General HiveMQ Platform Installation Information
This guide walks you through basic installation and optimization steps for the HiveMQ platform.
For more ways to try out and evaluate HiveMQ such as Docker and AWS, see Getting Started with HiveMQ.
You can download HiveMQ in a convenient ZIP package with all the executable files, initialization scripts, and example configurations you need to successfully install HiveMQ.
If you do not have a HiveMQ license, HiveMQ automatically runs in trial mode.
For more information on HiveMQ trial options, see Getting Started with HiveMQ.
For information on how to install your license, see Install a HiveMQ License.
The HiveMQ platform download package contains the following directories:
The conf/examples directory of your HiveMQ installation contains several useful example configuration files.
|
└─ hivemq-<version-number>
├── audit
├── backup
├── bin
│ ├── init-script
├── conf
│ ├── examples
├── data
├── extensions
│ ├── hivemq-allow-all-extension
│ ├── hivemq-enterprise-extensions-list
├── license
├── log
├── third-party-licenses
└── tools
│ ├── hivemq-swarm
│ ├── mqtt-cli
│ ├── rest-api| Directory | Content |
|---|---|
|
HiveMQ audit log files. |
|
HiveMQ backup files |
|
Startup scripts and binary files:
|
|
HiveMQ configuration files:
|
|
Persistent client data and cluster data. |
|
All HiveMQ Enterprise Extensions(disabled, by default), custom extensions to the HiveMQ installation, and the |
|
One or more HiveMQ license files. |
|
All HiveMQ log files. |
|
License information for all third-party libraries HiveMQ uses. |
|
HiveMQ Swarm, MQTT CLI, and HiveMQ REST API. |
HiveMQ Enterprise Extensions are preinstalled in your HiveMQ platform release bundle and disabled by default.
To enable a HiveMQ extension, locate the desired extension folder in the extensions directory of your HiveMQ installation and remove the DISABLED file (if present).
For more information, see HiveMQ Enterprise Extensions and Enable or Disable a HiveMQ Extension.
|
By default, HiveMQ only allows MQTT clients to connect if a security extension is present.
For testing purposes, HiveMQ includes a hivemq-allow-all-extension that authorizes all MQTT clients to connect to HiveMQ.
Before you use HiveMQ in production, you must add an appropriate security extension and remove the hivemq-allow-all-extension.
You can download the HiveMQ Enterprise Security Extension from the HiveMQ website or develop your own custom security extension to fit your business needs.
|
HiveMQ Platform Installation on Unix-based systems (Linux, macOS, Unix)
The default installation directory for HiveMQ is /opt/hivemq.
The default HiveMQ username is hivemq.
| Some of the following commands require root privileges. Log in as root user or use sudo to execute the commands. |
-
On the HiveMQ Download page of the official HiveMQ website, enter your email address, read and accept the terms of service, and select Download.zip to download the latest version of HiveMQ.
-
Verify the integrity of the downloaded zip file by using
shasum:Fetch the SHA checksum from the url
https://releases.hivemq.com/hivemq-<version>.zip.sha256, where<version>is the HiveMQ version you downloaded.Verify the checksum (replace
checksumwith the value from above):echo "<checksum> <dowloaded-zip-file-name>" | shasum -a 256 -cExampleecho "f56ab79993d7612bf6d702603d502c101b58a5247f3832a24ffa3602ce210643 hivemq-4.37.0.zip" | shasum -a 256 -cThere are two space characters between the checksum and the filename. Make sure the output of the above command is as follows:
<downloaded-zip-file-name>: OK -
Log in to your system as root user.
-
Move the ZIP download file to the directory where you want to install HiveMQ.
In this example, we use/opt.cd /opt -
Extract the files from the ZIP archive:
unzip hivemq-<version>.zip -
Create a HiveMQ symbolic link (symlink):
ln -s /opt/hivemq-<version> /opt/hivemq -
Create a HiveMQ user:
useradd -d /opt/hivemq hivemq -
Make scripts executable and change the owner to
hivemquser.
Thechmod 775command gives the user/owner and groups read, write, and execute rights. All others have read only access:chown -R hivemq:hivemq /opt/hivemq-<version> chown -R hivemq:hivemq /opt/hivemq cd /opt/hivemq chmod +x ./bin/run.sh -
Adjust the HiveMQ configuration properties to fit your business needs.
