16-bit index encoded as a 2-octet decimal value. |
OPC UA Adapter
The OPC UA adapter enables connections to OPC UA servers.
You can configure the adapter to read from an OPC UA server and publish to an MQTT topic (opcuaToMqtt) or write to an OPC UA server from an MQTT topic (mqttToOpcua).
Both directions require basic connectivity information for OPC UA to be configured.
The OPC UA adapter supports the following capabilities:
-
Read (Northbound): Subscribe to OPC UA nodes and publish data to MQTT topics.
-
Write (Southbound): Write data from MQTT messages to OPC UA nodes.
-
Discover: Browse and discover available nodes on the OPC UA server.
-
Bidirectional: Combine northbound and southbound operations simultaneously.
The connection creates subscriptions with the OPC UA server and discovers available nodes on the server.
| Unlike some other protocol adapters, the OPC UA adapter does not filter unchanged values. Every data notification received from the OPC UA server is published to MQTT, even if the value has not changed since the last notification. This behavior is inherent to the OPC UA subscription model, where the server determines when to send notifications based on the configured publishing interval and server queue settings. |
<protocol-adapters>
<opcua>
<config>
<id>opcua</id>
<overrideUri>false</overrideUri>
<uri>opc.tcp://opcua-server:4840</uri>
</config>
</opcua>
</protocol-adapters>As a next step, you can configure to read an OPC UA nodeId from the server and publish it to an MQTT topic.
OPC UA to MQTT: Northbound
This section shows you how to define an OPC UA to MQTT configuration. The OPC UA to MQTT direction is also called northbound.
| HiveMQ Edge 2024.8 introduced the concept of tags. Tags are used to simplify the usage of data from any protocol adapter. For more information, see Tags. |
<hivemq>
...
<protocol-adapters>
<protocol-adapter>
<adapterId>simulation-server-2</adapterId>
<protocolId>opcua</protocolId>
<config>
<uri>opc.tcp://CSM1.local:53530/OPCUA/SimulationServer</uri>
<opcuaToMqtt>
</opcuaToMqtt>
</config>
<northboundMappings>
<northboundMapping>
<tagName>temperature/for/machine_1</tagName>
<topic>machine/1/temperature</topic>
</northboundMapping>
</northboundMappings>
</southboundMappings>
<tags>
<tag>
<name>temperature/for/machine_1</name>
<description>This tag is about sensor data</description>
<definition>
<node>ns=1;i=1004</node>
</definition>
</tag>
</tags>
</protocol-adapter>
</protocol-adapters>
...
</hivemq>The configuration example defines a connection to an OPC UA server and a northbound mapping.
The northboundMappings section defines to read data from the temperature/for/machine_1 tag that is connected to the nodeId ns=1;i=1004.
The tag is published as an MQTT message to the machine/1/temperature topic .
The tag is defined in the <tags> section.
{
"value": 1000
}The OPC UA adapter publishes data values received from the OPC UA server. Depending on the data type and server configuration, the payload may include additional metadata such as timestamps and status information.
{
"value": 23.5,
"sourceTimestamp": "2024-01-15T10:30:00.000Z",
"serverTimestamp": "2024-01-15T10:30:00.001Z",
"statusCode": 0
}The payload fields are:
-
value: The actual data value from the OPC UA node. -
sourceTimestamp: The timestamp when the value was generated at the source (ISO 8601 format). -
serverTimestamp: The timestamp when the OPC UA server processed the value (ISO 8601 format). -
statusCode: The OPC UA status code indicating the quality of the data (0 indicates good quality).
Currently, the HiveMQ Edge OPC UA adapter supports subscriptions to individual OPC UA nodeIds.
The publishingInterval and serverQueueSize settings apply globally to all tags in the adapter.
Per-tag configuration of these values is not currently supported.
|
MQTT to OPC UA: Southbound
HiveMQ Edge can write to OPC UA nodes from any MQTT data sources. The southbound direction allows you to control OPC UA-connected devices by publishing MQTT messages that are converted to OPC UA write operations.
Mapping an MQTT topic filter to OPC UA data points works like the northbound mapping. The southbound mapping consists of a topic filter that includes a data schema of the MQTT payload and a tag to be written. An example configuration is shown below:
<hivemq>
<protocol-adapters>
<protocol-adapter>
<adapterId>simulation-server-2</adapterId>
<protocolId>opcua</protocolId>
<config>
<uri>opc.tcp://CSM1.local:53530/OPCUA/SimulationServer</uri>
<overrideUri>true</overrideUri>
<auth>
<basic>
<username>edge</username>
<password>password</password>
</basic>
<x509>
<enabled>true</enabled>
</x509>
</auth>
<tls>
<enabled>true</enabled>
<keystore>
<path>path/to/keystore</path>
<password>keystore-password</password>
<privateKeyPassword>private-key-password</privateKeyPassword>
</keystore>
<truststore>
<path>path/to/truststore</path>
<password>truststore-password</password>
</truststore>
</tls>
<security>
<policy>BASIC128RSA15</policy>
</security>
<opcuaToMqtt>
<publishingInterval>12</publishingInterval>
<serverQueueSize>13</serverQueueSize>
</opcuaToMqtt>
</config>
</northboundMappings>
<southboundMappings>
<southboundMapping>
<tagName>ns=1;i=1004</tagName>
<topicFilter>data/area1/#</topicFilter>
<fromNorthSchema>{}</fromNorthSchema>
</southboundMapping>
<southboundMapping>
<tagName>ns=2;i=1004</tagName>
<topicFilter>data/area2/#</topicFilter>
<fromNorthSchema>{}</fromNorthSchema>
</southboundMapping>
</southboundMappings>
<tags>
<tag>
<name>ns=1;i=1004</name>
<description>description1</description>
<definition>
<node>ns=1;i=1004</node>
</definition>
</tag>
<tag>
<name>ns=2;i=1004</name>
<description>description2</description>
<definition>
<node>ns=2;i=1004</node>
</definition>
</tag>
</tags>
</protocol-adapter>
</protocol-adapters>
</hivemq>OPC UA Adapter Properties
| Property Name | Default | Mandatory | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
URI of the OPC UA server to connect to |
URI (e.g., opc.tcp://server:4840) |
||
|
|
Override the endpoint URI returned from the OPC UA server with the hostname and port from the specified URI |
Boolean |
|
|
|
Overrides the Application URI used for OPC UA client identification. If not specified, uses the URI from the certificate SAN extension, or falls back to 'urn:hivemq:edge:client' |
String |
|
|
Authentication configuration for connecting to the OPC UA server |
Auth object OPC UA Authentication |
||
|
TLS configuration for secure connections |
TLS object Properties to configure TLS |
||
|
|
OPC UA Security Policy to use |
|
|
|
|
Message security mode. If not specified, defaults to |
|
|
|
Configuration for OPC UA to MQTT (Northbound) data flow |
OpcUaToMqtt object OPC UA Northbound config details |
||
|
Connection handling options for heartbeats and reconnects |
ConnectionOptions object OPC UA Connection Options |
OPC UA Northbound config details
| Property Name | Default | Mandatory | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
The interval in milliseconds at which the OPC UA server sends data notifications to HiveMQ Edge. Lower values result in more frequent updates but increase network and server load. |
Integer > 0 |
|
|
|
The number of data change notifications that the OPC UA server queues for each monitored item. Higher values can prevent data loss during network interruptions but increase memory usage on the server. |
Integer > 0 |
These settings apply globally to all tags configured for this adapter instance.
Per-tag configuration of publishingInterval and serverQueueSize is not currently supported.
|
OPC UA Connection Options
| Property Name | Default | Mandatory | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
OPC UA session timeout in milliseconds. Session will be renewed at this interval |
Integer (10000-3600000) |
|
|
|
Timeout for OPC UA requests in milliseconds |
Integer (5000-300000) |
|
|
|
Interval between OPC UA keep-alive pings in milliseconds |
Integer (1000-60000) |
|
|
|
Number of consecutive keep-alive failures before connection is considered dead |
Integer (1-10) |
|
|
|
Timeout for establishing connection to OPC UA server in milliseconds |
Integer (2000-300000) |
|
|
|
Interval between connection health checks in milliseconds |
Integer (10000-300000) |
|
|
|
Interval between connection retry attempts in milliseconds |
Integer (5000-300000) |
|
|
|
Enable automatic reconnection when health check detects connection issues |
Boolean |
|
|
|
Enable automatic reconnection when critical OPC UA service faults occur (e.g., session invalid, subscription lost). Recommended to keep enabled |
Boolean |
Tag Definitions for OPC UA
The general structure of tags is defined identically for each protocol adapter. The precise details of the definition vary per protocol adapter. In OPC UA, nodeIds are configured to address specific data points.
<hivemq>
<protocol-adapters>
<protocol-adapter>
<adapterId>...</adapterId>
<protocolId>opcua</protocolId>
<config>
...
</config>
<tags>
<tag>
<name>boiler/temperature</name>
<description>Provides the temperature inside the boiler</description>
<definition>
<node>ns=1;s=Temperature</node>
</definition>
</tag>
</tags>
</protocol-adapter>
</protocol-adapters>
</hivemq>The definition field is specific to OPC UA and contains the nodeId definition.
Tags are defined over a list of tag-items.
| Property Name | Default | Mandatory | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The OPC UA nodeId that identifies the data point on the server |
OPC UA nodeId addressing schema |
OPC UA NodeId Format
The OPC UA nodeId uses a specific addressing schema that consists of a namespace index and an identifier. The general format is:
ns=<namespace-index>;<identifier-type>=<identifier>
Where:
-
ns=<namespace-index>specifies the namespace (e.g.,ns=1,ns=2) -
<identifier-type>is one of:-
ifor numeric identifiers (e.g.,ns=1;i=1004) -
sfor string identifiers (e.g.,ns=1;s=Temperature) -
gfor GUID identifiers (e.g.,ns=1;g=550e8400-e29b-41d4-a716-446655440000) -
bfor opaque (ByteString) identifiers
-
ns=1;i=1004 # Numeric identifier in namespace 1
ns=2;s=Temperature # String identifier in namespace 2
ns=3;s=85/0:Sensor1 # String identifier with path-like structure| You can discover available nodeIds on your OPC UA server using an OPC UA browser tool. |
OPC UA Authentication
HiveMQ Edge supports three authentication modes against OPC UA servers:
-
Anonymous (default): No authentication credentials required.
-
Basic: Username and password authentication.
-
X509: Certificate-based authentication using client certificates.
OPC UA Anonymous Authentication
When no auth configuration is provided, the adapter connects to the OPC UA server anonymously.
This is the default behavior and is suitable for servers that do not require authentication.
<opcua>
<config>
<uri>opc.tcp://opcua-server:4840</uri>
<!-- No auth block = anonymous authentication -->
</config>
</opcua>OPC UA Basic Authentication
<opcua>
<config>
...
<auth>
<basic>
<username>edge</username>
<password>password</password>
</basic>
</auth>
...
</config>
</opcua>OPC UA TLS configuration
HiveMQ Edge supports connections to OPC UA servers with TLS and mutual TLS.
To utilize mTLS, specify a keystore and enable x509 authentication.
<opcua>
<config>
...
<tls>
<enabled>true</enabled>
</tls>
...
</config>
</opcua><opcua>
<config>
...
<tls>
<enabled>true</enabled>
<keystore>
<path>/path/to/my/keystore.jks</path>
<password>keystore-password</password>
<private-key-password>key-password</private-key-password>
</keystore>
<truststore>
<path>/path/to/my/truststore.jks</path>
<password>truststore-password</password>
</truststore>
</tls>
...
</config>
</opcua>The following example shows what to do if the applicationUri cannot be derived from the certificate.
<opcua>
<config>
...
<applicationUri>urn:my-opcua-client</applicationUri>
<tls>
<enabled>true</enabled>
<keystore>
<path>/path/to/my/keystore.jks</path>
<password>keystore-password</password>
<private-key-password>key-password</private-key-password>
</keystore>
<truststore>
<path>/path/to/my/truststore.jks</path>
<password>truststore-password</password>
</truststore>
</tls>
...
</config>
</opcua>| Property Name | Default | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Enables TLS encrypted connection |
|
|
|
Certificate validation level (see below for details) |
|
|
Keystore configuration containing the client certificate including the chain. Required for X509 authentication |
||
|
Path on the local file system to the keystore |
||
|
Password to open the keystore |
||
|
Password to access the private key |
||
|
|
Truststore configuration containing trusted server certificates or trusted intermediates |
|
|
Path on the local file system to the truststore |
||
|
Password to open the truststore |
TLS Certificate Validation Levels
The tlsChecks property controls how strictly the adapter validates server certificates:
-
NONE: No certificate validation is performed. Use only for testing or development environments.
-
APPLICATION_URI: Validates only the OPC UA Application URI in the certificate.
-
STANDARD (default): Performs standard certificate validation including Application URI validation, certificate validity period, and revocation checking.
-
ALL: Performs all available validation checks, including optional checks beyond the standard requirements.
Setting tlsChecks to NONE disables all certificate validation and should never be used in production environments as it exposes the connection to man-in-the-middle attacks.
|
OPC UA Security Configuration
The OPC UA adapter supports various security policy / message security mode combinations depending on the server it has to talk to.
In versions 2025.17 and before we automatically selected the first combination which matched the provided the requested security policy.
From version 2025.18 onwards the security policy and message security mode must be explicitly configured to avoid ambiguity.
<opcua>
<config>
...
<security>
<policy>BASIC128RSA15</policy>
<messageSecurityMode>SignAndEncrypt</messageSecurityMode>
</security>
...
</config>
</opcua>| Property Name | Default | Mandatory | Values | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
General security policy used for message exchange |
|
|
|
|
Message security mode used for message exchange. If not specified, defaults to |
BASIC128RSA15 and BASIC256 are deprecated security policies and should only be used if required by legacy OPC UA servers.
For new deployments, use BASIC256SHA256, AES128_SHA256_RSAOAEP, or AES256_SHA256_RSAPSS.
|
OPC UA Supported Data Types
The OPC UA adapter supports the following data types for both northbound (reading from OPC UA) and southbound (writing to OPC UA) operations:
| JSON Type | Description | OPC UA Types |
|---|---|---|
|
Boolean values (true/false) |
Boolean |
|
Integer numeric values |
Byte, SByte, Int16, UInt16, Int32, UInt32, Int64, UInt64 |
|
Floating-point numeric values |
Float, Double |
|
Text values |
String, LocalizedText, ByteString |
|
Date and time values (ISO 8601 format) |
DateTime |
|
Arrays of the above types |
Arrays of any supported type |
|
Complex structured data |
ExtensionObject, QualifiedName, NodeId |
The adapter automatically converts between OPC UA data types and their JSON representations when publishing to MQTT (northbound) or writing to OPC UA nodes (southbound).
S7 Adapter
The S7 adapter enables connections to Siemens S7 PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers). The adapter supports reading S7 tags and data blocks from S7-300, S7-400, S7-1200, S7-1500, and LOGO series controllers.
The adapter supports the following capability:
-
Read (Northbound): Poll S7 tags and data blocks and publish data to MQTT topics.
| The S7 protocol also uses the term "tags". These S7 tags are different from HiveMQ Edge tags. In this documentation, we refer to them as S7 tags when discussing PLC addressing. |
S7 PUT/GET must be enabled on the PLC, otherwise a connection with the S7 adapter is not possible.
The setting can be found in your TIA Portal in the General tab, under Protection & Security → Connection mechanisms → Permit access with PUT/GET communication from remote partner.
|
<hivemq>
<protocol-adapters>
<protocol-adapter>
<adapterId>my-s7-protocol-adapter</adapterId>
<protocolId>s7</protocolId>
<config>
<host>my.s7-device</host>
<port>102</port>
<controllerType>S7_1500</controllerType>
</config>
<northboundMappings>
<northboundMapping>
<topic>motor/speed</topic>
<tagName>motor_speed</tagName>
</northboundMapping>
</northboundMappings>
<tags>
<tag>
<name>motor_speed</name>
<description>The speed of the moto</description>
<definition>
<tagAddress>%ID103</tagAddress>
<dataType>DINT</dataType>
</definition>
</tag>
</tags>
</protocol-adapter>
</protocol-adapters>
</hivemq>S7 Adapter Properties (config)
| Property Name | Default | Mandatory | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The host or IPv4/IPv6 of the S7 device. |
Hostname or IP |
||
|
|
The port to which the adapter connects. |
Integer 1-65535 |
|
|
|
The series of the S7 PLC. |
|
|
|
|
Rack value for the remote main CPU. |
Integer |
|
|
|
Slot value for the remote main CPU. |
Integer |
|
|
|
Rack value for the remote secondary CPU. |
Integer |
|
|
|
Slot value for the remote secondary CPU. |
Integer |
|
|
|
Remote TSAP (Transport Services Access Point) value. Usually required only for PLCs from the LOGO series. |
Integer |
|
|
|
Enable keep-alive ping to prevent TCP timeouts. Recommended when polling interval exceeds 7 seconds. Automatically enabled if polling interval is >= 7000ms. |
Boolean |
|
|
Configuration for S7 to MQTT data flow |
S7 Northbound config
| Property Name | Default | Mandatory | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Time in milliseconds between polling cycles. |
Integer >= 1 |
|
|
|
Maximum number of consecutive polling errors before the adapter stops. Set to -1 for unlimited retries. |
Integer >= -1 |
|
|
|
When enabled, the adapter only publishes data when a value has changed since the last poll. This reduces MQTT traffic for slow-changing data. |
Boolean |
S7 Tag Definition
Tags in the S7 adapter define which PLC addresses to read.
| Property Name | Default | Mandatory | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The address of the S7 tag to read. See S7 Tag Address for format. |
String |
||
|
The data type of the tag value. See S7 Types for supported types. |
Enum |
S7 Tag Address
The general structure of tags is defined identically for each protocol adapter as described in Tags. The precise definition is different as listed below. In the following the S7 tags addresses are described. The S7 tag address for an S7 variable can be found in TIA Portal.
PLC (Programmable Logic Controllers) Tags
The address for tags can be found in TIA Portal in the Address column of the PLC Tags table .
For PLC tags, this value can be used as it is directly in HiveMQ Edge.
If you cannot get the addresses directly from TIA Portal, you can use the following format to construct the address:
Format for bit addresses:
%<Memory-Area-Code><Byte-Offset>.<Bit-Offset>Format for byte addresses
%<Memory-Area-Code><Memory-Size-Code><Byte-Offset>Example: %I205.0 or ´ %QB207
Where the Memory-Area-Code is one of I(Inputs), Q(Outputs), D(Direct peripheral access), M(Markers), C(Counter), T(Timer), DB(Data block).