For detailed information and configuration examples, see HiveMQ Configuration.
-
Register HiveMQ as a systemd service (optional):
cp /opt/hivemq/bin/init-script/hivemq.service /etc/systemd/system/hivemq.service -
To start the HiveMQ systemd service on boot, run:
systemctl enable hivemq
Set the heap that HiveMQ uses (Linux, macOS, Unix)
The heap that the HiveMQ process uses can be set as a variable in the run.sh file.
To set the heap value, add a line with the desired -Xmx to the VARIABLES configuration.
Example configuration with a 4 GB heap:
############## VARIABLES
JAVA_OPTS="$JAVA_OPTS -Xmx4g"Make the same changes to the recovery.sh file.
We recommended that you configure the JVM heap with 50% of the RAM that is available on the system on which you run HiveMQ.
| The HiveMQ process can use more RAM than the amount of RAM that you allocate to the JVM heap. |
Start HiveMQ Platform (Linux, macOS, Unix)
The following instructions show how to start HiveMQ after the installation.
Verify HiveMQ is running
-
Check if HiveMQ is listening to the default port for MQTT
netstat -an | grep 1883If you run HiveMQ as daemon:
/etc/init.d/hivemq statusIf you run HiveMQ with systemd:
systemctl status hivemq.service -
To debug the HiveMQ startup with systemd, you can inspect the output:
journalctl | grep -i hivemq
HiveMQ Platform Installation on Windows Server
Automated Installation of HiveMQ Platform as a Windows Service (PowerShell Script)
HiveMQ provides a PowerShell script to automate the download, installation, and configuration of all the necessary components needed to set up your HiveMQ Platform on a Windows operating system.
The HiveMQ PowerShell script for Windows Server automates the following actions:
-
Download link validation: Checks all required software download links to ensure the necessary components can be downloaded during the installation process.
Your Windows machine must have outbound internet access and be able to reach the following domains:-
hivemq.com: Required for downloading the HiveMQ Broker software. -
adoptium.net: Required for downloading the Eclipse Temurin OpenJDK JRE. -
github.com: Required for downloading the HiveMQ MQTT CLI. -
nssm.cc: Required for downloading the NSSM tool.
-
-
Java Runtime Environment (JRE) installation: Downloads and installs the appropriate Eclipse Temurin OpenJDK JRE version. Based on the HiveMQ version specified, the script determines the appropriate JDK version:
-
For HiveMQ versions 4.28.0 and above, OpenJDK 21.
-
For older HiveMQ versions, OpenJDK 11.
-
-
HiveMQ Broker installation: Downloads, validates checksum, and installs the specified version of HiveMQ to the default installation directory
C:\hivemq. -
HiveMQ Broker configuration: Creates a basic configuration file for HiveMQ with default settings. The default HiveMQ
config.xmlfile includes the following port settings:-
TCP listener on port
1883to allow MQTT clients to connect. -
Control Center listener on port
8080to enable access to the HiveMQ Control Center.
-
-
MQTT CLI installation: Downloads and installs the executable Windows version of the open-source MQTT CLI tool for testing and interaction.
-
Firewall rule configuration: Opens the necessary ports (1883 and 8080) in Microsoft Defender Firewall to allow external MQTT clients and users to connect to the HiveMQ Broker and the HiveMQ Control Center.
-
Port availability verification: Checks whether essential ports (1883 and 8080) are open and not in use to ensure that HiveMQ can bind to the required ports without conflicts.
-
JVM heap size configuration: Based on the available system memory, sets the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) heap size to allocate 50% of available memory RAM resources to HiveMQ for optimal operation.
-
HiveMQ Service creation and startup: Sets up HiveMQ to run as a Windows service using the NSSM tool to ensure HiveMQ runs continuously in the background and starts automatically with the system.
The following procedure guides you through all the steps needed to install HiveMQ on Windows Server with a PowerShell Script.