And Memory-Size-Code describes the size of the variable value.
The codes are X(1 bit or 8 bytes), B(1 byte), W(2 bytes), D(4 bytes).
For detailed information on which code maps to which type, see S7 Types.
Data blocks
The data block addressing scheme is:
%DB<Data-Block-Number>:<Byte-Offset>.<Bit-Offset>
%DB<Data-Block-Number>:<Byte-Offset>
Example: %DB10:20.0 or %DB10:22
The Data-Block-Number is displayed in the tree view on the left in your TIA Portal, behind the name of your data block, enclosed in [] brackets or on the top of the data block view.
The Byte-Offset (and Bit-Offset) can be found in TIA Portal in the Offset column in the data block view
Fixed offsets are only available for variables in data blocks if Optimized block access is turned off.
|
The setting for optimizing block access can be found in the properties of the data block in TIA Portal.
S7 Types
| Type | Description | Memory size code | MQTT payload example | Value range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1 bit |
|
|
|
|
1 byte unsigned |
|
|
|
|
1 byte signed |
|
|
|
|
1 byte unsigned |
|
|
|
|
2 byte signed |
|
|
|
|
2 byte unsigned |
|
|
|
|
4 byte signed |
|
|
|
|
4 byte unsigned |
|
|
|
|
8 byte signed |
|
|
|
|
8 byte unsigned |
|
|
|
|
2 byte unsigned |
|
|
|
|
4 byte unsigned |
|
|
|
|
8 byte unsigned |
|
|
|
|
4 byte floating point signed |
|
|
|
|
8 byte floating point signed |
|
|
|
|
1 byte character |
|
|
ascii alphabet |
|
2 byte character |
|
|
unicode alphabet |
|
ascii string |
|
|
ascii alphabet |
|
unicode string |
|
|
unicode alphabet |
|
4 byte signed, millisecond duration |
|
|
|
|
8 byte signed, nanosecond duration |
|
|
|
|
Date |
|
|
(ISO 8601) |
|
Time of day milliseconds |
|
|
(ISO 8601) |
|
Time of day nanoseconds |
|
|
(ISO 8601) |
|
DateTime milliseconds |
|
|
(ISO 8601) |
|
DateTime nanoseconds |
|
|
(ISO 8601) |
ADS / TwinCAT Adapter
The ADS adapter enables connections to Beckhoff and other TwinCAT 3 capable PLCs using the ADS (Automation Device Specification) protocol.
The adapter supports the following capability:
-
Read (Northbound): Poll ADS variables and publish data to MQTT topics.
<hivemq>
<protocol-adapters>
<protocol-adapter>
<adapterId>my-ads-protocol-adapter</adapterId>
<protocolId>ads</protocolId>
<config>
<host>my.ads-server.com</host>
<port>1234</port>
<targetAmsPort>123</targetAmsPort>
<sourceAmsPort>124</sourceAmsPort>
<targetAmsNetId>1.2.3.4.5.6</targetAmsNetId>
<sourceAmsNetId>1.2.3.4.5.7</sourceAmsNetId>
</config>
<northboundMappings>
<northboundMapping>
<topic>my/topic</topic>
<tagName>tag-name</tagName>
</northboundMapping>
</northboundMappings>
<tags>
<tag>
<name>tag-name</name>
<description>description</description>
<definition>
<tagAddress>123</tagAddress>
<dataType>BOOL</dataType>
</definition>
</tag>
</tags>
</protocol-adapter>
</protocol-adapters>
</hivemq><hivemq>
<protocol-adapters>
<protocol-adapter>
<adapterId>my-ads-protocol-adapter</adapterId>
<protocolId>ads</protocolId>
<config>
<host>my.ads-server.com</host>
<port>1234</port>
<targetAmsPort>1234</targetAmsPort>
<sourceAmsPort>12345</sourceAmsPort>
<targetAmsNetId>1.2.3.4.5.6</targetAmsNetId>
<sourceAmsNetId>1.2.3.4.5.7</sourceAmsNetId>
<adsToMqtt>
<pollingIntervalMillis>10</pollingIntervalMillis>
<maxPollingErrorsBeforeRemoval>9</maxPollingErrorsBeforeRemoval>
<publishChangedDataOnly>false</publishChangedDataOnly>
</adsToMqtt>
</config>
<northboundMappings>
<northboundMapping>
<topic>my/topic</topic>
<maxQos>1</maxQos>
<includeTagNames>true</includeTagNames>
<includeTimestamp>true</includeTimestamp>
<messageHandlingOptions>MQTTMessagePerSubscription</messageHandlingOptions>
<tagName>tag-name</tagName>
<mqttUserProperties>
<mqttUserProperty>
<name>name</name>
<value>value1</value>
</mqttUserProperty>
<mqttUserProperty>
<name>name</name>
<value>value2</value>
</mqttUserProperty>
</mqttUserProperties>
</northboundMapping>
<northboundMapping>
<topic>my/topic/2</topic>
<maxQos>1</maxQos>
<includeTagNames>true</includeTagNames>
<includeTimestamp>true</includeTimestamp>
<messageHandlingOptions>MQTTMessagePerSubscription</messageHandlingOptions>
<tagName>tag-name</tagName>
<mqttUserProperties>
<mqttUserProperty>
<name>name</name>
<value>value1</value>
</mqttUserProperty>
<mqttUserProperty>
<name>name</name>
<value>value2</value>
</mqttUserProperty>
</mqttUserProperties>
</northboundMapping>
</northboundMappings>
<tags>
<tag>
<name>tag-name</name>
<description>description</description>
<definition>
<tagAddress>123</tagAddress>
<dataType>WORD</dataType>
</definition>
</tag>
</tags>
</protocol-adapter>
</protocol-adapters>
</hivemq>ADS Adapter Properties (config)
| Property Name | Default | Mandatory | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The host or IPv4/IPv6 of the ADS device. |
Hostname or IP |
||
|
|
The TCP port to connect to. |
Integer 1-65535 |
|
|
The AMS Net ID of the device to connect to (6 octets). |
String (e.g., |
||
|
|
The AMS port number on the device to connect to. Typical TwinCAT runtime port is 851. |
Integer 1-65535 |
|
|
The AMS Net ID used by HiveMQ Edge (6 octets). |
String (e.g., |
||
|
|
The local AMS port number used by HiveMQ Edge. |
Integer 1-65535 |
|
|
|
Enable TCP keep-alive to maintain connection during inactivity. |
Boolean |
|
|
Configuration for ADS to MQTT data flow |
ADS Northbound config
| Property Name | Default | Mandatory | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Time in milliseconds between polling cycles. |
Integer >= 1 |
|
|
|
Maximum number of consecutive polling errors before the adapter stops. Set to -1 for unlimited retries. |
Integer >= -1 |
|
|
|
When enabled, the adapter only publishes data when a value has changed since the last poll. This reduces MQTT traffic for slow-changing data. |
Boolean |
ADS Tag Definition
Tags in the ADS adapter define which PLC variables to read.
| Property Name | Default | Mandatory | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The ADS address of the variable to read. See ADS Tag Address for format. |
String |
||
|
The data type of the variable. See ADS Types for supported types. |
Enum |
ADS Tag Address
The general structure of tags is defined identically for each protocol adapter as described in Tags.
The precise definition is different as listed below. In the following the S7 tags addresses are described.
The ADS tag address is the program name followed by the variable name separated by a dot, in the format:
<program-name>.<variable-name> .
Example program:
PROGRAM MAIN
VAR
iCounter : INT := 41;
MiCounter AT %MW2 : INT := 21;
QstrText AT %QB20 : STRING := 'abcdefg';
END_VARThe variable addresses for the protocol adapter are then:
-
MAIN.iCounter -
MAIN.MiCounter -
MAIN.QstrText
ADS Types
| Type | Description | MQTT payload example | Value range |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 bit |
|
|
|
1 byte unsigned |
|
|
|
1 byte signed |
|
|
|
1 byte unsigned |
|
|
|
2 byte signed |
|
|
|
2 byte unsigned |
|
|
|
4 byte signed |
|
|
|
4 byte unsigned |
|
|
|
8 byte signed |
|
|
|
8 byte unsigned |
|
|
|
2 byte unsigned |
|
|
|
4 byte unsigned |
|
|
|
8 byte unsigned |
|
|
|
4 byte floating point signed |
|
|
|
8 byte floating point signed |
|
|
|
ascii string |
|
|
|
unicode string |
|
|
|
4 byte unsigned, millisecond duration, UDINT |
|
|
|
8 byte unsigned, nanosecond duration, ULINT |
|
|
|
Date, UDINT |
|
|
|
Date, ULINT |
|
|
|
Time of day milliseconds, UDINT |
|
|
|
Time of day nanoseconds, ULINT |
|
|
|
DateTime milliseconds, UDINT |
|
|
|
DateTime nanoseconds, ULINT |
|
|
| Property Name | Default | Mandatory | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The defined address of the tag |
String |
||
|
The data type |
Selection of ADS data types |
EtherNet/IP Adapter
The EtherNet/IP adapter enables connections to Rockwell / Allen-Bradley PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) from the ControlLogix and CompactLogix series using the Ethernet/IP CIP protocol.
The adapter supports the following capability:
-
Read (Northbound): Poll EtherNet/IP tags and publish data to MQTT topics.