-
Download the PowerShell script from the HiveMQ support GitHub repository:
Install-HiveMQ-WindowsServer-Standalone.ps1 -
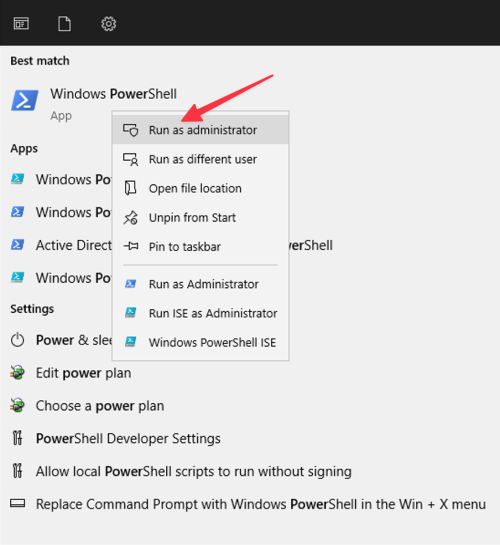
Right-click the Windows PowerShell icon and select Run as administrator:
-
Open a terminal window and enter the following command to temporarily set the current PowerShell session execution policy to Bypass:
Set-ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Scope Process -Force -
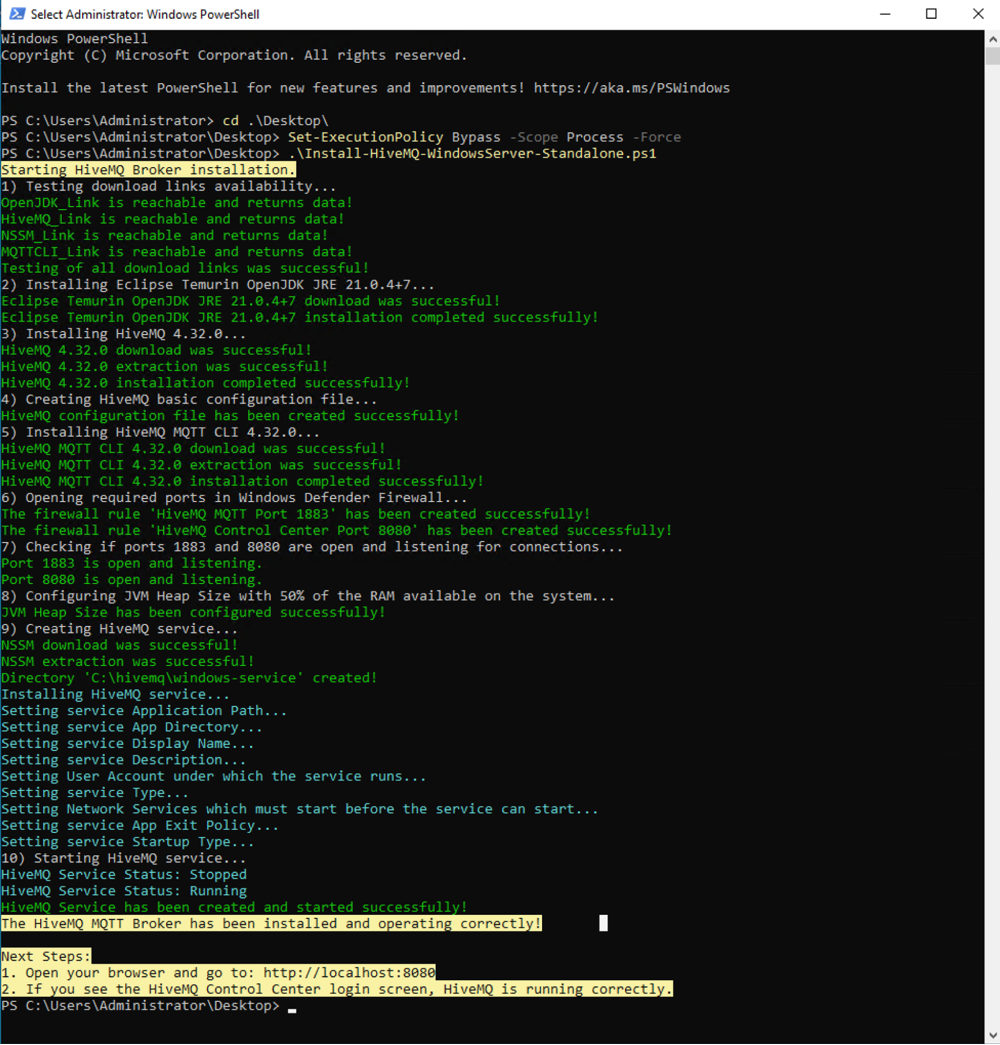
To install HiveMQ and observe the execution output in the terminal, navigate to the folder where you downloaded the PowerShell script and enter the following command to execute the
Install-HiveMQ-WindowsServer-Standalone.ps1script:.\Install-HiveMQ-WindowsServer-Standalone.ps1Optionally, you can define
-hivemqVersionand-installationFolderparameters directly in the command line to specify a different version of HiveMQ or a different installation folder:.\Install-HiveMQ-WindowsServer-Standalone.ps1 -hivemqVersion "4.32.0" -installationFolder "C:\hivemq"If HiveMQ is successfully installed, output similar to the following example displays:
-
To verify access to the HiveMQ Control Center on your Windows machine, open a browser window and navigate to
http://localhost:8080.. The default username isadminand the default password ishivemq.