<hivemq>
<protocol-adapters>
<protocol-adapter>
<adapterId>my-eip-protocol-adapter</adapterId>
<protocolId>eip</protocolId>
<config>
<port>1234</port>
<host>my.eip-server.com</host>
</config>
<northboundMappings>
<northboundMapping>
<topic>my/topic</topic>
<tagName>tag-name</tagName>
</northboundMapping>
</northboundMappings>
<tags>
<tag>
<name>tag-name</name>
<description>description</description>
<definition>
<address>addressy</address>
<dataType>BOOL</dataType>
</definition>
</tag>
</tags>
</protocol-adapter>
</protocol-adapters>
</hivemq><hivemq>
<protocol-adapters>
<protocol-adapter>
<adapterId>my-eip-protocol-adapter</adapterId>
<protocolId>eip</protocolId>
<config>
<host>my.eip-server.com</host>
<port>1234</port>
<backplane>4</backplane>
<slot>5</slot>
<eipToMqtt>
<pollingIntervalMillis>10</pollingIntervalMillis>
<maxPollingErrorsBeforeRemoval>9</maxPollingErrorsBeforeRemoval>
<publishChangedDataOnly>false</publishChangedDataOnly>
</eipToMqtt>
</config>
<northboundMappings>
<northboundMapping>
<topic>my/topic</topic>
<maxQos>1</maxQos>
<includeTagNames>true</includeTagNames>
<includeTimestamp>true</includeTimestamp>
<messageHandlingOptions>MQTTMessagePerSubscription</messageHandlingOptions>
<tagName>tag-name</tagName>
<mqttUserProperties>
<mqttUserProperty>
<name>name</name>
<value>value1</value>
</mqttUserProperty>
<mqttUserProperty>
<name>name</name>
<value>value2</value>
</mqttUserProperty>
</mqttUserProperties>
</northboundMapping>
<northboundMapping>
<topic>my/topic/2</topic>
<maxQos>1</maxQos>
<includeTagNames>true</includeTagNames>
<includeTimestamp>true</includeTimestamp>
<messageHandlingOptions>MQTTMessagePerSubscription</messageHandlingOptions>
<tagName>tag-name</tagName>
<mqttUserProperties>
<mqttUserProperty>
<name>name</name>
<value>value1</value>
</mqttUserProperty>
<mqttUserProperty>
<name>name</name>
<value>value2</value>
</mqttUserProperty>
</mqttUserProperties>
</northboundMapping>
</northboundMappings>
<tags>
<tag>
<name>tag-name</name>
<description>description</description>
<definition>
<address>addressy</address>
<dataType>BOOL</dataType>
</definition>
</tag>
</tags>
</protocol-adapter>
</protocol-adapters>
</hivemq>EtherNet/IP Adapter Properties (config)
| Property Name | Default | Mandatory | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The host or IPv4/IPv6 of the EtherNet/IP device. |
Hostname or IP |
||
|
The TCP port to connect to (typical EtherNet/IP port is 44818). |
Integer 1-65535 |
||
|
|
The backplane device value. |
Integer |
|
|
|
The slot device value (specifies which CPU slot to target). |
Integer |
|
|
Configuration for EtherNet/IP to MQTT data flow |
EtherNet/IP Northbound config
| Property Name | Default | Mandatory | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Time in milliseconds between polling cycles. |
Integer >= 1 |
|
|
|
Maximum number of consecutive polling errors before the adapter stops. Set to -1 for unlimited retries. |
Integer >= -1 |
|
|
|
When enabled, the adapter only publishes data when a value has changed since the last poll. This reduces MQTT traffic for slow-changing data. |
Boolean |
EtherNet/IP Tag Definition
Tags in the EtherNet/IP adapter define which Controller Tags to read.
| Property Name | Default | Mandatory | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The Controller Tag name as shown in Logix/Studio 5000. See EtherNet/IP Tag Address for details. |
String |
||
|
The data type of the tag. See EtherNet/IP Types for supported types. |
Enum |
EtherNet/IP Tag Address
The general structure of tags is defined identically for each protocol adapter as described in Tags. The tag address for EtherNet/IP is the name of the Controller Tag as shown in Logix/Studio 5000.
Example: at_int_tag
EtherNet/IP Types
| Type | Description | MQTT payload example | Value range |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 bit |
|
|
|
1 byte signed |
|
|
|
1 byte unsigned |
|
|
|
2 byte signed |
|
|
|
2 byte unsigned |
|
|
|
4 byte signed |
|
|
|
4 byte unsigned |
|
|
|
8 byte signed |
|
|
|
8 byte unsigned |
|
|
|
4 byte floating point signed |
|
|
|
8 byte floating point signed |
|
|
|
ascii string |
|
|
|
4 byte unsigned, millisecond duration, UDINT |
|
|
|
8 byte unsigned, nanosecond duration, ULINT |
|
|
| Property Name | Default | Mandatory | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The defined address of the tag |
String |
||
|
The data type |
Selection of EIP data types |
HTTP(s) Adapter
The HTTP adapter is useful when data points can be gathered via HTTP even when other IoT protocols are not available or other software systems should be integrated. The HTTP adapter polls data from a configurable endpoint and converts it into an MQTT message.
The adapter supports the following capabilities:
-
Read (Northbound): Poll HTTP endpoints and publish responses to MQTT topics.
The HTTP adapter does not have a publishChangedDataOnly option. Data is published on every polling interval regardless of whether it changed.
|
<hivemq>
<protocol-adapters>
<protocol-adapter>
<adapterId>my-http-adapter</adapterId>
<protocolId>http</protocolId>
<config>
<httpConnectTimeoutSeconds>5</httpConnectTimeoutSeconds>
<httpToMqtt>
<pollingIntervalMillis>1000</pollingIntervalMillis>
<maxPollingErrorsBeforeRemoval>10</maxPollingErrorsBeforeRemoval>
<assertResponseIsJson>false</assertResponseIsJson>
<httpPublishSuccessStatusCodeOnly>true</httpPublishSuccessStatusCodeOnly>
</httpToMqtt>
<allowUntrustedCertificates>false</allowUntrustedCertificates>
</config>
<northboundMappings>
<northboundMapping>
<tagName>sensor-tag</tagName>
<topic>sensors/temperature</topic>
<maxQos>1</maxQos>
<messageExpiryInterval>9223372036854775807</messageExpiryInterval>
</northboundMapping>
</northboundMappings>
<tags>
<tag>
<name>sensor-tag</name>
<description>Temperature sensor HTTP endpoint</description>
<definition>
<url>http://sensor.local/api/temperature</url>
<httpRequestMethod>GET</httpRequestMethod>
<httpRequestTimeoutSeconds>5</httpRequestTimeoutSeconds>
<httpRequestBodyContentType>JSON</httpRequestBodyContentType>
<httpHeaders>
<httpHeader>
<name>Authorization</name>
<value>Bearer token123</value>
</httpHeader>
</httpHeaders>
</definition>
</tag>
</tags>
</protocol-adapter>
</protocol-adapters>
</hivemq>HTTP Adapter Properties (config)
| Property Name | Default | Mandatory | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The unique identifier of the protocol adapter. |
String [a-zA-Z0-9-_] |
||
|
|
Timeout in seconds for HTTP connection establishment. |
Integer (1-60) |
|
|
|
Allow connections to untrusted SSL sources (expired certificates, self-signed, etc.). |
Boolean |
|
|
Configuration for HTTP to MQTT data flow |
HTTP Northbound config
| Property Name | Default | Mandatory | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Time in milliseconds between polling cycles. |
Integer >= 1 |
|
|
|
Maximum number of consecutive polling errors before the adapter stops. Minimum value is 3. |
Integer >= 3 |
|
|
|
When enabled, only publish MQTT messages when the HTTP response code is successful (200-299). |
Boolean |
|
|
|
When enabled, forces parsing the HTTP response as JSON regardless of the Content-Type header. |
Boolean |
HTTP Tag Definition
Tags in the HTTP adapter define HTTP endpoints to poll or send data to.
| Property Name | Default | Mandatory | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The URL of the HTTP endpoint. |
URL |
||
|
|
The HTTP method to use. |
|
|
|
|
Timeout in seconds for the HTTP request to complete. |
Integer (1-60) |
|
|
|
Content-Type for the request body. |
|
|
|
Request body content (required for POST/PUT methods). |
String |
||
|
List of custom HTTP headers to include in requests. |
List of HttpHeader |
| Property Name | Default | Mandatory | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The name of the HTTP header. |
String |
||
|
The value of the HTTP header. |
String |
The adapter automatically adds a User-Agent: HiveMQ-Edge; <version> header to all requests.
|
File Adapter
The File adapter polls and publishes the content of files on a regular basis. The adapter supports different input formats and makes it possible to read information from systems that cannot communicate via the network or defined APIs.
The adapter supports the following capability:
-
Read (Northbound): Poll files from the local file system and publish content to MQTT topics.
| The File adapter will ingest the whole content of the file (maximum 64KB per file). You can use HiveMQ Data Hub to extract specific information from the content of a file or transform a payload to fit your business needs. |
The File adapter does not have a publishChangedDataOnly option. Files are polled and published on every interval regardless of whether the content has changed.
|
Example configuration to read a file from /tmp/sensor.json.
<hivemq>
<protocol-adapters>
<protocol-adapter>
<adapterId>my-file-protocol-adapter</adapterId>
<protocolId>file</protocolId>
<config>
<fileToMqtt></fileToMqtt>
</config>
<northboundMappings>
<northboundMapping>
<topic>my/topic</topic>
<tagName>tag1</tagName>
</northboundMapping>
</northboundMappings>
<tags>
<tag>
<name>tag1</name>
<description>decsription</description>
<definition>
<filePath>/tmp/sensor.json</filePath>
<contentType>TEXT_JSON</contentType>
</definition>
</tag>
</tags>
</protocol-adapter>
</protocol-adapters>
</hivemq>Example
Suppose a file named /tmp/sensor.json has the following example content:
{ "value": "42" }Create the config as introduced above, the following MQTT payload is generated and shown below:
You can use any MQTT tool that is capable of showing an MQTT topic’s content.
In the example, we use mqtt sub -t 'file-input'
|
{
"timestamp" : 1730122091809,
"value" : {
"value" : "42"
},
"tagName" : "value",
"contentType" : "application/json"
}File Adapter Properties (config)
| Property Name | Default | Mandatory | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The unique identifier of the protocol adapter. |
String [a-zA-Z0-9-_] |
||
|
Configuration for File to MQTT data flow |
File Northbound config
| Property Name | Default | Mandatory | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Time in milliseconds between polling cycles. |
Integer >= 1 |
|
|
|
Maximum number of consecutive polling errors before the adapter stops. Set to -1 for unlimited retries. |
Integer >= -1 |
File Tag Definition
Tags in the File adapter define which files to poll.
| Property Name | Default | Mandatory | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The absolute path to the file to be read. |
Path |
||
|
The content type of the file. |
See Content Types |
File Content Types
| Type | MIME Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
application/octet-stream |
Binary data (Base64 encoded in MQTT payload) |
|
text/plain |
Plain text content (UTF-8) |
|
application/json |
JSON content (parsed into JSON tree) |
|
application/xml |
XML content (treated as plain text) |
|
text/csv |
CSV content (treated as plain text) |
Common Configurations
| Property Name | Default | Mandatory | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The topic to which the response is published. |
MQTT topic |
||
|
|
MQTT Payload QoS |
Integer (0-2) |
|
|
|
Include the name of the Tag in the payload. |
Boolean |
|
|
|
Add a timestamp to the MQTT payload. |
Boolean |
|
|
|
The message expiry interval in seconds for MQTT 5 messages. Messages are removed from queues after this interval. |
Long > 0 |
|
|
List of |
|||
|
|
Specifies whether the adapter only publishes data when a field value change is detected. (Not available for all protocol adapters) |
Boolean |
MQTT User Properties for Protocol Adapters
MQTT User Properties can be added to each MQTT message created out of a Protocol Adapter payload. Any number of User Properties can be created. For more information of MQTT User Properties, read MQTT 5 User Properties.
| Property Name | Default | Mandatory | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Name of the Key of the MQTT User Property |
String |
||
|
Name of the Key of the MQTT User Property |
String |
BACnet Adapter
HiveMQ Edge supports the BACnet/IP protocol with the BACnet protocol adapter.
The adapter supports the following capability:
-
Read (Northbound): Poll BACnet objects and publish data to MQTT topics.
| The BACnet adapter is not pre-packaged with HiveMQ Edge and must be installed separately. |
Download and Install
The BACnet adapter file is available for download from the HiveMQ download server. You can replace the version number
to the latest HiveMQ Edge version. The downloaded .jar file must be copied into the modules directory of your HiveMQ deployment
Afterward, HiveMQ Edge must be restarted to use the protocol adapter.
Install in Docker
If you want to add the BACnet adapter to your Docker image, you can use the following snippet to get started:
ARG HIVEMQ_EDGE_VERSION
FROM hivemq/hivemq-edge:${HIVEMQ_EDGE_VERSION}
ARG HIVEMQ_EDGE_VERSION
ADD hivemq-edge-module-bacnetip-${HIVEMQ_EDGE_VERSION}-all.jar /opt/hivemq/modules/The Dockerfile adds the pre-downloaded BACNet adapter to the HiveMQ Edge modules folder.
To build the final image, enter the following command:
docker build --build-arg HIVEMQ_EDGE_VERSION=2025.2 -t my-custom-hivemq-edge .The build argument HIVEMQ_EDGE_VERSION specifies the HiveMQ Edge version.
Configuration
<hivemq>
<protocol-adapters>
<protocol-adapter>
<adapterId>my-bacnetip-protocol-adapter</adapterId>
<protocolId>bacnet</protocolId>
<config>
<host>192.168.0.255</host>
<port>47808</port>
<deviceId>500</deviceId>
<subnetBroadcastAddress>192.168.0.255</subnetBroadcastAddress>
<discoveryIntervalMillis>10000</discoveryIntervalMillis>
<bacnetipToMqtt>
<pollingIntervalMillis>10</pollingIntervalMillis>
<maxPollingErrorsBeforeRemoval>9</maxPollingErrorsBeforeRemoval>
<publishChangedDataOnly>false</publishChangedDataOnly>
</bacnetipToMqtt>
</config>
<northboundMappings>
<northboundMapping>
<topic>my/topic</topic>
<maxQos>1</maxQos>
<includeTimestamp>false</includeTimestamp>
<includeTagNames>true</includeTagNames>
<tagName>tag1</tagName>
</northboundMapping>
</northboundMappings>
<tags>
<tag>
<name>tag1</name>
<description>description1</description>
<definition>
<deviceInstanceNumber>1</deviceInstanceNumber>
<objectInstanceNumber>1</objectInstanceNumber>
<objectType>ANALOG_INPUT</objectType>
<propertyType>ACKED_TRANSITIONS</propertyType>
</definition>
</tag>
</tags>
</protocol-adapter>
</protocol-adapters>
</hivemq>| Property Name | Default | Mandatory | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
IP Address or hostname of the device to connect to |
Hostname or IP |
||
|
|
The port number on the device to connect to |
Port |
|
|
The device ID of the client used to obtain data via the BACnet/IP network |
1-65535 |
||
|
The broadcast address of the BACnet/IP network |
IP |
||
|
|
The time in milliseconds between checking the network for new devices |
Milliseconds |
|
|
Object to define configuration of mappings from BACnet to MQTT |
Object, BACnet to MQTT config |
| Property Name | Default | Mandatory | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Time in milliseconds between pollings of this endpoint |
Milliseconds |
|
|
|
Maximum number of errors polling the endpoint before the polling daemon is stopped (-1 for unlimited retries) |