-
To verify that HiveMQ starts as expected upon reboot, restart your Windows machine.
-
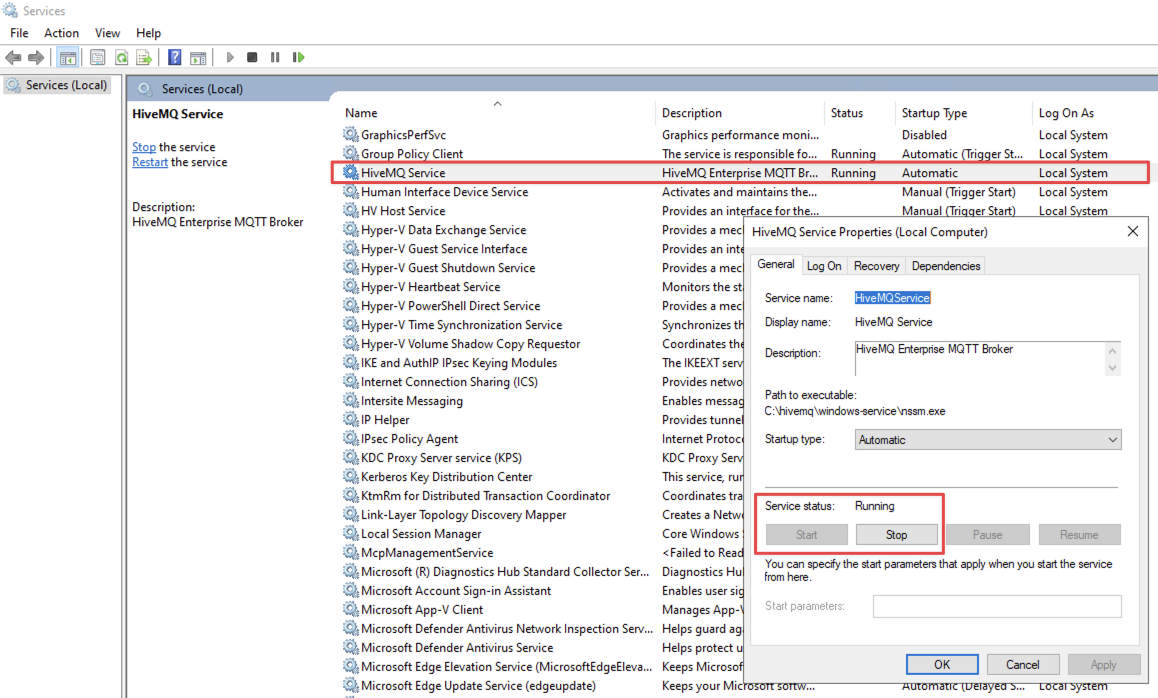
At this point, you can Start and Stop the HiveMQ application with the installed Windows service:
You can use the following PowerShell cmdlet to display your hivemq.logfiles in the console:Get-Content C:\hivemq\log\hivemq.log -Wait
Automated Uninstallation of HiveMQ Platform (PowerShell Script)
The following procedure guides you through all the steps needed to uninstall HiveMQ on Windows Server, which was installed using the previous PowerShell installation script.
| The HiveMQ PowerShell uninstall script renames the HiveMQ installation directory instead of deleting it. This method allows you to retain your configurations and data for future use. |
-
Download the PowerShell uninstall script from the HiveMQ support GitHub repository: Uninstall-HiveMQ-WindowsServer-Standalone.ps1.