Milliseconds |
|
|
|
Specifies whether the adapter only publishes data items that have changed since the last poll |
|
| Property Name | Default | Mandatory | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
The instance number of the remote device on the network |
Integer |
|
|
|
The object number of the object on the remote device |
Integer |
|
|
The type of the object |
|||
|
|
The property of the object to fetch |
Object Types
-
ANALOG_INPUT(0)
-
ANALOG_OUTPUT(1)
-
ANALOG_VALUE(2)
-
BINARY_INPUT(3)
-
BINARY_OUTPUT(4)
-
BINARY_VALUE(5)
-
CALENDAR(6)
-
COMMAND(7)
-
DEVICE(8)
-
EVENT_ENROLLMENT(9)
-
FILE(10)
-
GROUP(11)
-
LOOP(12)
-
MULTI_STATE_INPUT(13)
-
MULTI_STATE_OUTPUT(14)
-
NOTIFICATION_CLASS(15)
-
PROGRAM(16)
-
SCHEDULE(17)
-
AVERAGING(18)
-
MULTI_STATE_VALUE(19)
-
TREND_LOG(20)
-
LIFE_SAFETY_POINT(21)
-
LIFE_SAFETY_ZONE(22)
-
ACCUMULATOR(23)
-
PULSE_CONVERTER(24)
-
EVENT_LOG(25)
-
GLOBAL_GROUP(26)
-
TREND_LOG_MULTIPLE(27)
-
LOAD_CONTROL(28)
-
STRUCTURED_VIEW(29)
-
ACCESS_DOOR(30)
-
TIMER(31)
-
ACCESS_CREDENTIAL(32)
-
ACCESS_POINT(33)
-
ACCESS_RIGHTS(34)
-
ACCESS_USER(35)
-
ACCESS_ZONE(36)
-
CREDENTIAL_DATA_INPUT(37)
-
NETWORK_SECURITY(38)
-
BITSTRING_VALUE(39)
-
CHARACTERSTRING_VALUE(40)
-
DATE_PATTERN_VALUE(41)
-
DATE_VALUE(42)
-
DATETIME_PATTERN_VALUE(43)
-
DATETIME_VALUE(44)
-
INTEGER_VALUE(45)
-
LARGE_ANALOG_VALUE(46)
-
OCTETSTRING_VALUE(47)
-
POSITIVE_INTEGER_VALUE(48)
-
TIME_PATTERN_VALUE(49)
-
TIME_VALUE(50)
-
NOTIFICATION_FORWARDER(51)
-
ALERT_ENROLLMENT(52)
-
CHANNEL(53)
-
LIGHTING_OUTPUT(54)
-
BINARY_LIGHTING_OUTPUT(55)
-
NETWORK_PORT(56)
-
ELEVATOR_GROUP(57)
-
ESCALATOR(58)
-
LIFT(59)
Property Types
-
ACKED_TRANSITIONS(0)
-
ACK_REQUIRED(1)
-
ACTION(2)
-
ACTION_TEXT(3)
-
ACTIVE_TEXT(4)
-
ACTIVE_VT_SESSIONS(5)
-
ALARM_VALUE(6)
-
ALARM_VALUES(7)
-
ALL(8)
-
ALL_WRITES_SUCCESSFUL(9)
-
APDU_SEGMENT_TIMEOUT(10)
-
APDU_TIMEOUT(11)
-
APPLICATION_SOFTWARE_VERSION(12)
-
ARCHIVE(13)
-
BIAS(14)
-
CHANGE_OF_STATE_COUNT(15)
-
CHANGE_OF_STATE_TIME(16)
-
NOTIFICATION_CLASS(17)
-
CONTROLLED_VARIABLE_REFERENCE(19)
-
CONTROLLED_VARIABLE_UNITS(20)
-
CONTROLLED_VARIABLE_VALUE(21)
-
COV_INCREMENT(22)
-
DATE_LIST(23)
-
DAYLIGHT_SAVINGS_STATUS(24)
-
DEADBAND(25)
-
DERIVATIVE_CONSTANT(26)
-
DERIVATIVE_CONSTANT_UNITS(27)
-
DESCRIPTION(28)
-
DESCRIPTION_OF_HALT(29)
-
DEVICE_ADDRESS_BINDING(30)
-
DEVICE_TYPE(31)
-
EFFECTIVE_PERIOD(32)
-
ELAPSED_ACTIVE_TIME(33)
-
ERROR_LIMIT(34)
-
EVENT_ENABLE(35)
-
EVENT_STATE(36)
-
EVENT_TYPE(37)
-
EXCEPTION_SCHEDULE(38)
-
FAULT_VALUES(39)
-
FEEDBACK_VALUE(40)
-
FILE_ACCESS_METHOD(41)
-
FILE_SIZE(42)
-
FILE_TYPE(43)
-
FIRMWARE_REVISION(44)
-
HIGH_LIMIT(45)
-
INACTIVE_TEXT(46)
-
IN_PROCESS(47)
-
INSTANCE_OF(48)
-
INTEGRAL_CONSTANT(49)
-
INTEGRAL_CONSTANT_UNITS(50)
-
LIMIT_ENABLE(52)
-
LIST_OF_GROUP_MEMBERS(53)
-
LIST_OF_OBJECT_PROPERTY_REFERENCES(54)
-
LOCAL_DATE(56)
-
LOCAL_TIME(57)
-
LOCATION(58)
-
LOW_LIMIT(59)
-
MANIPULATED_VARIABLE_REFERENCE(60)
-
MAXIMUM_OUTPUT(61)
-
MAX_APDU_LENGTH_ACCEPTED(62)
-
MAX_INFO_FRAMES(63)
-
MAX_MASTER(64)
-
MAX_PRES_VALUE(65)
-
MINIMUM_OFF_TIME(66)
-
MINIMUM_ON_TIME(67)
-
MINIMUM_OUTPUT(68)
-
MIN_PRES_VALUE(69)
-
MODEL_NAME(70)
-
MODIFICATION_DATE(71)
-
NOTIFY_TYPE(72)
-
NUMBER_OF_APDU_RETRIES(73)
-
NUMBER_OF_STATES(74)
-
OBJECT_IDENTIFIER(75)
-
OBJECT_LIST(76)
-
OBJECT_NAME(77)
-
OBJECT_PROPERTY_REFERENCE(78)
-
OBJECT_TYPE(79)
-
OPTIONAL(80)
-
OUT_OF_SERVICE(81)
-
OUTPUT_UNITS(82)
-
EVENT_PARAMETERS(83)
-
POLARITY(84)
-
PRESENT_VALUE(85)
-
PRIORITY(86)
-
PRIORITY_ARRAY(87)
-
PRIORITY_FOR_WRITING(88)
-
PROCESS_IDENTIFIER(89)
-
PROGRAM_CHANGE(90)
-
PROGRAM_LOCATION(91)
-
PROGRAM_STATE(92)
-
PROPORTIONAL_CONSTANT(93)
-
PROPORTIONAL_CONSTANT_UNITS(94)
-
PROTOCOL_OBJECT_TYPES_SUPPORTED(96)
-
PROTOCOL_SERVICES_SUPPORTED(97)
-
PROTOCOL_VERSION(98)
-
READ_ONLY(99)
-
REASON_FOR_HALT(100)
-
RECIPIENT_LIST(102)
-
RELIABILITY(103)
-
RELINQUISH_DEFAULT(104)
-
REQUIRED(105)
-
RESOLUTION(106)
-
SEGMENTATION_SUPPORTED(107)
-
SETPOINT(108)
-
SETPOINT_REFERENCE(109)
-
STATE_TEXT(110)
-
STATUS_FLAGS(111)
-
SYSTEM_STATUS(112)
-
TIME_DELAY(113)
-
TIME_OF_ACTIVE_TIME_RESET(114)
-
TIME_OF_STATE_COUNT_RESET(115)
-
TIME_SYNCHRONIZATION_RECIPIENTS(116)
-
UNITS(117)
-
UPDATE_INTERVAL(118)
-
UTC_OFFSET(119)
-
VENDOR_IDENTIFIER(120)
-
VENDOR_NAME(121)
-
VT_CLASSES_SUPPORTED(122)
-
WEEKLY_SCHEDULE(123)
-
ATTEMPTED_SAMPLES(124)
-
AVERAGE_VALUE(125)
-
BUFFER_SIZE(126)
-
CLIENT_COV_INCREMENT(127)
-
COV_RESUBSCRIPTION_INTERVAL(128)
-
EVENT_TIME_STAMPS(130)
-
LOG_BUFFER(131)
-
LOG_DEVICE_OBJECT_PROPERTY(132)
-
ENABLE(133)
-
LOG_INTERVAL(134)
-
MAXIMUM_VALUE(135)
-
MINIMUM_VALUE(136)
-
NOTIFICATION_THRESHOLD(137)
-
PROTOCOL_REVISION(139)
-
RECORDS_SINCE_NOTIFICATION(140)
-
RECORD_COUNT(141)
-
START_TIME(142)
-
STOP_TIME(143)
-
STOP_WHEN_FULL(144)
-
TOTAL_RECORD_COUNT(145)
-
VALID_SAMPLES(146)
-
WINDOW_INTERVAL(147)
-
WINDOW_SAMPLES(148)
-
MAXIMUM_VALUE_TIMESTAMP(149)
-
MINIMUM_VALUE_TIMESTAMP(150)
-
VARIANCE_VALUE(151)
-
ACTIVE_COV_SUBSCRIPTIONS(152)
-
BACKUP_FAILURE_TIMEOUT(153)
-
CONFIGURATION_FILES(154)
-
DATABASE_REVISION(155)
-
DIRECT_READING(156)
-
LAST_RESTORE_TIME(157)
-
MAINTENANCE_REQUIRED(158)
-
MEMBER_OF(159)
-
MODE(160)
-
OPERATION_EXPECTED(161)
-
SETTING(162)
-
SILENCED(163)
-
TRACKING_VALUE(164)
-
ZONE_MEMBERS(165)
-
LIFE_SAFETY_ALARM_VALUES(166)
-
MAX_SEGMENTS_ACCEPTED(167)
-
PROFILE_NAME(168)
-
AUTO_SLAVE_DISCOVERY(169)
-
MANUAL_SLAVE_ADDRESS_BINDING(170)
-
SLAVE_ADDRESS_BINDING(171)
-
SLAVE_PROXY_ENABLE(172)
-
LAST_NOTIFY_RECORD(173)
-
SCHEDULE_DEFAULT(174)
-
ACCEPTED_MODES(175)
-
ADJUST_VALUE(176)
-
COUNT(177)
-
COUNT_BEFORE_CHANGE(178)
-
COUNT_CHANGE_TIME(179)
-
COV_PERIOD(180)
-
INPUT_REFERENCE(181)
-
LIMIT_MONITORING_INTERVAL(182)
-
LOGGING_OBJECT(183)
-
LOGGING_RECORD(184)
-
PRESCALE(185)
-
PULSE_RATE(186)
-
SCALE(187)
-
SCALE_FACTOR(188)
-
UPDATE_TIME(189)
-
VALUE_BEFORE_CHANGE(190)
-
VALUE_SET(191)
-
VALUE_CHANGE_TIME(192)
-
ALIGN_INTERVALS(193)
-
INTERVAL_OFFSET(195)
-
LAST_RESTART_REASON(196)
-
LOGGING_TYPE(197)
-
RESTART_NOTIFICATION_RECIPIENTS(202)
-
TIME_OF_DEVICE_RESTART(203)
-
TIME_SYNCHRONIZATION_INTERVAL(204)
-
TRIGGER(205)
-
UTC_TIME_SYNCHRONIZATION_RECIPIENTS(206)
-
NODE_SUBTYPE(207)
-
NODE_TYPE(208)
-
STRUCTURED_OBJECT_LIST(209)
-
SUBORDINATE_ANNOTATIONS(210)
-
SUBORDINATE_LIST(211)
-
ACTUAL_SHED_LEVEL(212)
-
DUTY_WINDOW(213)
-
EXPECTED_SHED_LEVEL(214)
-
FULL_DUTY_BASELINE(215)
-
REQUESTED_SHED_LEVEL(218)
-
SHED_DURATION(219)
-
SHED_LEVEL_DESCRIPTIONS(220)
-
SHED_LEVELS(221)
-
STATE_DESCRIPTION(222)
-
DOOR_ALARM_STATE(226)
-
DOOR_EXTENDED_PULSE_TIME(227)
-
DOOR_MEMBERS(228)
-
DOOR_OPEN_TOO_LONG_TIME(229)
-
DOOR_PULSE_TIME(230)
-
DOOR_STATUS(231)
-
DOOR_UNLOCK_DELAY_TIME(232)
-
LOCK_STATUS(233)
-
MASKED_ALARM_VALUES(234)
-
SECURED_STATUS(235)
-
ABSENTEE_LIMIT(244)
-
ACCESS_ALARM_EVENTS(245)
-
ACCESS_DOORS(246)
-
ACCESS_EVENT(247)
-
ACCESS_EVENT_AUTHENTICATION_FACTOR(248)
-
ACCESS_EVENT_CREDENTIAL(249)
-
ACCESS_EVENT_TIME(250)
-
ACCESS_TRANSACTION_EVENTS(251)
-
ACCOMPANIMENT(252)
-
ACCOMPANIMENT_TIME(253)
-
ACTIVATION_TIME(254)
-
ACTIVE_AUTHENTICATION_POLICY(255)
-
ASSIGNED_ACCESS_RIGHTS(256)
-
AUTHENTICATION_FACTORS(257)
-
AUTHENTICATION_POLICY_LIST(258)
-
AUTHENTICATION_POLICY_NAMES(259)
-
AUTHENTICATION_STATUS(260)
-
AUTHORIZATION_MODE(261)
-
BELONGS_TO(262)
-
CREDENTIAL_DISABLE(263)
-
CREDENTIAL_STATUS(264)
-
CREDENTIALS(265)
-
CREDENTIALS_IN_ZONE(266)
-
DAYS_REMAINING(267)
-
ENTRY_POINTS(268)
-
EXIT_POINTS(269)
-
EXPIRATION_TIME(270)
-
EXTENDED_TIME_ENABLE(271)
-
FAILED_ATTEMPT_EVENTS(272)
-
FAILED_ATTEMPTS(273)
-
FAILED_ATTEMPTS_TIME(274)
-
LAST_ACCESS_EVENT(275)
-
LAST_ACCESS_POINT(276)
-
LAST_CREDENTIAL_ADDED(277)
-
LAST_CREDENTIAL_ADDED_TIME(278)
-
LAST_CREDENTIAL_REMOVED(279)
-
LAST_CREDENTIAL_REMOVED_TIME(280)
-
LAST_USE_TIME(281)
-
LOCKOUT(282)
-
LOCKOUT_RELINQUISH_TIME(283)
-
MAX_FAILED_ATTEMPTS(285)
-
MEMBERS(286)
-
MUSTER_POINT(287)
-
NEGATIVE_ACCESS_RULES(288)
-
NUMBER_OF_AUTHENTICATION_POLICIES(289)
-
OCCUPANCY_COUNT(290)
-
OCCUPANCY_COUNT_ADJUST(291)
-
OCCUPANCY_COUNT_ENABLE(292)
-
OCCUPANCY_LOWER_LIMIT(294)
-
OCCUPANCY_LOWER_LIMIT_ENFORCED(295)
-
OCCUPANCY_STATE(296)
-
OCCUPANCY_UPPER_LIMIT(297)
-
OCCUPANCY_UPPER_LIMIT_ENFORCED(298)
-
PASSBACK_MODE(300)
-
PASSBACK_TIMEOUT(301)
-
POSITIVE_ACCESS_RULES(302)
-
REASON_FOR_DISABLE(303)
-
SUPPORTED_FORMATS(304)
-
SUPPORTED_FORMAT_CLASSES(305)
-
THREAT_AUTHORITY(306)
-
THREAT_LEVEL(307)
-
TRACE_FLAG(308)
-
TRANSACTION_NOTIFICATION_CLASS(309)
-
USER_EXTERNAL_IDENTIFIER(310)
-
USER_INFORMATION_REFERENCE(311)
-
USER_NAME(317)
-
USER_TYPE(318)
-
USES_REMAINING(319)
-
ZONE_FROM(320)
-
ZONE_TO(321)
-
ACCESS_EVENT_TAG(322)
-
GLOBAL_IDENTIFIER(323)
-
VERIFICATION_TIME(326)
-
BASE_DEVICE_SECURITY_POLICY(327)
-
DISTRIBUTION_KEY_REVISION(328)
-
DO_NOT_HIDE(329)
-
KEY_SETS(330)
-
LAST_KEY_SERVER(331)
-
NETWORK_ACCESS_SECURITY_POLICIES(332)
-
PACKET_REORDER_TIME(333)
-
SECURITY_PDU_TIMEOUT(334)
-
SECURITY_TIME_WINDOW(335)
-
SUPPORTED_SECURITY_ALGORITHMS(336)
-
UPDATE_KEY_SET_TIMEOUT(337)
-
BACKUP_AND_RESTORE_STATE(338)
-
BACKUP_PREPARATION_TIME(339)
-
RESTORE_COMPLETION_TIME(340)
-
RESTORE_PREPARATION_TIME(341)
-
BIT_MASK(342)
-
BIT_TEXT(343)
-
IS_UTC(344)
-
GROUP_MEMBERS(345)
-
GROUP_MEMBER_NAMES(346)
-
MEMBER_STATUS_FLAGS(347)
-
REQUESTED_UPDATE_INTERVAL(348)
-
COVU_PERIOD(349)
-
COVU_RECIPIENTS(350)
-
EVENT_MESSAGE_TEXTS(351)
-
EVENT_MESSAGE_TEXTS_CONFIG(352)
-
EVENT_DETECTION_ENABLE(353)
-
EVENT_ALGORITHM_INHIBIT(354)
-
EVENT_ALGORITHM_INHIBIT_REF(355)
-
TIME_DELAY_NORMAL(356)
-
RELIABILITY_EVALUATION_INHIBIT(357)
-
FAULT_PARAMETERS(358)
-
FAULT_TYPE(359)
-
LOCAL_FORWARDING_ONLY(360)
-
PROCESS_IDENTIFIER_FILTER(361)
-
SUBSCRIBED_RECIPIENTS(362)
-
PORT_FILTER(363)
-
AUTHORIZATION_EXEMPTIONS(364)
-
ALLOW_GROUP_DELAY_INHIBIT(365)
-
CHANNEL_NUMBER(366)
-
CONTROL_GROUPS(367)
-
EXECUTION_DELAY(368)
-
LAST_PRIORITY(369)
-
WRITE_STATUS(370)
-
PROPERTY_LIST(371)
-
SERIAL_NUMBER(372)
-
BLINK_WARN_ENABLE(373)
-
DEFAULT_FADE_TIME(374)
-
DEFAULT_RAMP_RATE(375)
-
DEFAULT_STEP_INCREMENT(376)
-
EGRESS_TIME(377)
-
IN_PROGRESS(378)
-
INSTANTANEOUS_POWER(379)
-
LIGHTING_COMMAND(380)
-
LIGHTING_COMMAND_DEFAULT_PRIORITY(381)
-
MAX_ACTUAL_VALUE(382)
-
MIN_ACTUAL_VALUE(383)
-
POWER(384)
-
TRANSITION(385)
-
EGRESS_ACTIVE(386)
-
INTERFACE_VALUE(387)
-
FAULT_HIGH_LIMIT(388)
-
FAULT_LOW_LIMIT(389)
-
LOW_DIFF_LIMIT(390)
-
STRIKE_COUNT(391)
-
TIME_OF_STRIKE_COUNT_RESET(392)
-
DEFAULT_TIMEOUT(393)
-
INITIAL_TIMEOUT(394)
-
LAST_STATE_CHANGE(395)
-
STATE_CHANGE_VALUES(396)
-
TIMER_RUNNING(397)
-
TIMER_STATE(398)
-
APDU_LENGTH(399)
-
IP_ADDRESS(400)
-
IP_DEFAULT_GATEWAY(401)
-
IP_DHCP_ENABLE(402)
-
IP_DHCP_LEASE_TIME(403)
-
IP_DHCP_LEASE_TIME_REMAINING(404)
-
IP_DHCP_SERVER(405)
-
IP_DNS_SERVER(406)
-
BACNET_IP_GLOBAL_ADDRESS(407)
-
BACNET_IP_MODE(408)
-
BACNET_IP_MULTICAST_ADDRESS(409)
-
BACNET_IP_NAT_TRAVERSAL(410)
-
IP_SUBNET_MASK(411)
-
BACNET_IP_UDP_PORT(412)
-
BBMD_ACCEPT_FD_REGISTRATIONS(413)
-
BBMD_BROADCAST_DISTRIBUTION_TABLE(414)
-
BBMD_FOREIGN_DEVICE_TABLE(415)
-
CHANGES_PENDING(416)
-
COMMAND(417)
-
FD_BBMD_ADDRESS(418)
-
FD_SUBSCRIPTION_LIFETIME(419)
-
LINK_SPEED(420)
-
LINK_SPEEDS(421)
-
LINK_SPEED_AUTONEGOTIATE(422)
-
MAC_ADDRESS(423)
-
NETWORK_INTERFACE_NAME(424)
-
NETWORK_NUMBER(425)
-
NETWORK_NUMBER_QUALITY(426)
-
NETWORK_TYPE(427)
-
ROUTING_TABLE(428)
-
VIRTUAL_MAC_ADDRESS_TABLE(429)
-
COMMAND_TIME_ARRAY(430)
-
CURRENT_COMMAND_PRIORITY(431)
-
LAST_COMMAND_TIME(432)
-
VALUE_SOURCE(433)
-
VALUE_SOURCE_ARRAY(434)
-
BACNET_IPV6_MODE(435)
-
IPV6_ADDRESS(436)
-
IPV6_PREFIX_LENGTH(437)
-
BACNET_IPV6_UDP_PORT(438)
-
IPV6_DEFAULT_GATEWAY(439)
-
BACNET_IPV6_MULTICAST_ADDRESS(440)
-
IPV6_DNS_SERVER(441)
-
IPV6_AUTO_ADDRESSING_ENABLE(442)
-
IPV6_DHCP_LEASE_TIME(443)
-
IPV6_DHCP_LEASE_TIME_REMAINING(444)
-
IPV6_DHCP_SERVER(445)
-
IPV6_ZONE_INDEX(446)
-
ASSIGNED_LANDING_CALLS(447)
-
CAR_ASSIGNED_DIRECTION(448)
-
CAR_DOOR_COMMAND(449)
-
CAR_DOOR_STATUS(450)
-
CAR_DOOR_TEXT(451)
-
CAR_DOOR_ZONE(452)
-
CAR_DRIVE_STATUS(453)
-
CAR_LOAD(454)
-
CAR_LOAD_UNITS(455)
-
CAR_MODE(456)
-
CAR_MOVING_DIRECTION(457)
-
CAR_POSITION(458)
-
ELEVATOR_GROUP(459)
-
ENERGY_METER(460)
-
ENERGY_METER_REF(461)
-
ESCALATOR_MODE(462)
-
FAULT_SIGNALS(463)
-
FLOOR_TEXT(464)
-
GROUP_ID(465)
-
GROUP_MODE(467)
-
HIGHER_DECK(468)
-
INSTALLATION_ID(469)
-
LANDING_CALLS(470)
-
LANDING_CALL_CONTROL(471)
-
LANDING_DOOR_STATUS(472)
-
LOWER_DECK(473)
-
MACHINE_ROOM_ID(474)
-
MAKING_CAR_CALL(475)
-
NEXT_STOPPING_FLOOR(476)
-
OPERATION_DIRECTION(477)
-
PASSENGER_ALARM(478)
-
POWER_MODE(479)
-
REGISTERED_CAR_CALL(480)
-
ACTIVE_COV_MULTIPLE_SUBSCRIPTIONS(481)
-
PROTOCOL_LEVEL(482)
-
REFERENCE_PORT(483)
-
DEPLOYED_PROFILE_LOCATION(484)
-
PROFILE_LOCATION(485)
-
TAGS(486)
-
SUBORDINATE_NODE_TYPES(487)
-
SUBORDINATE_TAGS(488)
-
SUBORDINATE_RELATIONSHIPS(489)
-
DEFAULT_SUBORDINATE_RELATIONSHIP(490)
-
REPRESENTS(491);
MTConnect Adapter
The MTConnect protocol adapter enables connections to MTConnect agents via HTTP/HTTPS.