If you are using the default HiveMQ installation folder, C:\hivemq, you can execute the following commands in the PowerShell console to uninstall HiveMQ. -
Open a terminal window and enter the following command to temporarily set the current PowerShell session execution policy to Bypass:
Set-ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Scope Process -Force -
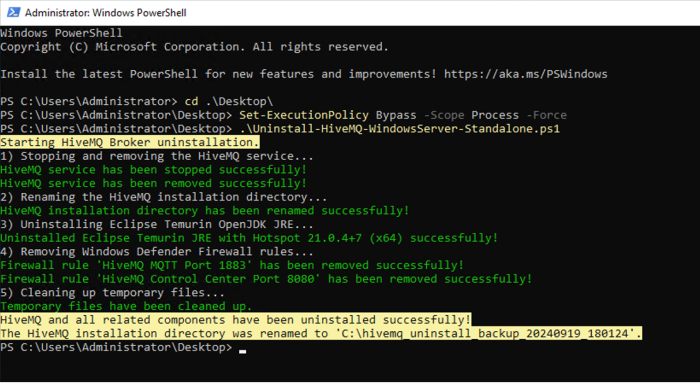
To uninstall HiveMQ and observe the execution output in the terminal, navigate to the folder where you downloaded the PowerShell script and enter the following command to execute the
Uninstall-HiveMQ-WindowsServer-Standalone.ps1script:.\Uninstall-HiveMQ-WindowsServer-Standalone.ps1If you are not using the default installation folder,C:\hivemq, specify the-installationFolderparameter directly in the command line and set where the HiveMQ installation folder is located in your environment:.\Uninstall-HiveMQ-WindowsServer-Standalone.ps1 -installationFolder "F:\hivemq"If HiveMQ is successfully uninstalled, output similar to the following example displays:
Manual Setup of HiveMQ on Windows Server
Requirements
-
Running Windows environment
-
OpenJDK 21 is required.
-
On the HiveMQ Download page of the official HiveMQ website, enter your email address, read and accept the terms of service, and select Download.zip to download the latest version of HiveMQ.
-
Extract the
hivemq-<version>.zipto theC:\drive.
For example,C:\hivemq-4.27.0. -
Rename the folder so the file path is
C:\hivemq.
For example, files in the folder have the following structure:C:\hivemq\bin.
-
Set the heap that HiveMQ uses (Windows)
The heap that the HiveMQ process uses can be set as a variable in the run.bat file.
We recommended that you configure the JVM heap with 50% of the RAM that is available on the system on which you run HiveMQ.
To set the heap value, add a line with the desired -Xmx to the VARIABLES configuration as follows:
-
Go to
C:\hivemq\bin -
Open the
run.batfile with notepad or the text editor of your choice. -
In the
VARIABLESsection of therun.batfile, add the heap configuration.
The following code example sets the heap size to the recommended 50% of the available RAM:
set "JAVA_OPTS=%JAVA_OPTS% -XX:+UnlockExperimentalVMOptions -XX:InitialRAMPercentage=40 -XX:MaxRAMPercentage=50 -XX:MinRAMPercentage=30" -
Save the file.
Make the same changes to the recovery.bat file.
| The HiveMQ process can use more RAM than the amount of RAM that you allocate to the JVM heap. |
Start HiveMQ Platform manually (Windows)
-
Go to
C:\hivemq\bin -
Right-click the
run.batfile and run the file as an administrator.
Keep in mind that a click with the left mouse button (QuickEdit) stops the output of the command line.
If you click the command line before the Started HiveMQ in xxx ms message displays, you pause the HiveMQ startup process.To resume the startup, click the right mouse button. Clicks that occur after the HiveMQ startup is complete do not impact the execution of HiveMQ. |
Install a HiveMQ License
To install a HiveMQ license, move the hivemq.lic file that you received with your purchase into the license folder of your HiveMQ installation.
HiveMQ automatically and dynamically recognizes licenses during runtime. There is no need to restart HiveMQ when you add or change your HiveMQ license.
|
If no valid HiveMQ license is present, HiveMQ starts in trial mode.
HiveMQ trials are for evaluation and testing purposes only.
Production usage without a valid production license is strictly prohibited. Our standard trial supports 25 connections. If your evaluation requires more connections, please contact us. |
When HiveMQ detects a valid license file, HiveMQ logs a statement similar to the following:
2020-08-20 20:49:44,322 INFO - Found valid site license (hivemq.lic) issued to XXX for max XXX CPU cores, valid until XXX.Multiple HiveMQ Licenses
New HiveMQ licenses can be added during runtime. When multiple valid license files are available in a HiveMQ installation, HiveMQ automatically selects the license that allows the highest CPU count.