The adapter supports the following capability:
-
Read (Northbound): Poll MTConnect agents and publish data to MQTT topics.
The MTConnect adapter does not have a publishChangedDataOnly option. Data is published on every polling interval regardless of whether it changed.
|
The MTConnect protocol adapter supports the following official MTConnect schemas and custom MTConnect schemas:
| Schema | Version |
|---|---|
Assets |
1.2 - 2.4 |
Devices |
1.0 - 2.4 |
Error |
1.1 - 2.4 |
Streams |
1.1 - 2.4 |
<hivemq>
<protocol-adapters>
<protocol-adapter>
<protocolId>mtconnect</protocolId>
<adapterId>my-mtconnect-protocol-adapter</adapterId>
<config>
<id>my-mtconnect</id>
<allowUntrustedCertificates>true</allowUntrustedCertificates>
<pollingIntervalMillis>500</pollingIntervalMillis>
<maxPollingErrorsBeforeRemoval>5</maxPollingErrorsBeforeRemoval>
</config>
<northboundMappings>
<northboundMapping>
<topic>MTConnect/my-steams</topic>
<tagName>tag1</tagName>
</northboundMapping>
</northboundMappings>
<tags>
<tag>
<name>tag1</name>
<description>description1</description>
<definition>
<url>http://my-mtconnect.com</url>
<enableSchemaValidation>true</enableSchemaValidation>
<includeNull>false</includeNull>
<httpConnectTimeoutSeconds>5</httpConnectTimeoutSeconds>
<httpHeaders>
<httpHeader>
<name>header-name</name>
<value>header-value</value>
</httpHeader>
</httpHeaders>
</definition>
</tag>
</tags>
</protocol-adapter>
</protocol-adapters>
</hivemq>| Property Name | Default | Mandatory | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Defines whether untrusted HTTP sources such as expired certificates can be accepted. |
|
|
|
The unique identifier of the protocol adapter. |
String |
||
|
|
The number of times the adapter attempts to sample while an error condition is detected. If the configured maximum is exceeded, the sampling job ceases to execute until the connection is re-established. |
Integer > 0 |
|
|
|
Time in milliseconds that the endpoint is polled. |
Integer > 0 |
| Property Name | Default | Mandatory | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Defines whether XML schema validation is performed. If your XML payloads conform to the official MTConnect schema, schema validation can help translate from the XML payload to a JSON payload more accurately. Otherwise, set schema validation to |
|
|
|
|
Defines the maximum time (in seconds) to wait for the underlying HTTP connection to be established. |
Integer >= 1 |
|
|
The HTTP headers in the requests to be sent to the MTConnect agent. |
List |
||
|
|
Specifies whether fields with null values are included in the JSON payload. |
|
|
|
Specifies the MTConnect agent endpoint the adapter polls. The MTConnect protocol adapter supports the MTConnect data types: Assets, Devices, Error, and Streams. |
String |
| Property Name | Default | Mandatory | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The name of the HTTP header. |
String |
||
|
The value of the HTTP header. |
String |
Databases Adapter
The databases protocol adapter facilitates the integration of various database engines (PostgreSQL, MySQL, and MS SQL) with HiveMQ Edge.
The adapter supports the following capability:
-
Read (Northbound): Execute SQL queries and publish results to MQTT topics.
The Databases adapter does not have a publishChangedDataOnly option. Query results are published on every polling interval regardless of whether the data has changed.
|
Key Features
-
Supports PostgreSQL, MySQL, and MS SQL databases.
-
Supports one MQTT message per row in the result set (configurable via
spiltLinesInIndividualMessages).
<hivemq>
<protocol-adapters>
<protocol-adapter>
<protocolId>databases</protocolId>
<adapterId>my-databases-protocol-adapter</adapterId>
<configVersion>1</configVersion>
<config>
<type>MYSQL</type>
<server>abc</server>
<port>5432</port>
<database>db</database>
<username>root</username>
<password>pass</password>
<encrypt>true</encrypt>
<trustCertificate>true</trustCertificate>
<connectionTimeoutSeconds>30</connectionTimeoutSeconds>
<pollingIntervalMillis>1000</pollingIntervalMillis>
<maxPollingErrorsBeforeRemoval>10</maxPollingErrorsBeforeRemoval>
<id>test</id>
</config>
<tags>
<tag>
<name>test</name>
<description>test</description>
<definition>
<query>select * from test;</query>
<spiltLinesInIndividualMessages>true</spiltLinesInIndividualMessages>
</definition>
</tag>
</tags>
<southboundMappings/>
<northboundMappings>
<northboundMapping>
<topic>test</topic>
<tagName>test</tagName>
<maxQos>0</maxQos>
<messageHandlingOptions>MQTTMessagePerTag</messageHandlingOptions>
<includeTagNames>false</includeTagNames>
<includeTimestamp>true</includeTimestamp>
<mqttUserProperties/>
<messageExpiryInterval>9223372036854775807</messageExpiryInterval>
</northboundMapping>
</northboundMappings>
</protocol-adapter>
</protocol-adapters>
</hivemq>| Property Name | Default | Mandatory | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The unique identifier of the protocol adapter. |
String |
||
|
The type of database to connect to. |
POSTGRESQL, MYSQL or MSSQL |
||
|
The hostname or IP address of the database server. |
String |
||
|
|
The port number of the database server. |
Integer 1 - 65535 |
|
|
The name of the database to connect to. |
String |
||
|
The username to connect to the database. |
String |
||
|
The password to connect to the database. |
String |
||
|
|
Whether to use an encrypted connection to the database. |
Boolean |
|
|
|
Whether to trust the server certificate when using an encrypted connection. |
Boolean |
|
|
|
The maximum time in seconds to wait for the database connection to be established. |
Integer > 0 |
|
|
|
The number of times the adapter attempts to sample while an error condition is detected. If the configured maximum is exceeded, the sampling job ceases to execute until the connection is re-established. |
Integer > 0 |
|
|
|
Time in milliseconds that the endpoint is polled. |
Integer > 0 |
| Property Name | Default | Mandatory | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The SQL query to execute against the database. The query must return a result set. |
String |
||
|
|
Whether to split the result set into individual messages. If set to |
Boolean |
Contribute a Custom Adapter
The HiveMQ Edge protocol adapter SDK (Java Doc) can be utilized to implement a custom protocol adapter. For a step-by-step tutorial, see How to Build a File-based Protocol Adapter for HiveMQ Edge.