If multiple valid licenses that allow the same CPU count are present, HiveMQ automatically selects the license that is valid longest.
You do not need to restart HiveMQ when you switch or add licenses during runtime.
|
Get a HiveMQ license
To obtain a HiveMQ license, contact sales@hivemq.com.
|
HiveMQ Sanity Checks
To quickly identify critical issues that can prevent your HiveMQ implementation from functioning as expected, HiveMQ automatically runs a brief set of tests to evaluate your current system configuration.
This type of testing is known as a sanity check.
HiveMQ runs an initial sanity check at startup and repeats testing every 12 hours (to catch configuration changes that are made during runtime). Each completed sanity check consists of several individual tests. For example, a test to verify the current open-file limits on your system and a test to verify if necessary file-access permissions are correctly configured.
HiveMQ logs a warning for each individual test in the completed sanity check that fails. The WARN log statement gives you detailed information about the test result and recommendations on how to correct the issue.
| The presence of a failed sanity check does not prevent HiveMQ startup. The purpose of the HiveMQ log statements that a sanity check generates for failed tests is to help you identify inadequate or incorrect HiveMQ configurations and suggest appropriate action. |
Open File Limit Test
The open file limit is the maximum number of files or network connections a process can open in the current active session.
When an insufficient open file limit is specified for HiveMQ, a Too many open files error (or similar) can occur and prevent HiveMQ from functioning properly.
The open file limit test in the HiveMQ sanity check verifies whether the currently configured open file limits for HiveMQ are sufficient. The recommended hard and soft open file limits for HiveMQ are 1,000,000 each.
If your current open file soft-limit configuration is insufficient, HiveMQ prints the following warning to your HiveMQ log file:
Soft limit for open files ({your-current-soft-limit}) is lower than the recommended limit (1000000). Please increase the open file limit to at least the recommended limit.
If your current open file hard-limit configuration is insufficient, HiveMQ prints the following warning to your HiveMQ log file:
Hard limit for open files ({your-current-hard-limit}) is lower than the recommended limit (1000000). Please increase the open file limit to at least the recommended limit.
For information on how to increase your open file limit, see Increase open file limit.
You can view the open file limits that are currently configured for HiveMQ in the com.hivemq.system.os.process.open-file-limit.hard.current and com.hivemq.system.os.process.open-file-limit.soft.current metrics. For more information, see Standard HiveMQ Metrics. |
System Access Permissions Test
To operate correctly, HiveMQ requires access to various files and directories on your infrastructure. Your operating system controls access to files and directories with permissions that specify what users or processes are allowed to do in a particular file or directory.
HiveMQ sanity checks verify three types of Linux directory permissions:
-
Read (r): Allows the user or process to view the list of files a directory contains.
-
Write (w): Allows the user or process to edit, remove, or rename files that are stored in a directory.
-
Execute (x): Allows a user or process to change to a directory and use the files that the directory contains.
The system-access permissions test in the HiveMQ sanity check verifies whether your currently configured system permissions grant HiveMQ sufficient access to necessary files and directories.
If your currently configured system permissions lack a required permission, HiveMQ prints the following warning to your HiveMQ log file for the appropriate directory:
{file-name|directory-name} ({path}) is not {readable/writable/executable}. Please make sure that the {file|directory} has the correct {read/write/execute} permission.
| Folder name | Read | Write | Execute | Behavior the lack of permission causes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
HiveMQ cannot start |
|||
|
Logging is not available |
|||
|
HiveMQ license is not read |
|||
|
HiveMQ extensions cannot be discovered |
|||
|
Unexpected extension behavior can occur |
|||
|
Backups cannot be retrieved with the REST API |
|||
|
Audit logs cannot be written |
|||
|
Unexpected behavior occurs |
|||
|
RocksDB is unavailable |
|||
|
Heap dumps cannot be created |
HiveMQ increments the com.hivemq.system.sanity-checks.failed.count metric when one or more tests in a sanity check fails.
For example, if two tests in a sanity check generate warnings, the com.hivemq.system.sanity-checks.failed.count increases by 1. For more information, see Standard HiveMQ Metrics.
|